Immuno-SABER enables highly multiplexed and amplified protein imaging in tissues
- PMID: 31427819
- PMCID: PMC6728175
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-019-0207-y
Immuno-SABER enables highly multiplexed and amplified protein imaging in tissues
Abstract
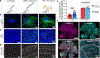
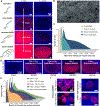
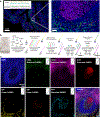
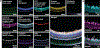
Spatial mapping of proteins in tissues is hindered by limitations in multiplexing, sensitivity and throughput. Here we report immunostaining with signal amplification by exchange reaction (Immuno-SABER), which achieves highly multiplexed signal amplification via DNA-barcoded antibodies and orthogonal DNA concatemers generated by primer exchange reaction (PER). SABER offers independently programmable signal amplification without in situ enzymatic reactions, and intrinsic scalability to rapidly amplify and visualize a large number of targets when combined with fast exchange cycles of fluorescent imager strands. We demonstrate 5- to 180-fold signal amplification in diverse samples (cultured cells, cryosections, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections and whole-mount tissues), as well as simultaneous signal amplification for ten different proteins using standard equipment and workflows. We also combined SABER with expansion microscopy to enable rapid, multiplexed super-resolution tissue imaging. Immuno-SABER presents an effective and accessible platform for multiplexed and amplified imaging of proteins with high sensitivity and throughput.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
SABER amplifies FISH: enhanced multiplexed imaging of RNA and DNA in cells and tissues.Nat Methods. 2019 Jun;16(6):533-544. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0404-0. Epub 2019 May 20. Nat Methods. 2019. PMID: 31110282 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Sequential in Situ Multiplexing with DNA Exchange Imaging in Neuronal Cells and Tissues.Nano Lett. 2017 Oct 11;17(10):6131-6139. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b02716. Epub 2017 Oct 2. Nano Lett. 2017. PMID: 28933153 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-barcoded signal amplification for imaging mass cytometry enables sensitive and highly multiplexed tissue imaging.Nat Methods. 2023 Sep;20(9):1304-1309. doi: 10.1038/s41592-023-01976-y. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Nat Methods. 2023. PMID: 37653118 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemistry and mass spectrometry for highly multiplexed cellular molecular imaging.Lab Invest. 2015 Apr;95(4):397-405. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.2. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Lab Invest. 2015. PMID: 25730370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Low-Cost Modular Imaging System for Rapid, Multiplexed Immunofluorescence Detection in Clinical Tissues.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 10;24(8):7008. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087008. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Highly Multiplexed Tissue Imaging in Precision Oncology and Translational Cancer Research.Cancer Discov. 2024 Nov 1;14(11):2071-2088. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-23-1165. Cancer Discov. 2024. PMID: 39485249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiplexed Immunophenotyping of Lymphoma Tissue Samples.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2865:375-393. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4188-0_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39424733
-
Single-shot 20-fold expansion microscopy.Nat Methods. 2024 Oct 11. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02454-9. Online ahead of print. Nat Methods. 2024. PMID: 39394503
-
NanoPlex: a universal strategy for fluorescence microscopy multiplexing using nanobodies with erasable signals.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 10;15(1):8771. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53030-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39384781 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell and spatial omics unravel the spatiotemporal biology of tumour border invasion and haematogenous metastasis.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Oct;14(10):e70036. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70036. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39350478 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Giesen CW, Schapiro HAO, D.; Zivanovic N; Jacobs A; Hattendorf B; Schüffler PJ; Grolimund D; Buhmann JM; Brandt S; Varga Z; Wild PJ; Günther D; Bodenmiller B Highly multiplexed imaging of tumor tissues with subcellular resolution by mass cytometry. Nature Methods 11, 417–425 (2014). - PubMed
Methods References
-
- Pierce MB & Dirks RM A Partition Function Algorithm for Nucleic Acid Secondary Structure Including Pseudoknots. J Comput Chem 24, 1664–1677 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Dirks RM & Pierce NA An algorithm for computing nucleic acid base-pairing probabilities including pseudoknots. J Comput Chem 25, 1295–1304 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

