The mesenchymal stem cell secretome as an acellular regenerative therapy for liver disease
- PMID: 31270691
- PMCID: PMC6698261
- DOI: 10.1007/s00535-019-01599-1
The mesenchymal stem cell secretome as an acellular regenerative therapy for liver disease
Abstract
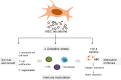
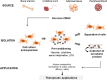
The use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) for tissue repair has garnered much interest and has been evaluated in several disease settings. Recent evidence indicates that the beneficial effects observed with MSC-based therapy can be mediated through the paracrine release of extracellular vesicles and other soluble proteins or biologically active molecules, which collectively constitute the MSC secretome. In this concise overview, we highlight results from preclinical and other studies that demonstrate the therapeutic efficacy of the MSC secretome for diseases that are characterized by liver injury or fibrosis. The potential for the use of the MSC secretome as an acellular regenerative therapy and approaches for the isolation of a secretome product for therapeutic applications are highlighted. The use of the MSC secretome as an acellular therapeutic agent could provide several advantages over the use of cell-based therapies for liver diseases.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles; Regenerative medicine; Secretome product; Stem cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular Mechanisms Responsible for Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome.Cells. 2019 May 16;8(5):467. doi: 10.3390/cells8050467. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31100966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell secretome for lung regeneration: The long way through "pharmaceuticalization" for the best formulation.J Control Release. 2019 Sep 10;309:11-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.07.022. Epub 2019 Jul 18. J Control Release. 2019. PMID: 31326462 Review.
-
Harnessing the mesenchymal stem cell secretome for regenerative urology.Nat Rev Urol. 2019 Jun;16(6):363-375. doi: 10.1038/s41585-019-0169-3. Nat Rev Urol. 2019. PMID: 30923338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The secretome of mesenchymal stem cells and oxidative stress: challenges and opportunities in cell-free regenerative medicine.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Jul;48(7):5607-5619. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06360-7. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34191238 Review.
-
Therapeutic Properties of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells: The Need of Cell Priming for Cell-Free Therapies in Regenerative Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 14;22(2):763. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020763. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33466583 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mesenchyme Stem Cell-Derived Conditioned Medium as a Potential Therapeutic Tool in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 16;10(9):2298. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092298. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal/stem cell secretome and cord blood serum in prostate cancer progression.Hum Cell. 2023 May;36(3):1160-1172. doi: 10.1007/s13577-023-00880-z. Epub 2023 Feb 19. Hum Cell. 2023. PMID: 36806993 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome: A Potential Therapeutic Option for Autoimmune and Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases.Cells. 2022 Jul 26;11(15):2300. doi: 10.3390/cells11152300. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35892597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human umbilical cord/placenta mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium attenuates intestinal fibrosis in vivo and in vitro.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Mar 7;15(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03678-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38454492 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Liver Fibrosis: Novel Strategies, Mechanisms, and Clinical Practice.Stem Cells Int. 2021 Aug 10;2021:6546780. doi: 10.1155/2021/6546780. eCollection 2021. Stem Cells Int. 2021. PMID: 34434239 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fouraschen SM, et al. Secreted factors of human liver-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote liver regeneration early after partial hepatectomy. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(13):2410–2419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

