The small members of the JMJD protein family: Enzymatic jewels or jinxes?
- PMID: 31034925
- PMCID: PMC6525012
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.04.002
The small members of the JMJD protein family: Enzymatic jewels or jinxes?
Abstract
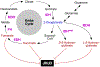
Jumonji C domain-containing (JMJD) proteins are mostly epigenetic regulators that demethylate histones. However, a hitherto neglected subfamily of JMJD proteins, evolutionarily distant and characterized by their relatively small molecular weight, exerts different functions by hydroxylating proteins and RNA. Recently, unsuspected proteolytic and tyrosine kinase activities were also ascribed to some of these small JMJD proteins, further increasing their enzymatic versatility. Here, we discuss the ten human small JMJD proteins (HIF1AN, HSPBAP1, JMJD4, JMJD5, JMJD6, JMJD7, JMJD8, RIOX1, RIOX2, TYW5) and their diverse physiological functions. In particular, we focus on the roles of these small JMJD proteins in cancer and other maladies and how they are modulated in diseased cells by an altered metabolic milieu, including hypoxia, reactive oxygen species and oncometabolites. Because small JMJD proteins are enzymes, they are amenable to inhibition by small molecules and may represent novel targets in the therapy of cancer and other diseases.
Keywords: Cancer; Demethylation; Hydroxylation; Jumonji; Oncometabolite.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

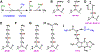
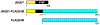
Similar articles
-
Versatile JMJD proteins: juggling histones and much more.Trends Biochem Sci. 2024 Sep;49(9):804-818. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2024.06.009. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Trends Biochem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38926050 Review.
-
JMJD family proteins in cancer and inflammation.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Sep 1;7(1):304. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01145-1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36050314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The JMJD Family Histone Demethylases in Crosstalk Between Inflammation and Cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 26;13:881396. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.881396. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35558079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crucial Functions of the JMJD1/KDM3 Epigenetic Regulators in Cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2021 Jan;19(1):3-13. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0404. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Mol Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 32605929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clipping of arginine-methylated histone tails by JMJD5 and JMJD7.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Sep 12;114(37):E7717-E7726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1706831114. Epub 2017 Aug 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28847961 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances and Therapeutic Implications of 2-Oxoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenases in Ischemic Stroke.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jul;61(7):3949-3975. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03790-1. Epub 2023 Dec 2. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38041714 Review.
-
Molecular Signatures of JMJD10/MINA53 in Gastric Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 2;12(5):1141. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051141. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32370161 Free PMC article.
-
JMJD5 inhibits lung cancer progression by regulating glucose metabolism through the p53/TIGAR pathway.Med Oncol. 2023 Apr 12;40(5):145. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02016-7. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37043051
-
First-in-Class Inhibitors of the Ribosomal Oxygenase MINA53.J Med Chem. 2021 Dec 9;64(23):17031-17050. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00605. Epub 2021 Nov 29. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34843649 Free PMC article.
-
JMJD8 Promotes Malignant Progression of Lung Cancer by Maintaining EGFR Stability and EGFR/PI3K/AKT Pathway Activation.J Cancer. 2021 Jan 1;12(4):976-987. doi: 10.7150/jca.50234. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33442397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kooistra SM, Helin K, Molecular mechanisms and potential functions of histone demethylases, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 13 (2012) 297–311. - PubMed
-
- Markolovic S, Leissing TM, Chowdhury R, Wilkins SE, Lu X, Schofield CJ, Structure- function relationships of human JmjC oxygenases-demethylases versus hydroxylases, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 41 (2016) 62–72. - PubMed
-
- Hewitson KS, McNeill LA, Riordan MV, Tian YM, Bullock AN, Welford RW, Elkins JM, Oldham NJ, Bhattacharya S, Gleadle JM, Ratcliffe PJ, Pugh CW, Schofield CJ, Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) asparagine hydroxylase is identical to factor inhibiting HIF (FIH) and is related to the cupin structural family, J. Biol. Chem 277 (2002) 26351–26355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

