Effectiveness and safety of aripiprazole oral solution in the acute treatment of schizophrenia in Chinese patients
- PMID: 39734212
- PMCID: PMC11684257
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-024-06455-y
Effectiveness and safety of aripiprazole oral solution in the acute treatment of schizophrenia in Chinese patients
Abstract
Background: This study investigates the effectiveness and safety of aripiprazole oral solution in Chinese patients with schizophrenia.
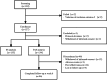
Methods: This was a multicenter, single-arm phase IV study involving 134 patients in China in the acute stage of schizophrenia from May 2021 to July 2022. The patients received aripiprazole oral solution 10 - 30 mg/d for 12 weeks. The effectiveness endpoints included the Positive and Negative Symptom Scale (PANSS) and the Clinical Global Impression (CGI) scale score. The safety endpoints included adverse events, laboratory inspection indicators (including the serum prolactin level [PRL]), and waist circumferences (WC).
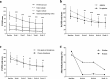
Results: Ultimately, 86 patients (64.18%) completed the trial, and 21 patients (15.67%) dropped out due to poor effectiveness. From baseline to week eight, 43.28% of patients had a PANSS reduction of ≥ 50%, 82.84% of patients improved in the CGI-Improvement (CGI-I scale score of 1 - 3), and the percentage of patients with abnormal PRL and waist circumferences decreased significantly. In total, 45 patients (33.58%) experienced mild adverse drug reactions predominately manifested as extrapyramidal symptoms (EPSs; 9.70%), constipation (8.96%), and palpitations (7.46%). Upon further subgroup analysis, aripiprazole oral solution demonstrated significantly improved effectiveness in first-episode schizophrenia patients and those with symptoms of agitation.
Conclusions: Aripiprazole oral solution displayed positive clinical effectiveness and favorable tolerability in Chinese patients in the acute stage of schizophrenia.
Clinical trial registration: Clinical trial registration number: ChiCTR2100044653. Name of trial registration: A real-world study of Aripiprazole Oral Solution in the treatment of schizophrenia (Registration date: 25/03/2021). The full trial protocol can be accessed at the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry ( http://www.chictr.org.cn/ ).
Keywords: Aripiprazole oral solution; Chinese; Schizophrenia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All procedures of the present study were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study protocols were approved by the clinical research ethics committees of Beijing Anding Hospital, Capital Medical University. All the individuals were aware of the purpose of the study and signed an informed consent form. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial on the Efficacy, Safety and Tolerability of Modified-Release Methylphenidate (MPH-MR) in Chinese Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).CNS Drugs. 2025 Mar;39(3):289-304. doi: 10.1007/s40263-024-01136-6. Epub 2024 Dec 13. CNS Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39671144 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Peripheral blood complement factors C2 and C3 as biomarkers of clinical efficacy in patients with first-episode schizophrenia after aripiprazole treatment.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Dec 31;24(1):961. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-06437-0. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39741241 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of race on efficacy and safety during treatment with olanzapine in schizophrenia, schizophreniform or schizoaffective disorder.BMC Psychiatry. 2010 Nov 3;10:89. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-10-89. BMC Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 21047395 Free PMC article.
-
Oral budesonide for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 26;2015(10):CD007698. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007698.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26497719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Etrolizumab for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 2;2015(12):CD011661. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011661.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26630451 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lewis DA, Lieberman JA. Catching up on schizophrenia: natural history and neurobiology. Neuron. 2000;28(2):325–34. - PubMed
-
- Curto M, Fazio F, Ulivieri M, Navari S, Lionetto L, Baldessarini RJ. Improving adherence to pharmacological treatment for schizophrenia: a systematic assessment. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021;22(9):1143–55. - PubMed
-
- Stahl SM. Dopamine system stabilizers, aripiprazole, and the next generation of antipsychotics, part 1, “Goldilocks” actions at dopamine receptors. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62(11):841–2. - PubMed
-
- Stahl SM. Dopamine system stabilizers, aripiprazole, and the next generation of antipsychotics, part 2: illustrating their mechanism of action. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62(12):923–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

