- Matplotlib Basics
- Matplotlib - Home
- Matplotlib - Introduction
- Matplotlib - Vs Seaborn
- Matplotlib - Environment Setup
- Matplotlib - Anaconda distribution
- Matplotlib - Jupyter Notebook
- Matplotlib - Pyplot API
- Matplotlib - Simple Plot
- Matplotlib - Saving Figures
- Matplotlib - Markers
- Matplotlib - Figures
- Matplotlib - Styles
- Matplotlib - Legends
- Matplotlib - Colors
- Matplotlib - Colormaps
- Matplotlib - Colormap Normalization
- Matplotlib - Choosing Colormaps
- Matplotlib - Colorbars
- Matplotlib - Working With Text
- Matplotlib - Text properties
- Matplotlib - Subplot Titles
- Matplotlib - Images
- Matplotlib - Image Masking
- Matplotlib - Annotations
- Matplotlib - Arrows
- Matplotlib - Fonts
- Matplotlib - Font Indexing
- Matplotlib - Font Properties
- Matplotlib - Scales
- Matplotlib - LaTeX
- Matplotlib - LaTeX Text Formatting in Annotations
- Matplotlib - PostScript
- Matplotlib - Mathematical Expressions
- Matplotlib - Animations
- Matplotlib - Celluloid Library
- Matplotlib - Blitting
- Matplotlib - Toolkits
- Matplotlib - Artists
- Matplotlib - Styling with Cycler
- Matplotlib - Paths
- Matplotlib - Path Effects
- Matplotlib - Transforms
- Matplotlib - Ticks and Tick Labels
- Matplotlib - Radian Ticks
- Matplotlib - Dateticks
- Matplotlib - Tick Formatters
- Matplotlib - Tick Locators
- Matplotlib - Basic Units
- Matplotlib - Autoscaling
- Matplotlib - Reverse Axes
- Matplotlib - Logarithmic Axes
- Matplotlib - Symlog
- Matplotlib - Unit Handling
- Matplotlib - Ellipse with Units
- Matplotlib - Spines
- Matplotlib - Axis Ranges
- Matplotlib - Axis Scales
- Matplotlib - Axis Ticks
- Matplotlib - Formatting Axes
- Matplotlib - Axes Class
- Matplotlib - Twin Axes
- Matplotlib - Figure Class
- Matplotlib - Multiplots
- Matplotlib - Grids
- Matplotlib - Object-oriented Interface
- Matplotlib - PyLab module
- Matplotlib - Subplots() Function
- Matplotlib - Subplot2grid() Function
- Matplotlib - Anchored Artists
- Matplotlib - Manual Contour
- Matplotlib - Coords Report
- Matplotlib - AGG filter
- Matplotlib - Ribbon Box
- Matplotlib - Fill Spiral
- Matplotlib - Findobj Demo
- Matplotlib - Hyperlinks
- Matplotlib - Image Thumbnail
- Matplotlib - Plotting with Keywords
- Matplotlib - Create Logo
- Matplotlib - Multipage PDF
- Matplotlib - Multiprocessing
- Matplotlib - Print Stdout
- Matplotlib - Compound Path
- Matplotlib - Sankey Class
- Matplotlib - MRI with EEG
- Matplotlib - Stylesheets
- Matplotlib - Background Colors
- Matplotlib - Basemap
- Matplotlib Event Handling
- Matplotlib - Event Handling
- Matplotlib - Close Event
- Matplotlib - Mouse Move
- Matplotlib - Click Events
- Matplotlib - Scroll Event
- Matplotlib - Keypress Event
- Matplotlib - Pick Event
- Matplotlib - Looking Glass
- Matplotlib - Path Editor
- Matplotlib - Poly Editor
- Matplotlib - Timers
- Matplotlib - Viewlims
- Matplotlib - Zoom Window
- Matplotlib Widgets
- Matplotlib - Cursor Widget
- Matplotlib - Annotated Cursor
- Matplotlib - Buttons Widget
- Matplotlib - Check Buttons
- Matplotlib - Lasso Selector
- Matplotlib - Menu Widget
- Matplotlib - Mouse Cursor
- Matplotlib - Multicursor
- Matplotlib - Polygon Selector
- Matplotlib - Radio Buttons
- Matplotlib - RangeSlider
- Matplotlib - Rectangle Selector
- Matplotlib - Ellipse Selector
- Matplotlib - Slider Widget
- Matplotlib - Span Selector
- Matplotlib - Textbox
- Matplotlib Plotting
- Matplotlib - Line Plots
- Matplotlib - Area Plots
- Matplotlib - Bar Graphs
- Matplotlib - Histogram
- Matplotlib - Pie Chart
- Matplotlib - Scatter Plot
- Matplotlib - Box Plot
- Matplotlib - Arrow Demo
- Matplotlib - Fancy Boxes
- Matplotlib - Zorder Demo
- Matplotlib - Hatch Demo
- Matplotlib - Mmh Donuts
- Matplotlib - Ellipse Demo
- Matplotlib - Bezier Curve
- Matplotlib - Bubble Plots
- Matplotlib - Stacked Plots
- Matplotlib - Table Charts
- Matplotlib - Polar Charts
- Matplotlib - Hexagonal bin Plots
- Matplotlib - Violin Plot
- Matplotlib - Event Plot
- Matplotlib - Heatmap
- Matplotlib - Stairs Plots
- Matplotlib - Errorbar
- Matplotlib - Hinton Diagram
- Matplotlib - Contour Plot
- Matplotlib - Wireframe Plots
- Matplotlib - Surface Plots
- Matplotlib - Triangulations
- Matplotlib - Stream plot
- Matplotlib - Ishikawa Diagram
- Matplotlib - 3D Plotting
- Matplotlib - 3D Lines
- Matplotlib - 3D Scatter Plots
- Matplotlib - 3D Contour Plot
- Matplotlib - 3D Bar Plots
- Matplotlib - 3D Wireframe Plot
- Matplotlib - 3D Surface Plot
- Matplotlib - 3D Vignettes
- Matplotlib - 3D Volumes
- Matplotlib - 3D Voxels
- Matplotlib - Time Plots and Signals
- Matplotlib - Filled Plots
- Matplotlib - Step Plots
- Matplotlib - XKCD Style
- Matplotlib - Quiver Plot
- Matplotlib - Stem Plots
- Matplotlib - Visualizing Vectors
- Matplotlib - Audio Visualization
- Matplotlib - Audio Processing
- Matplotlib Useful Resources
- Matplotlib - Quick Guide
- Matplotlib - Cheatsheet
- Matplotlib - Useful Resources
- Matplotlib - Discussion
Matplotlib - Event Plot
An event plot is used to display the occurrences of events over a specific period of time. It consists of points (markers) along a timeline, where each point indicate the happening of a specific event. The vertical axis indicates different types of events, and the horizontal axis represents time.
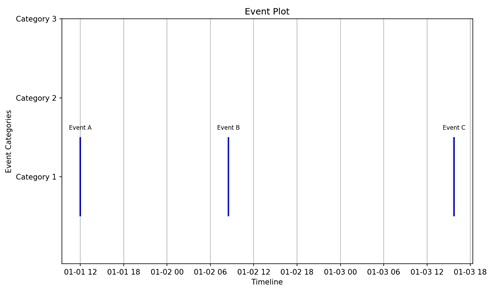
Event Plot in Matplotlib
We can create event plots in Matplotlib using the eventplot() function. This function allows you to specify the positions of the events to be plotted. Each vertical line or marker in the plot represents a particular event, and the resulting visualization displays the relationships between different events in a dataset.
The eventplot() Function
The eventplot() function in Matplotlib takes a list of arrays as input, where each array represents the positions of events along the timeline for a specific category or set. Event markers are then plotted at these positions, creating a visual representation of the events in different categories over time.
Following is the syntax of the eventplot() function in Matplotlib −
matplotlib.pyplot.eventplot(positions, orientation='horizontal', lineoffsets=1, linelengths=1, linewidths=None, colors=None, linestyles='solid', alpha=None, **kwargs)
Where,
- positions is the sequence specifying the positions of the events along the chosen orientation.
- orientation specifies whether the events are plotted vertically or horizontally. Default is 'horizontal'.
- lineoffsets is the vertical or horizontal offset from the baseline where the events are plotted.
- linelengths is the length of the lines or markers representing the events.
- linewidths is the width of the lines representing the events. If None, the default linewidth is used.
- colors is the sequence of colors for the events.
- linestyles is the line style of the events. Default is 'solid'.
- alpha represents the pacity of the lines or markers.
- **kwargs is the additional keyword arguments for customizing the event plot.
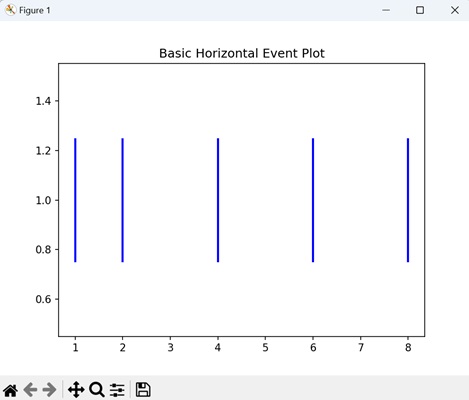
Basic Horizontal Event Plot
A basic horizontal event plot is like a timeline where specific moments are highlighted. Imagine a horizontal line representing time, and then, at certain points along that line, you have events marked by vertical lines. Each of these lines indicates a particular occurrence or moment in time.
Example
In the following example, we are creating a simple horizontal event plot with events at positions 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8. The events are represented by blue vertical lines with a specified line length "0.5", linewidth "2", and color "blue" −
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Event positions
events = [1, 2, 4, 6, 8]
# Creating a basic horizontal event plot
plt.eventplot(events, orientation='horizontal', linelengths=0.5, linewidths=2, colors='blue')
plt.title('Basic Horizontal Event Plot')
plt.show()
Output
After executing the above code, we get the following output −
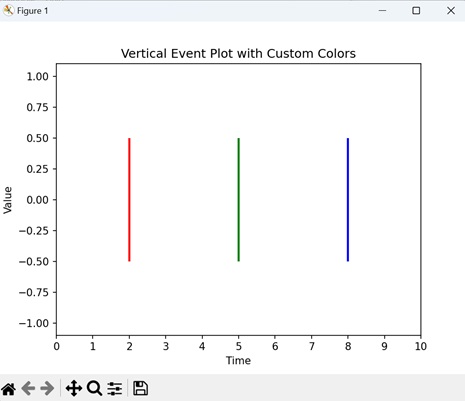
Vertical Event Plot with Custom Colors
In Matplotlib, a vertical event plot with custom colors is a visual representation of events occurring at different points in time, displayed along a vertical timeline. Each event is marked by a distinct color, making it easy to identify and understand the occurrences.
Example
In here, we are creating an event plot with events at positions '2', '5', and '8'. The events have custom colors 'red', 'green' and 'blue' to distinguish them −
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# positions of events
events = [2, 5, 8]
# colors for each event
event_colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue']
# Ensuring that events and event_colors have the same length
if len(events) != len(event_colors):
raise ValueError("The lengths of events and event_colors must be equal.")
# Creating a figure and axis
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# Plotting vertical lines for each event with custom colors using eventplot
ax.eventplot(events, lineoffsets=0, linelengths=1, colors=[event_colors], linewidths=2)
# Setting labels and title
ax.set_xlabel('Time')
ax.set_ylabel('Value')
ax.set_title('Vertical Event Plot with Custom Colors')
# Setting x-axis ticks
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(0, 11, 1))
# Displaying the plot
plt.show()
Output
Following is the output of the above code −
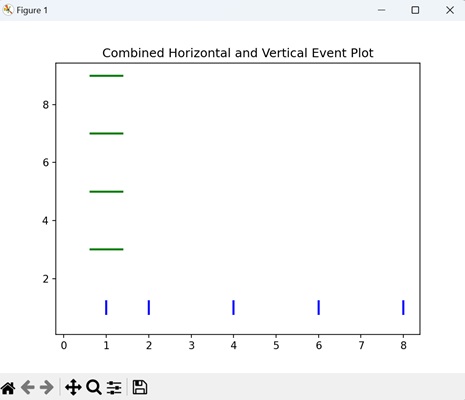
Combined Horizontal and Vertical Event Plot
A combined horizontal and vertical event plot displays events occurring at different times and positions simultaneously. Vertical events are represented by lines along the timeline, while horizontal events are marked by lines extending vertically. It is like merging two types of timelines in one plot.
Example
Now, we are combining both horizontal and vertical event plots in a single visualization. Horizontal events are at positions 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 (blue lines), and vertical events are at positions 3, 5, 7, and 9 (green lines) −
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Event positions
horizontal_events = [1, 2, 4, 6, 8]
vertical_events = [3, 5, 7, 9]
# Creating a combined event plot
plt.eventplot(horizontal_events, orientation='horizontal', linelengths=0.5, linewidths=2, colors='blue')
plt.eventplot(vertical_events, orientation='vertical', linelengths=0.8, linewidths=2, colors='green')
plt.title('Combined Horizontal and Vertical Event Plot')
plt.show()
Output
Output of the above code is as follows −
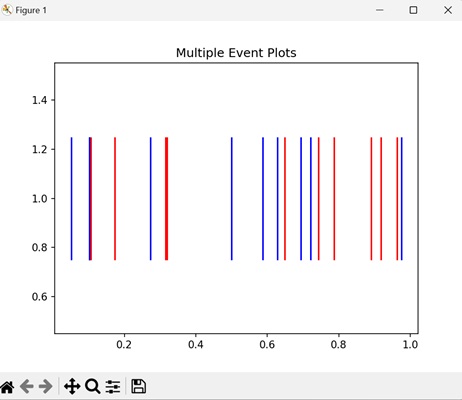
Multiple Event Plots
In Matplotlib, when you want to compare events from different datasets, you can create multiple event plots. Each plot represents a set of events, and by stacking them together on the same axis, you can easily observe how events are distributed across various timeframes. This helps in visually comparing the timing and frequency of events from different sources, making it easy to identify patterns.
Example
In the example below, we are generating two sets of random event positions and creating a single plot with multiple event plots on one axis. Each set of events is plotted with a different color ('b' for blue and 'r' for red), allowing for easy comparison between the two datasets −
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Generating random event positions for two sets
events1 = np.random.rand(10)
events2 = np.random.rand(10)
# Creating multiple event plots on one axis
plt.eventplot(events1, orientation='horizontal', linelengths=0.5, colors='b')
plt.eventplot(events2, orientation='horizontal', linelengths=0.5, colors='r')
plt.title('Multiple Event Plots')
plt.show()
Output
The output obtained is as shown below −