Light-Seq: light-directed in situ barcoding of biomolecules in fixed cells and tissues for spatially indexed sequencing
- PMID: 36216958
- PMCID: PMC9636025
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-022-01604-1
Light-Seq: light-directed in situ barcoding of biomolecules in fixed cells and tissues for spatially indexed sequencing
Abstract
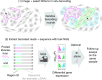
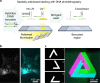
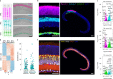
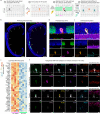
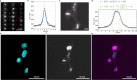
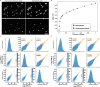
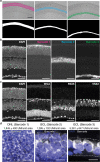
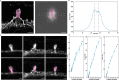
We present Light-Seq, an approach for multiplexed spatial indexing of intact biological samples using light-directed DNA barcoding in fixed cells and tissues followed by ex situ sequencing. Light-Seq combines spatially targeted, rapid photocrosslinking of DNA barcodes onto complementary DNAs in situ with a one-step DNA stitching reaction to create pooled, spatially indexed sequencing libraries. This light-directed barcoding enables in situ selection of multiple cell populations in intact fixed tissue samples for full-transcriptome sequencing based on location, morphology or protein stains, without cellular dissociation. Applying Light-Seq to mouse retinal sections, we recovered thousands of differentially enriched transcripts from three cellular layers and discovered biomarkers for a very rare neuronal subtype, dopaminergic amacrine cells, from only four to eight individual cells per section. Light-Seq provides an accessible workflow to combine in situ imaging and protein staining with next generation sequencing of the same cells, leaving the sample intact for further analysis post-sequencing.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.Y.K., N.L., P.Y. and S.K.S. are inventors on patent applications covering the method. Multiple authors are involved in commercialization of the technique and engage with Digital Biology, Inc. (J.Y.K. and E.R.W. are co-founders and employees; P.Y. is co-founder, equity holder, director and consultant; S.K.S. is anticipated to be a consulting scientific co-founder; N.L. is a consulting founding scientist; J.J.J. is an employee.) P.Y. is also a co-founder, equity holder, director and consultant of Ultivue, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Large field of view and spatial region of interest transcriptomics in fixed tissue.Commun Biol. 2024 Aug 20;7(1):1020. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06694-5. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39164496 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrop enables droplet-based single-cell ATAC-seq and single-cell RNA-seq using dissolvable hydrogel beads.Elife. 2022 Feb 23;11:e73971. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73971. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35195064 Free PMC article.
-
SCITO-seq: single-cell combinatorial indexed cytometry sequencing.Nat Methods. 2021 Aug;18(8):903-911. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01222-3. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Nat Methods. 2021. PMID: 34354295 Free PMC article.
-
Computational solutions for spatial transcriptomics.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Sep 1;20:4870-4884. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.08.043. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36147664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation of Single-Cell RNA-Seq Libraries for Next Generation Sequencing.Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2014 Jul 1;107:4.22.1-4.22.17. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb0422s107. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24984854 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Next-generation spatial transcriptomics: unleashing the power to gear up translational oncology.MedComm (2020). 2024 Oct 6;5(10):e765. doi: 10.1002/mco2.765. eCollection 2024 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39376738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large field of view and spatial region of interest transcriptomics in fixed tissue.Commun Biol. 2024 Aug 20;7(1):1020. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06694-5. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39164496 Free PMC article.
-
Optics-free reconstruction of 2D images via DNA barcode proximity graphs.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 8:2024.08.06.606834. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.06.606834. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39149271 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Deep 3D histology powered by tissue clearing, omics and AI.Nat Methods. 2024 Jul;21(7):1153-1165. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02327-1. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Nat Methods. 2024. PMID: 38997593 Review.
-
Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Spatial Transcriptomics: A Perspective from Barcoding Chemistry.JACS Au. 2024 Apr 15;4(5):1723-1743. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.4c00118. eCollection 2024 May 27. JACS Au. 2024. PMID: 38818076 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nitta N, et al. Intelligent image-activated cell sorting. Cell. 2018;175:266–276.e13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

