Whether your website collects users' data or content to train AI or you want to keep third parties from extracting data from your website for AI training purposes, legal agreements can help protect your business.
This article explains why you need legal agreements for AI training and how to comply with applicable laws, get a license to utilize user content to train AI, and protect your website from unauthorized data extraction for AI training purposes.
TermsFeed is the world's leading generator of legal agreements for websites and apps. With TermsFeed, you can generate:
- 1. What is AI Training?
- 2. What Legal Agreements Do You Need for AI Training?
- 2.1. What is a Privacy Policy?
- 2.2. What is a Terms and Conditions Agreement?
- 3. Why Do You Need a Privacy Policy and a Terms and Conditions Agreement for AI Training?
- 4. What Laws Apply to AI Training?
- 5. How a Privacy Policy Can Help You Comply With Applicable Laws
- 6. How a Terms and Conditions Agreement Can Help You Get a License to Use UGC to Train AI
- 7. How a Terms and Conditions Agreement Can Help Protect Your Website From Unauthorized Data Extraction
- 8. How to Get Consent to Your Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions Agreement
- 9. How to Display Your Terms and Conditions Agreement and Privacy Policy
- 10. Summary
What is AI Training?
AI training is the practice of instructing an AI model to recognize patterns and make predictions and decisions based on data.
Consider generative AI: Generative AI is technology that can be used to create new content such as text, images, audio, or videos based on user prompts. It depends on training from massive amounts of data and user content to formulate relevant results. Automated programs are often used to collect AI training data from the internet.
For example, ChatGPT is a form of generative AI that can create text in response to a user's prompts. Its training has relied in part on data from sources such as the data repository Common Crawl, a site that extracts data through web crawling.
Thanks to AI training, ChatGPT can be used for numerous text-related purposes, even writing poetry.
What Legal Agreements Do You Need for AI Training?
You should have a Privacy Policy to explain:
- How you process (use) users' data to train AI
- How users can exercise their privacy rights
You should have a Terms and Conditions agreement to:
- Obtain a license to use user-generated content (UGC) for AI training or
- Prohibit third parties from extracting data from your website for AI training purposes
What is a Privacy Policy?
A Privacy Policy is a legal agreement that explains how you collect and use consumers' personal information and how users can exercise their privacy rights.
Personal information is any data that can be used to identify an individual, such as names, addresses, Social Security and driver's license numbers, and health and financial information.
A Privacy Policy generally includes the following clauses:
- What information the business collects or processes
- The business's reasons for collecting or processing personal data
- Third parties the business shares personal information with
- The types of personal information the business shares with third parties
- How the business keeps personal data safe
- How long the business retains personal information
- How users can exercise their privacy rights
- The business's contact information
IBM's Privacy Statement includes clauses about the types of personal information it collects, who it shares personal information with, how it keeps data safe, and how users can exercise their rights, among others:

What is a Terms and Conditions Agreement?
A Terms and Conditions agreement (also called a Terms of Use or Terms of Service agreement) is a document that outlines the rules users must agree to in order to use your services.
A Terms and Conditions agreement typically includes the following clauses:
- Intellectual property
- Grounds for termination
- Governing law
- Third-party links
- Limitation of liability
- User-generated content policies
- Restricted uses
- Payment terms
Hulu's Terms agreement includes clauses about subscriptions and billing, limitation of liability, and copyright infringement, among others:

Why Do You Need a Privacy Policy and a Terms and Conditions Agreement for AI Training?
There are a few reasons why you need legal agreements for AI training, including to comply with applicable laws, to protect your business, and for transparency purposes.
Reasons why you should have legal agreements for AI training include to:
- Comply with privacy and AI laws
- Get a license to use UGC to train AI
- Notify users about how you use their personal data to train AI and how they can exercise their rights
- Protect your website from third-party data extraction
Let's look at some of the laws that may apply in the context of AI training.
What Laws Apply to AI Training?
Businesses that use consumers' personal data, user generated content (UGC), or copyrighted materials for AI training may be required to comply with state and global privacy and data protection laws as well as AI-specific legislation.
Privacy laws including the European Union's Global Data Privacy Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA/CPRA) require applicable businesses to explain how they handle consumers' personal information and how users can exercise their privacy rights.
The GDPR requires anyone who collects or processes personal data belonging to EU residents to notify them at the time of collection about why they are processing the data and whether they intend to share the data with any third parties, among other information.
Article 13 of the GDPR explains that data controllers (those who collect and make decisions about how to use personal data) must inform EU residents at the point of collection about why the data is being processed and any third parties the data will be shared with:

Similarly, the CCPA/CPRA requires applicable businesses to notify California residents about the types of personal information they collect and what they use it for at or before collection.
AI laws such as the European Union Artificial Intelligence Act (EU AI Act) and the Colorado Artificial Intelligence Act (CAIA) are designed to regulate the development and use of AI.
The EU AI Act applies to AI systems based on their level of risk. For example, the law doesn't typically apply to low-risk AI systems (such as spam filters or video games), although companies can still comply voluntarily.
EU AI Act requirements for companies responsible for higher-risk AI systems include:
- Informing users that they are interacting with AI (such as with chatbots)
- Labeling certain AI-generated content
- Implementing risk-mitigation and quality-management strategies for high-risk AI systems
- Banning AI systems that threaten individuals' fundamental rights, such as those that allow social scoring
Additionally, businesses that use text and data mining techniques to extract data from websites to develop or train generative AI models may need to get consent from rights holders before accessing copyrighted materials.
Recital 105 of the EU AI Act explains that businesses that extract data from websites to train AI may be required to get authorization from copyright rights holders before accessing their copyrighted content:

Article 50, Section 1 of the EU AI Act explains that unless it's obvious, companies are required to inform users that they are interacting with an AI system:

As with the EU AI Act, the CAIA requires deployers of AI systems that interact with consumers to inform consumers that they are engaging with an AI system.
Businesses that don't inform users before collecting or processing their personal information or UGC or use data extraction programs that don't obtain permission before collecting copyrighted content or personal data to be used for AI training purposes may be in violation of these laws.
If you collect or process users' personal information, copyrighted content, or UGC for AI training, maintaining legal agreements can help you comply with applicable laws.
How a Privacy Policy Can Help You Comply With Applicable Laws
When it comes to collecting large amounts of data, it can be difficult to monitor whether the data contains personal information or copyrighted content and is therefore subject to applicable privacy and AI laws.
It's best to err on the side of caution and inform users and get their consent before collecting or using personal information, UGC, or copyrighted content for AI training purposes.
Maintaining a Privacy Policy that includes information about how you use data or content to train AI and how users can withdraw their consent to have their personal data or content used for AI training can help you comply with relevant laws.
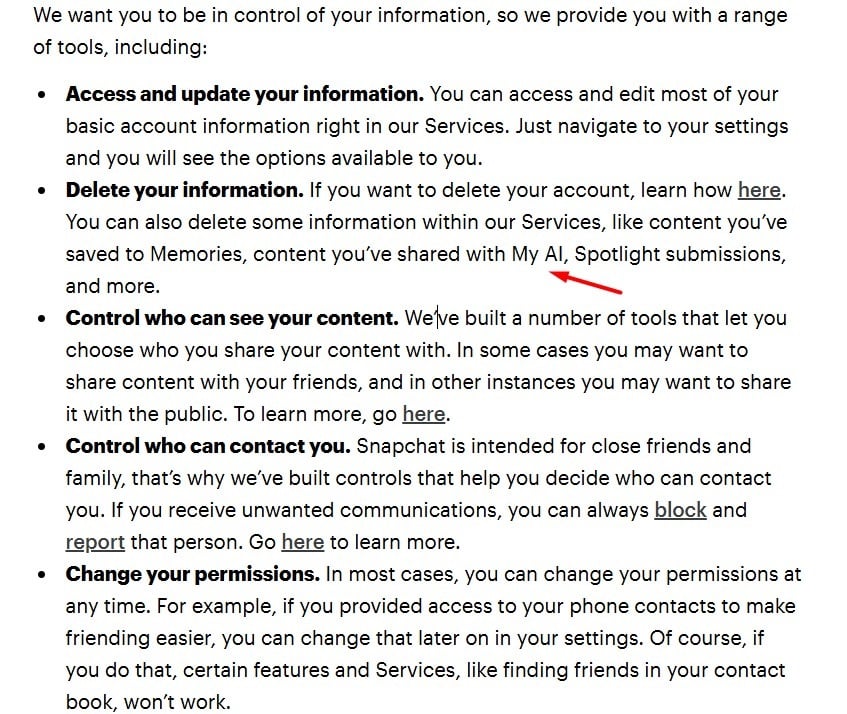
Snap's Privacy Policy explains that it uses conversations Snapchat users have with its My AI chatbot for AI training purposes:

Snap's Privacy Policy also lists users' privacy rights, including their right to delete any content they have shared with its generative AI chatbot:
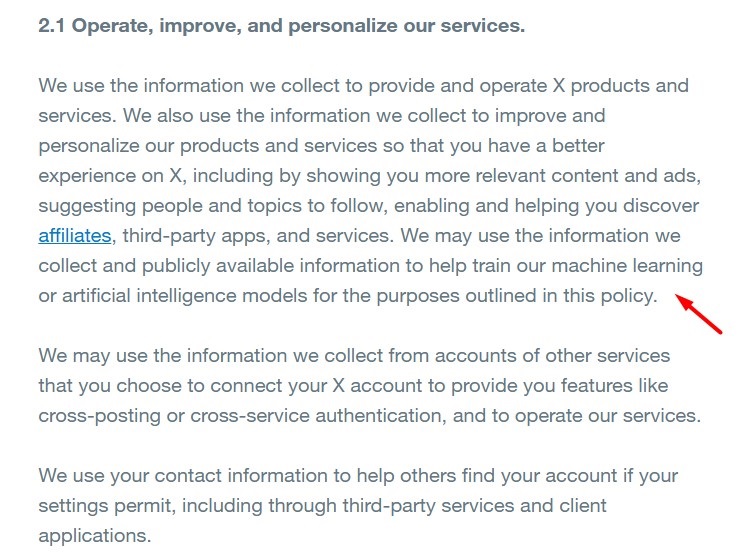
X's Privacy Policy explains that it may use the information it collects to train its AI models:
How a Terms and Conditions Agreement Can Help You Get a License to Use UGC to Train AI
You should get a license from users if you use UGC to train an AI model. You can do this by creating a clause within your Terms and Conditions agreement that explains that when users upload their content to your platform, they automatically grant you a license to use UGC for AI training.
Roblox's Terms of Use agreement explains that when users publish UGC they grant Roblox a license to use it for purposes including training machine learning models:

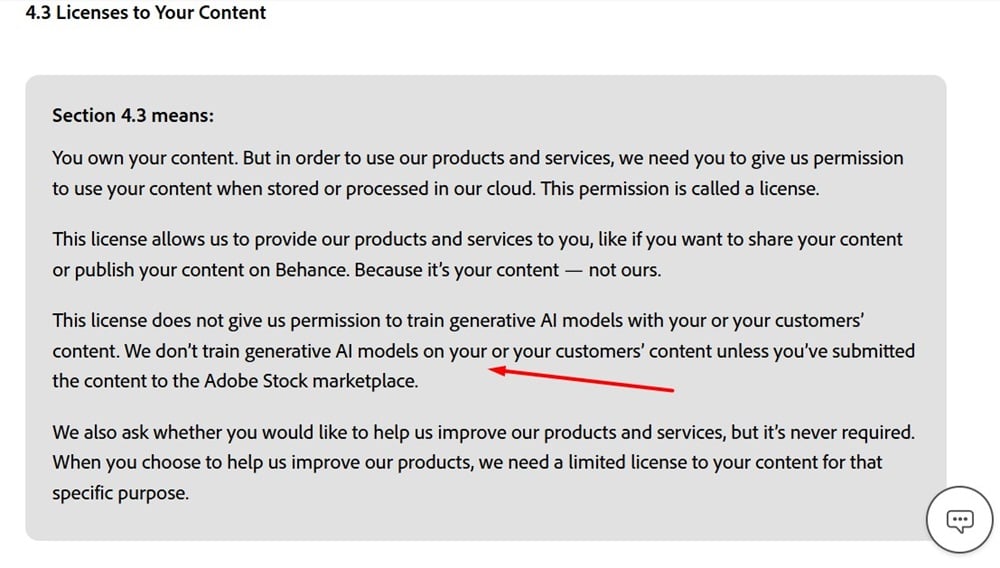
Adobe's General Terms of Use agreement lets users know that it does not use UGC to train generative AI models unless the content has been submitted to the Adobe Stock marketplace:
Activision's Terms of Use agreement explains that when users submit UGC, they automatically grant it a license to use the UGC for any reason and without notice or compensation:

How a Terms and Conditions Agreement Can Help Protect Your Website From Unauthorized Data Extraction
Many companies want to keep AI models from using data from their websites. One way to protect your website data is to include a clause in your Terms and Conditions agreement that prohibits the use of any content or data from your website for AI training purposes.
Ryanair's Terms of Use agreement explains that the use of automated software to extract data from its website for commercial reasons is prohibited:

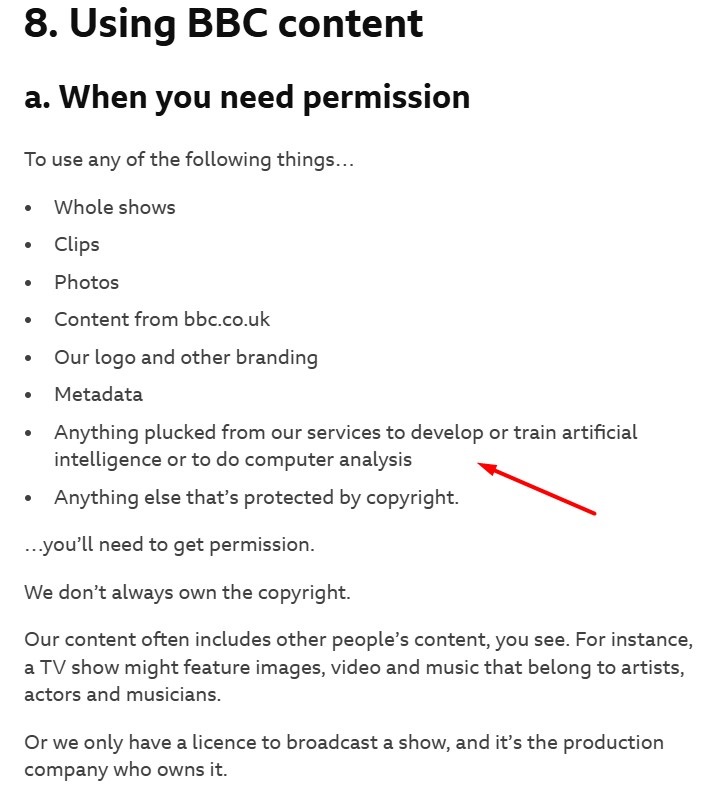
Likewise, the BBC's Terms of Use agreement lets users know that they are not allowed to use any content or data from its services to develop or train AI:
Keep in mind that it's not enough to simply have a data extraction clause within your Terms and Conditions agreement. To make the document legally binding, you need to ensure that users have read and agree to the entire Terms and Conditions agreement.
Next, let's take a look at how you can get user consent to your legal agreements.
How to Get Consent to Your Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions Agreement
Once you have written your Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions agreement, it's essential to get users to read and consent to your legal agreements.
You can increase the likelihood that your legal agreements will be legally enforceable by using a clickwrap agreement. A clickwrap agreement is a way for a company to collect user consent online.
One way to use a clickwrap agreement is through the use of a checkbox next to a statement that users have read and agree to your legal agreements. The statement should include clearly labeled links to the legal agreements you need users to consent to.
For instance, let's say you have a clause in your Terms and Conditions agreement that prohibits data extraction. If a bot or automated web scraping tool isn't designed to automatically find and respond to clickwrap agreements and it attempts to extract data from your website, the developer of the bot or tool could be held responsible for violating your Terms and Conditions agreement.
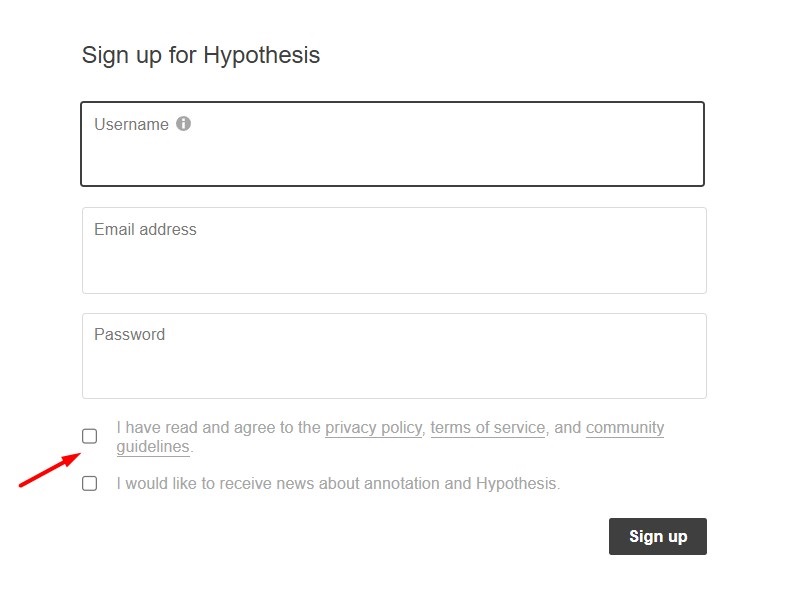
When users go to sign up for an account with Hypothesis, they must first tick a checkbox next to a statement that says they agree to its Privacy Policy, Terms of Service agreement, and Community Guidelines document:
How to Display Your Terms and Conditions Agreement and Privacy Policy
You should put links to your legal agreements where users can easily find them and wherever you collect personal information or UGC to be used for AI training.
Common places to put links include:
- Website footer
- Account creation/login pages
- Newsletter subscription area
- Ecommerce checkout page
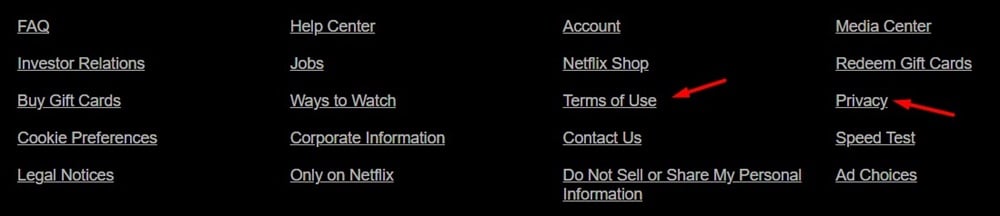
Netflix's website footer contains links to its Terms of Use agreement and Privacy Statement:
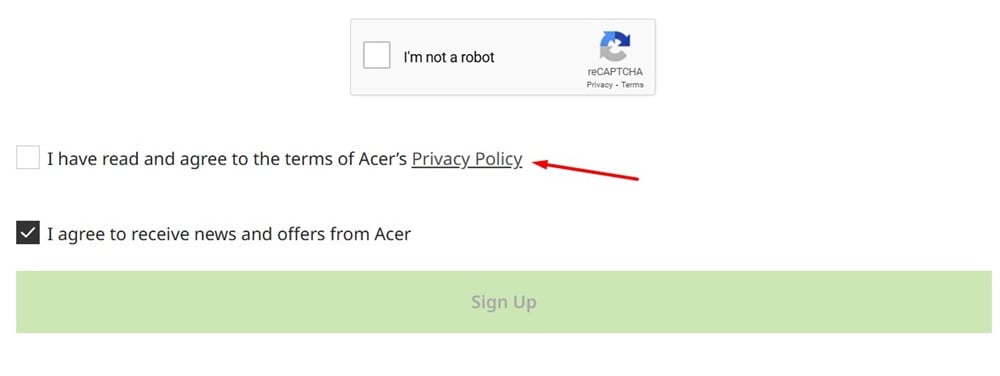
Acer includes a link to its Privacy Policy within a clickwrap agreement on its account sign-up page:
Summary
AI training is teaching an AI model to identify patterns and make predictions based on large amounts of data.
A Terms and Conditions agreement is a document that describes the expectations users must agree to in order to use your services.
A Privacy Policy is a legal document that explains how you handle users' personal information and how they can exercise their rights.
You need legal agreements for AI training to:
- Comply with applicable laws
- Get a license to use UGC for AI training purposes
- Let users know how you use their data to train AI
- Explain how users can exercise their privacy rights
- Keep third parties from extracting data from your website for AI training purposes
Privacy and AI laws may require you to:
- Let users know how you handle their data
- Inform users that they are interacting with an AI system
- Get consent before using certain data or content for AI training purposes
- Give users a way to opt out of AI training data processing activities
Maintaining a clearly written, regularly updated Privacy Policy that contains information about how you treat users' data and how they can exercise their rights can help you comply with applicable laws.
You can include a clause within your Terms and Conditions agreement that lets users know that they automatically grant you a license to use UGC for AI training purposes.
You can also use your Terms and Conditions agreement to let users know that they are not allowed to extract data from your website or use your website's content for AI training purposes.
Using a clickwrap agreement to get consent to your legal agreements can help make them more legally enforceable.
You should display links to your legal agreements wherever you collect users' personal information and where users can easily find them.

Comprehensive compliance starts with a Privacy Policy.
Comply with the law with our agreements, policies, and consent banners. Everything is included.