Centella Asiatica Improves Memory and Promotes Antioxidative Signaling in 5XFAD Mice
- PMID: 31817977
- PMCID: PMC6943631
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox8120630
Centella Asiatica Improves Memory and Promotes Antioxidative Signaling in 5XFAD Mice
Abstract
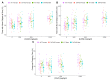
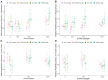
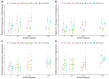
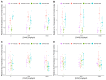
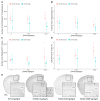
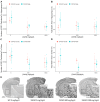
Centella asiatica (CA) herb is a traditional medicine, long reputed to provide cognitive benefits. We have reported that CA water extract (CAW) treatment improves cognitive function of aged Alzheimer's disease (AD) model Tg2576 and wild-type (WT) mice, and induces an NRF2-regulated antioxidant response in aged WT mice. Here, CAW was administered to AD model 5XFAD female and male mice and WT littermates (age: 7.6 +/ - 0.6 months), and object recall and contextual fear memory were tested after three weeks treatment. CAW's impact on amyloid-β plaque burden, and markers of neuronal oxidative stress and synaptic density, was assessed after five weeks treatment. CAW antioxidant activity was evaluated via nuclear transcription factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (NRF2) and NRF2-regulated antioxidant response element gene expression. Memory improvement in both genders and genotypes was associated with dose-dependent CAW treatment without affecting plaque burden, and marginally increased synaptic density markers in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. CAW treatment increased Nrf2 in hippocampus and other NRF2 targets (heme oxygenase-1, NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1, glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit). Reduced plaque-associated SOD1, an indicator of oxidative stress, was observed in the hippocampi and cortices of CAW-treated 5XFAD mice. We postulate that CAW treatment leads to reduced oxidative stress, contributing to improved neuronal health and cognition.
Keywords: 5XFAD; Alzheimer’s disease; Centella asiatica; NRF2; antioxidant; cognitive function; memory; mouse model; neuritic dystrophy; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prolonged Treatment with Centella asiatica Improves Memory, Reduces Amyloid-β Pathology, and Activates NRF2-Regulated Antioxidant Response Pathway in 5xFAD Mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;81(4):1453-1468. doi: 10.3233/JAD-210271. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 33935097 Free PMC article.
-
Centella asiatica attenuates hippocampal mitochondrial dysfunction and improves memory and executive function in β-amyloid overexpressing mice.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018 Dec;93:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 22. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30253196 Free PMC article.
-
Mode of administration influences plasma levels of active Centella asiatica compounds in 5xFAD mice while markers of neuroinflammation remain unaltered.Front Neurosci. 2024 Mar 25;18:1277626. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1277626. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38591068 Free PMC article.
-
Centella asiatica Alters Metabolic Pathways Associated With Alzheimer's Disease in the 5xFAD Mouse Model of ß-Amyloid Accumulation.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 16;12:788312. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.788312. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34975484 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeoylquinic Acids in Centella asiatica Reverse Cognitive Deficits in Male 5XFAD Alzheimer's Disease Model Mice.Nutrients. 2020 Nov 13;12(11):3488. doi: 10.3390/nu12113488. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33202902 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Mixture of Gotu Kola, Cnidium Fruit, and Goji Berry Enhances Memory Functions by Inducing Nerve-Growth-Factor-Mediated Actions Both In Vitro and In Vivo.Nutrients. 2020 May 11;12(5):1372. doi: 10.3390/nu12051372. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32403381 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of age-related cognitive decline and anxiety in mice by Centella asiatica extract varies by sex, dose and mode of administration.Front Aging. 2024 May 6;5:1357922. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2024.1357922. eCollection 2024. Front Aging. 2024. PMID: 38770167 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into antioxidant activities and anti-skin-aging potential of callus extract from Centella asiatica (L.).Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 29;11(1):13459. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92958-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34188145 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Stress and Oxidative Stress as Common Factors of the Pathogenesis of Depression and Alzheimer's Disease: The Role of Antioxidants in Prevention and Treatment.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Sep 9;10(9):1439. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091439. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional knowledge of medicinal plants on Gau Island, Fiji: differences between sixteen villages with unique characteristics of cultural value.J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2021 Oct 11;17(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13002-021-00481-w. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2021. PMID: 34635130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wattanathorn J., Mator L., Muchimapura S., Tongun T., Pasuriwong O., Piyawatkul N., Yimtae K., Sripanidkulchai B., Singkhoraard J. Positive modulation of cognition and mood in the healthy elderly volunteer following the administration of Centella asiatica. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008;116:325–332. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2007.11.038. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

