The role of mucin 1 in respiratory diseases
- PMID: 33536260
- PMCID: PMC9488590
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0149-2020
The role of mucin 1 in respiratory diseases
Abstract
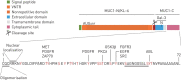
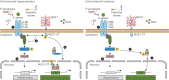
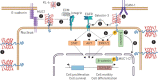
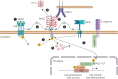
Recent evidence has demonstrated that mucin 1 (MUC1) is involved in many pathological processes that occur in the lung. MUC1 is a transmembrane protein mainly expressed by epithelial and hematopoietic cells. It has a receptor-like structure, which can sense the external environment and activate intracellular signal transduction pathways through its cytoplasmic domain. The extracellular domain of MUC1 can be released to the external environment, thus acting as a decoy barrier to mucosal pathogens, as well as serving as a serum biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of several respiratory diseases such as lung cancer and interstitial lung diseases. Furthermore, bioactivated MUC1-cytoplasmic tail (CT) has been shown to act as an anti-inflammatory molecule in several airway infections and mediates the expression of anti-inflammatory genes in lung diseases such as chronic rhinosinusitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and severe asthma. Bioactivated MUC1-CT has also been reported to interact with several effectors linked to cellular transformation, contributing to the progression of respiratory diseases such as lung cancer and pulmonary fibrosis. In this review, we summarise the current knowledge of MUC1 as a promising biomarker and drug target for lung disease.
Copyright ©ERS 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: B. Ballester has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: J. Milara Payá has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: J. Cortijo Gimeno has nothing to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mucin 1 downregulation associates with corticosteroid resistance in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Feb;135(2):470-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.07.011. Epub 2014 Aug 23. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25159466
-
Mucin 1 deficiency mediates corticosteroid insensitivity in asthma.Allergy. 2019 Jan;74(1):111-121. doi: 10.1111/all.13546. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Allergy. 2019. PMID: 29978485
-
The Role of the Cell Surface Mucin MUC1 as a Barrier to Infection and Regulator of Inflammation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Apr 24;9:117. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00117. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31069176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MUC1 deficiency mediates corticosteroid resistance in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Respir Res. 2018 Nov 20;19(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0927-4. Respir Res. 2018. PMID: 30458870 Free PMC article.
-
MUC1 Mucin: A Putative Regulatory (Checkpoint) Molecule of T Cells.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 22;9:2391. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02391. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30405607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Transgenic Mice Carrying the Human MUC5B rs35705950 Variant.Cells. 2024 Sep 11;13(18):1523. doi: 10.3390/cells13181523. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39329706 Free PMC article.
-
Baseline Blood Levels of Mucin-1 Are Associated with Crucial On-Treatment Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Receiving Antifibrotic Pirfenidone.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 8;12(2):402. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020402. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398004 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 and Epithelial MUC1 Mucin-Interactions Supporting Cancer Development.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 9;15(10):2680. doi: 10.3390/cancers15102680. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37345016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salivary Transmembrane Mucins of the MUC1 Family (CA 15-3, CA 27.29, MCA) in Breast Cancer: The Effect of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2).Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 12;16(20):3461. doi: 10.3390/cancers16203461. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456554 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting necroptosis: a promising avenue for respiratory disease treatment.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Aug 28;22(1):418. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01804-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39192326 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
