Comparative effects of topiramate and naltrexone on neural activity during anticipatory anxiety in individuals with alcohol use disorder
- PMID: 39558663
- PMCID: PMC11573881
- DOI: 10.1093/alcalc/agae078
Comparative effects of topiramate and naltrexone on neural activity during anticipatory anxiety in individuals with alcohol use disorder
Abstract
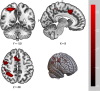
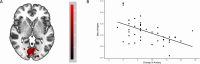
Topiramate has been found to be effective in reducing alcohol use and may also attenuate anxiety severity in patients with alcohol use disorder (AUD). This study compared the neural response of treatment-seeking patients with AUD on either topiramate or naltrexone during an anticipatory anxiety task. Participants were 42 patients with AUD who were randomized to receive either topiramate (n = 23; titrated dose up to 200 mg/day) or naltrexone (n = 19; 50 mg/day) for 12-weeks as part of a larger randomized controlled trial. Following 6 weeks of treatment, participants completed an anticipatory anxiety task during a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) session. The task presented a series of high-threat and low-threat stimuli followed by an unpleasant or pleasant image, respectively. Primary whole-brain analyses revealed no significant differences in neural activation between the topiramate and naltrexone groups. Deactivation for safe cues relative to threat cues was observed within the precuneus, inferior parietal lobule and the cingulate gyrus. In the precentral and middle frontal gyri, threat cues elicited greater activation. Exploratory analyses revealed an effect of change in anxiety from baseline to week 6, with a greater reduction associated with a reduced response to threat cues relative to safe cues in the cuneus and lingual gyrus. The current study is the first to examine and compare neural activation during anticipatory anxiety in treatment-seeking individuals on topiramate and naltrexone. This preliminary research contributes to our understanding of the therapeutic mechanisms of these alcohol pharmacotherapies.
Keywords: alcohol use disorder; anxiety; fMRI; naltrexone; topiramate.
© The Author(s) 2024. Medical Council on Alcohol and Oxford University Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neural cue reactivity and intrinsic functional connectivity in individuals with alcohol use disorder following treatment with topiramate or naltrexone.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025 Jan 24. doi: 10.1007/s00213-025-06745-7. Online ahead of print. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025. PMID: 39853353
-
Effects of topiramate on neural responses to alcohol cues in treatment-seeking individuals with alcohol use disorder: preliminary findings from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021 Jul;46(8):1414-1420. doi: 10.1038/s41386-021-00968-w. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33558678 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparing Three Ways to Help Cancer Survivors Plan for Follow-Up Care [Internet].Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2022 May. Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2022 May. PMID: 39666842 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Drug therapy for obstructive sleep apnoea in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 May 31;2013(5):CD003002. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003002.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23728641 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association, 2013. 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596. - DOI

