Prospects for Using Expression Patterns of Paramyxovirus Receptors as Biomarkers for Oncolytic Virotherapy
- PMID: 33291506
- PMCID: PMC7762160
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12123659
Prospects for Using Expression Patterns of Paramyxovirus Receptors as Biomarkers for Oncolytic Virotherapy
Abstract
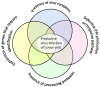
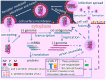
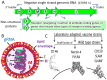
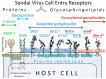
The effectiveness of oncolytic virotherapy in cancer treatment depends on several factors, including successful virus delivery to the tumor, ability of the virus to enter the target malignant cell, virus replication, and the release of progeny virions from infected cells. The multi-stage process is influenced by the efficiency with which the virus enters host cells via specific receptors. This review describes natural and artificial receptors for two oncolytic paramyxoviruses, nonpathogenic measles, and Sendai viruses. Cell entry receptors are proteins for measles virus (MV) and sialylated glycans (sialylated glycoproteins or glycolipids/gangliosides) for Sendai virus (SeV). Accumulated published data reviewed here show different levels of expression of cell surface receptors for both viruses in different malignancies. Patients whose tumor cells have low or no expression of receptors for a specific oncolytic virus cannot be successfully treated with the virus. Recent published studies have revealed that an expression signature for immune genes is another important factor that determines the vulnerability of tumor cells to viral infection. In the future, a combination of expression signatures of immune and receptor genes could be used to find a set of oncolytic viruses that are more effective for specific malignancies.
Keywords: Sendai virus; biomarkers; gangliosides; glycosphingolipid receptors; measles virus; oncolytic virotherapy; oncolytic viruses; protein receptors; receptor retargeting; viral oncolysis; virus receptor expression; virus receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Olga V. Matveeva belong to a company (Sendai Viralytics LLC). The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Measles to the Rescue: A Review of Oncolytic Measles Virus.Viruses. 2016 Oct 22;8(10):294. doi: 10.3390/v8100294. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27782084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Oncolysis by Paramyxovirus Sendai.Acta Naturae. 2015 Apr-Jun;7(2):6-16. Acta Naturae. 2015. PMID: 26085940 Free PMC article.
-
[Oncolytic Paramyxoviruses: Mechanism of Action, Preclinical and Clinical Studies].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2018 May-Jun;52(3):360-379. doi: 10.7868/S0026898418030023. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2018. PMID: 29989571 Review. Russian.
-
Novel oncolytic viral therapies in patients with thoracic malignancies.Oncolytic Virother. 2016 Dec 21;6:1-9. doi: 10.2147/OV.S116012. eCollection 2017. Oncolytic Virother. 2016. PMID: 28053943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncolysis by paramyxoviruses: preclinical and clinical studies.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2015;2:15017-. doi: 10.1038/mto.2015.17. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2015. PMID: 26640815 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Immunotherapeutic Efficacy of Retargeted oHSVs Designed for Propagation in an Ad Hoc Cell Line.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 12;13(2):266. doi: 10.3390/cancers13020266. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33445744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Fusion and Syncytia Formation in Cancer.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2024;71:433-465. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-37936-9_20. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2024. PMID: 37996689 Review.
-
Extracellular Events Involved in Cancer Cell-Cell Fusion.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 16;23(24):16071. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416071. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncolytic Viro-Immunotherapy: An Emerging Option in the Treatment of Gliomas.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 5;12:721830. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.721830. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34675919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Unconventional Case Study of Neoadjuvant Oncolytic Virotherapy for Recurrent Breast Cancer.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Aug 23;12(9):958. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12090958. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339989 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

