Clinical Implementation and Initial Experience With a 1.5 Tesla MR-Linac for MR-Guided Radiation Therapy for Gynecologic Cancer: An R-IDEAL Stage 1 and 2a First in Humans Feasibility Study of New Technology Implementation
- PMID: 35278717
- PMCID: PMC9233002
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prro.2022.03.002
Clinical Implementation and Initial Experience With a 1.5 Tesla MR-Linac for MR-Guided Radiation Therapy for Gynecologic Cancer: An R-IDEAL Stage 1 and 2a First in Humans Feasibility Study of New Technology Implementation
Abstract
Purpose: Magnetic resonance imaging-guided linear accelerator systems (MR-linacs) can facilitate the daily adaptation of radiation therapy plans. Here, we report our early clinical experience using a MR-linac for adaptive radiation therapy of gynecologic malignancies.
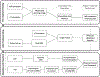
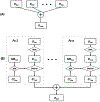
Methods and materials: Treatments were planned with an Elekta Monaco v5.4.01 and delivered by a 1.5 Tesla Elekta Unity MR-linac. The system offers a choice of daily adaptation based on either position (ATP) or shape (ATS) of the tumor and surrounding normal structures. The ATS approach has the option of manually editing the contours of tumors and surrounding normal structures before the plan is adapted. Here, we documented the duration of each treatment fraction; set-up variability (assessed by isocenter shifts in each plan) between fractions; and, for quality assurance, calculated the percentage of plans meeting the γ-criterion of 3%/3-mm distance to agreement. Deformable accumulated dose calculations were used to compare accumulated versus planned dose for patient treated with exclusively ATP fractions.
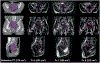
Results: Of the 10 patients treated with 90 fractions on the MR-linac, most received boost doses to recurrence in nodes or isolated tumors. Each treatment fraction lasted a median 32 minutes; fractions were shorter with ATP than with ATS (30 min vs 42 min, P < .0001). The γ criterion for all fraction plans exceeded >90% (median, 99.9%; range, 92.4%-100%; ie, all plans passed quality assurance testing). The average extent of isocenter shift was <0.5 cm in each axis. The accumulated dose to the gross tumor volume was within 5% of the reference plan for all ATP cases. Accumulated doses for lesions in the pelvic periphery were within <1% of the reference plan as opposed to -1.6% to -4.4% for central pelvic tumors.
Conclusions: The MR-linac is a reliable and clinically feasible tool for treating patients with gynecologic cancer.
Copyright © 2022 American Society for Radiation Oncology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
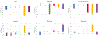
Similar articles
-
Initial Feasibility and Clinical Implementation of Daily MR-Guided Adaptive Head and Neck Cancer Radiation Therapy on a 1.5T MR-Linac System: Prospective R-IDEAL 2a/2b Systematic Clinical Evaluation of Technical Innovation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 Apr 1;109(5):1606-1618. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.12.015. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 33340604 Free PMC article.
-
Dose accumulation of daily adaptive plans to decide optimal plan adaptation strategy for head-and-neck patients treated with MR-Linac.Med Dosim. 2022 Spring;47(1):103-109. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2021.08.005. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Med Dosim. 2022. PMID: 34756493 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric analysis of MR-LINAC treatment plans for salvage spine SBRT re-irradiation.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2022 Oct;23(10):e13752. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13752. Epub 2022 Aug 25. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2022. PMID: 36004700 Free PMC article.
-
Adoption of Hybrid MRI-Linac Systems for the Treatment of Brain Tumors: A Systematic Review of the Current Literature Regarding Clinical and Technical Features.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15330338231199286. doi: 10.1177/15330338231199286. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 37774771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical application of MR-Linac in tumor radiotherapy: a systematic review.Radiat Oncol. 2023 Mar 14;18(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13014-023-02221-8. Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36918884 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of intrafractional spinal cord and spinal canal movement during stereotactic MR-guided online adaptive radiotherapy for kidney cancer.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 30;19(10):e0312032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312032. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39475854 Free PMC article.
-
Beginning of clinical treatment using the 1.5 Tesla MR-Linac system in Japan: a narrative review.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Feb 29;13(2):1131-1138. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-1649. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38482421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MR-LINAC, a New Partner in Radiation Oncology: Current Landscape.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 8;16(2):270. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020270. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

