Accelerated identification of disease-causing variants with ultra-rapid nanopore genome sequencing
- PMID: 35347328
- PMCID: PMC9287171
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-022-01221-5
Accelerated identification of disease-causing variants with ultra-rapid nanopore genome sequencing
Abstract
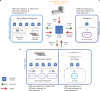
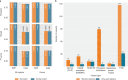
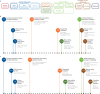
Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) can identify variants that cause genetic disease, but the time required for sequencing and analysis has been a barrier to its use in acutely ill patients. In the present study, we develop an approach for ultra-rapid nanopore WGS that combines an optimized sample preparation protocol, distributing sequencing over 48 flow cells, near real-time base calling and alignment, accelerated variant calling and fast variant filtration for efficient manual review. Application to two example clinical cases identified a candidate variant in <8 h from sample preparation to variant identification. We show that this framework provides accurate variant calls and efficient prioritization, and accelerates diagnostic clinical genome sequencing twofold compared with previous approaches.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.E.G. owns stock in INVITAE, Illumina and PacBio. K.S. has performed paid internships at NVIDIA Corp. and Google LLC, and presented a talk at an ONT-sponsored event. P.C., G.B, A.K., M.N. and A.C. are employees of Google LLC and own Alphabet stock as part of the standard compensation package. D.R.G., J.G. and C.J.W. are employees of Oxford Nanopore Technologies and share/share option holders. M.S., A.S. and T.Z. are employees of NVIDIA Corp. and own NVIDIA stock as part of the standard compensation package. M.J. has received reimbursement for travel, accommodation and conference fees to speak at events organized by ONT. F.J.S. received travel compensation from Pacific Biotechnology and Oxford Nanopore Technologies. E.A.A. is cofounder of Personalis, Deepcell, and Svexa, Advisor to Apple, and a Non-Executive Director of AstraZeneca. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Comparison of Structural Variant Calling from Short-Read and Nanopore-Based Whole-Genome Sequencing Using Optical Genome Mapping as a Benchmark.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;15(7):925. doi: 10.3390/genes15070925. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39062704 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing of human genomes with nanopore technology.Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 23;10(1):1869. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09637-5. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31015479 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Read Whole-Genome Sequencing Using a Nanopore Sequencer and Detection of Structural Variants in Cancer Genomes.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2632:177-189. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2996-3_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36781729
-
Nanopore sequencing technology, bioinformatics and applications.Nat Biotechnol. 2021 Nov;39(11):1348-1365. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01108-x. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Nat Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34750572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Application of nanopore sequencing in environmental microbiology research].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022 Jan 25;38(1):5-13. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.210085. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35142114 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Dispatches from Biotech beginning BeginNGS: Rapid newborn genome sequencing to end the diagnostic and therapeutic odyssey.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2022 Jun;190(2):243-256. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.32005. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2022. PMID: 36218021 Free PMC article.
-
TDFPS-Designer: an efficient toolkit for barcode design and selection in nanopore sequencing.Genome Biol. 2024 Nov 4;25(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s13059-024-03423-3. Genome Biol. 2024. PMID: 39497190 Free PMC article.
-
Primed and ready: nanopore metabarcoding can now recover highly accurate consensus barcodes that are generally indel-free.BMC Genomics. 2024 Sep 9;25(1):842. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10767-4. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39251911 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of long-read sequencing for All of Us.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 29;15(1):837. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44804-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38281971 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated multi-omics for rapid rare disease diagnosis on a national scale.Nat Med. 2023 Jul;29(7):1681-1691. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02401-9. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Nat Med. 2023. PMID: 37291213 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

