- Matplotlib Basics
- Matplotlib - Home
- Matplotlib - Introduction
- Matplotlib - Vs Seaborn
- Matplotlib - Environment Setup
- Matplotlib - Anaconda distribution
- Matplotlib - Jupyter Notebook
- Matplotlib - Pyplot API
- Matplotlib - Simple Plot
- Matplotlib - Saving Figures
- Matplotlib - Markers
- Matplotlib - Figures
- Matplotlib - Styles
- Matplotlib - Legends
- Matplotlib - Colors
- Matplotlib - Colormaps
- Matplotlib - Colormap Normalization
- Matplotlib - Choosing Colormaps
- Matplotlib - Colorbars
- Matplotlib - Working With Text
- Matplotlib - Text properties
- Matplotlib - Subplot Titles
- Matplotlib - Images
- Matplotlib - Image Masking
- Matplotlib - Annotations
- Matplotlib - Arrows
- Matplotlib - Fonts
- Matplotlib - Font Indexing
- Matplotlib - Font Properties
- Matplotlib - Scales
- Matplotlib - LaTeX
- Matplotlib - LaTeX Text Formatting in Annotations
- Matplotlib - PostScript
- Matplotlib - Mathematical Expressions
- Matplotlib - Animations
- Matplotlib - Celluloid Library
- Matplotlib - Blitting
- Matplotlib - Toolkits
- Matplotlib - Artists
- Matplotlib - Styling with Cycler
- Matplotlib - Paths
- Matplotlib - Path Effects
- Matplotlib - Transforms
- Matplotlib - Ticks and Tick Labels
- Matplotlib - Radian Ticks
- Matplotlib - Dateticks
- Matplotlib - Tick Formatters
- Matplotlib - Tick Locators
- Matplotlib - Basic Units
- Matplotlib - Autoscaling
- Matplotlib - Reverse Axes
- Matplotlib - Logarithmic Axes
- Matplotlib - Symlog
- Matplotlib - Unit Handling
- Matplotlib - Ellipse with Units
- Matplotlib - Spines
- Matplotlib - Axis Ranges
- Matplotlib - Axis Scales
- Matplotlib - Axis Ticks
- Matplotlib - Formatting Axes
- Matplotlib - Axes Class
- Matplotlib - Twin Axes
- Matplotlib - Figure Class
- Matplotlib - Multiplots
- Matplotlib - Grids
- Matplotlib - Object-oriented Interface
- Matplotlib - PyLab module
- Matplotlib - Subplots() Function
- Matplotlib - Subplot2grid() Function
- Matplotlib - Anchored Artists
- Matplotlib - Manual Contour
- Matplotlib - Coords Report
- Matplotlib - AGG filter
- Matplotlib - Ribbon Box
- Matplotlib - Fill Spiral
- Matplotlib - Findobj Demo
- Matplotlib - Hyperlinks
- Matplotlib - Image Thumbnail
- Matplotlib - Plotting with Keywords
- Matplotlib - Create Logo
- Matplotlib - Multipage PDF
- Matplotlib - Multiprocessing
- Matplotlib - Print Stdout
- Matplotlib - Compound Path
- Matplotlib - Sankey Class
- Matplotlib - MRI with EEG
- Matplotlib - Stylesheets
- Matplotlib - Background Colors
- Matplotlib - Basemap
- Matplotlib Event Handling
- Matplotlib - Event Handling
- Matplotlib - Close Event
- Matplotlib - Mouse Move
- Matplotlib - Click Events
- Matplotlib - Scroll Event
- Matplotlib - Keypress Event
- Matplotlib - Pick Event
- Matplotlib - Looking Glass
- Matplotlib - Path Editor
- Matplotlib - Poly Editor
- Matplotlib - Timers
- Matplotlib - Viewlims
- Matplotlib - Zoom Window
- Matplotlib Widgets
- Matplotlib - Cursor Widget
- Matplotlib - Annotated Cursor
- Matplotlib - Buttons Widget
- Matplotlib - Check Buttons
- Matplotlib - Lasso Selector
- Matplotlib - Menu Widget
- Matplotlib - Mouse Cursor
- Matplotlib - Multicursor
- Matplotlib - Polygon Selector
- Matplotlib - Radio Buttons
- Matplotlib - RangeSlider
- Matplotlib - Rectangle Selector
- Matplotlib - Ellipse Selector
- Matplotlib - Slider Widget
- Matplotlib - Span Selector
- Matplotlib - Textbox
- Matplotlib Plotting
- Matplotlib - Line Plots
- Matplotlib - Area Plots
- Matplotlib - Bar Graphs
- Matplotlib - Histogram
- Matplotlib - Pie Chart
- Matplotlib - Scatter Plot
- Matplotlib - Box Plot
- Matplotlib - Arrow Demo
- Matplotlib - Fancy Boxes
- Matplotlib - Zorder Demo
- Matplotlib - Hatch Demo
- Matplotlib - Mmh Donuts
- Matplotlib - Ellipse Demo
- Matplotlib - Bezier Curve
- Matplotlib - Bubble Plots
- Matplotlib - Stacked Plots
- Matplotlib - Table Charts
- Matplotlib - Polar Charts
- Matplotlib - Hexagonal bin Plots
- Matplotlib - Violin Plot
- Matplotlib - Event Plot
- Matplotlib - Heatmap
- Matplotlib - Stairs Plots
- Matplotlib - Errorbar
- Matplotlib - Hinton Diagram
- Matplotlib - Contour Plot
- Matplotlib - Wireframe Plots
- Matplotlib - Surface Plots
- Matplotlib - Triangulations
- Matplotlib - Stream plot
- Matplotlib - Ishikawa Diagram
- Matplotlib - 3D Plotting
- Matplotlib - 3D Lines
- Matplotlib - 3D Scatter Plots
- Matplotlib - 3D Contour Plot
- Matplotlib - 3D Bar Plots
- Matplotlib - 3D Wireframe Plot
- Matplotlib - 3D Surface Plot
- Matplotlib - 3D Vignettes
- Matplotlib - 3D Volumes
- Matplotlib - 3D Voxels
- Matplotlib - Time Plots and Signals
- Matplotlib - Filled Plots
- Matplotlib - Step Plots
- Matplotlib - XKCD Style
- Matplotlib - Quiver Plot
- Matplotlib - Stem Plots
- Matplotlib - Visualizing Vectors
- Matplotlib - Audio Visualization
- Matplotlib - Audio Processing
- Matplotlib Useful Resources
- Matplotlib - Quick Guide
- Matplotlib - Cheatsheet
- Matplotlib - Useful Resources
- Matplotlib - Discussion
Matplotlib - Toolkits
A toolkit consists of a set of tools for a specific purpose. It contains different resources or software that work together to help you achieve a task. It is like having a handy package with everything you need to get a job done efficiently. Toolkits are often used in various fields, like technology, education, or research.
Toolkits in Matplotlib
Matplotlib toolkits are additional sets of tools and functions that you can use to extend the capabilities of Matplotlib. These toolkits are like add-ons that give you extra features for creating specific types of plots or addressing certain requirements.
For example, if you want to create 3D plots, you can use the "mplot3d" toolkit that comes with Matplotlib. It provides functions and classes specifically designed for 3D plotting.
Let us explore various toolkits in this tutorial −
The mpl_toolkits.mplot3d (3D Plotting)
The mpl_toolkits.mplot3d toolkit is used to create three-dimensional plots, including 3D scatter plots, surface plots, and wireframe plots. To use this toolkit, import a module called "Axes3D" −
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
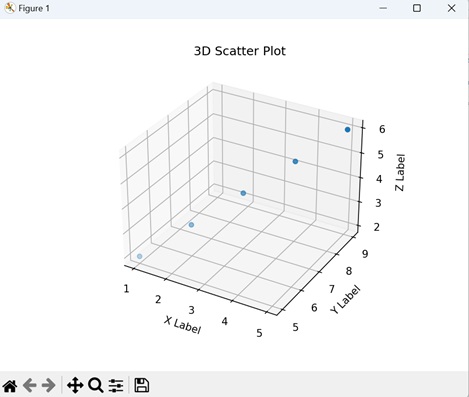
Example
In the following example, we are creating a 3D scatter plot using the "mpl_toolkits.mplot3d" toolkit. We use the scatter() function to plot points in a 3D space, where the "x", "y", and "z" lists represent the coordinates of the data points −
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
# Creating a 3D scatter plot
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
x, y, z = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [5, 6, 7, 8, 9], [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
ax.scatter(x, y, z)
# Customizing the plot
ax.set_xlabel('X Label')
ax.set_ylabel('Y Label')
ax.set_zlabel('Z Label')
ax.set_title('3D Scatter Plot')
plt.show()
Output
Following is the output of the above code −
The mpl_toolkits.axes_grid: Axes Grid
The mpl_toolkits.axes_grid toolkit is a set of tools that helps you create complex layouts of subplots and arrange custom axes in Matplotlib. To use this toolkit, import a specific module called "ImageGrid" −
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import ImageGrid
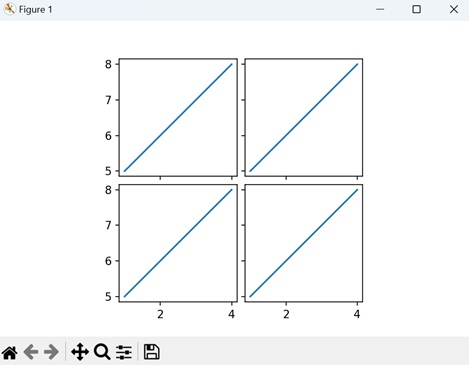
Example
Here, we are creating a grid of subplots (2 rows and 2 columns) using the "mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1" toolkit. The for loop iterates over each subplot in the grid, and a simple line plot is added to each subplot using the plot() function −
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import ImageGrid
# Creating a grid of subplots
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
grid = ImageGrid(fig, 111, nrows_ncols=(2, 2), axes_pad=0.1,)
# Plotting on each subplot
for ax in grid:
ax.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8])
plt.show()
Output
The resulting visualization displays a 2x2 grid of subplots, each containing a line plot as shown below −
The mpl_toolkits.axisartist (Custom Axes)
The mpl_toolkits.axisartist toolkit offers additional features for creating customized axes and tick arrangements. To use this toolkit, import the module "Subplot" −from mpl_toolkits.axisartist import Subplot
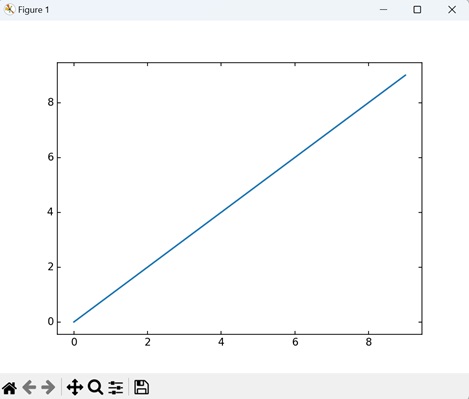
Example
Now, we are creating a custom subplot with enhanced axes using the "mpl_toolkits.axisartist" toolkit. We then use the plot() function to add a simple line plot to the custom subplot −
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.axisartist import Subplot # Creating a custom subplot with enhanced axes fig = plt.figure() ax = Subplot(fig, 111) fig.add_subplot(ax) # Plotting on the custom subplot ax.plot(range(10)) # Displaying the plot plt.show()
Output
Output of the above code is as follows −
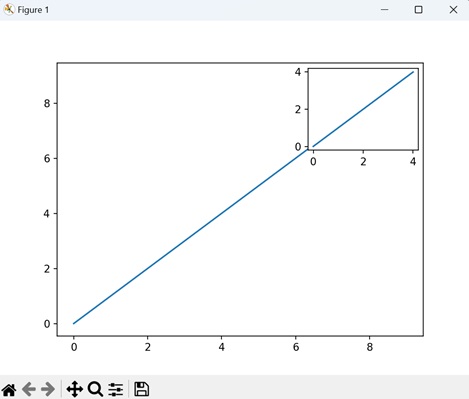
The mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator
The mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator enables the placement of inset axes within a larger plot, allowing for detailed views. To use this toolkit, import the module "inset_axes" −
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator import inset_axes
Example
In the following example, we are creating a main plot and an inset plot using the "mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator" toolkit. We use the inset_axes() function to define the inset axes, specifying its width, height, and location. Thereafter, we populate both the main plot and the inset plot with simple line plots using the plot() function −
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator import inset_axes # Creating a main plot fig, ax = plt.subplots() # Defining the inset axes axins = inset_axes(ax, width='30%', height='30%', loc='upper right') # Plotting on both axes ax.plot(range(10)) axins.plot(range(5)) # Displaying the plot plt.show()
Output
We get the output as shown below −