Rhabdomyosarcoma
- PMID: 30617281
- PMCID: PMC7456566
- DOI: 10.1038/s41572-018-0051-2
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Abstract
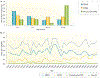
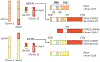
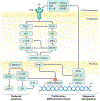
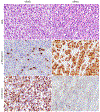
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is the most common soft tissue sarcoma in children and represents a high-grade neoplasm of skeletal myoblast-like cells. Decades of clinical and basic research have gradually improved our understanding of the pathophysiology of RMS and helped to optimize clinical care. The two major subtypes of RMS, originally characterized on the basis of light microscopic features, are driven by fundamentally different molecular mechanisms and pose distinct clinical challenges. Curative therapy depends on control of the primary tumour, which can arise at many distinct anatomical sites, as well as controlling disseminated disease that is known or assumed to be present in every case. Sophisticated risk stratification for children with RMS incorporates various clinical, pathological and molecular features, and that information is used to guide the application of multifaceted therapy. Such therapy has historically included cytotoxic chemotherapy as well as surgery, ionizing radiation or both. This Primer describes our current understanding of RMS epidemiology, disease susceptibility factors, disease mechanisms and elements of clinical care, including diagnostics, risk-based care of newly diagnosed and relapsed disease and the prevention and management of late effects in survivors. We also outline potential opportunities to further translate new biological insights into improved clinical outcomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Clinical and prognostic analysis of single-center multidisciplinary treatment for rhabdomyosarcoma in children].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Oct 2;57(10):767-773. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2019.10.008. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31594063 Chinese.
-
[Diagnosis and treatment of childhood soft tissue sarcomas].Magy Onkol. 2014 Mar;58(1):59-64. Epub 2014 Mar 1. Magy Onkol. 2014. PMID: 24712008 Review. Hungarian.
-
Anaplasia in childhood rhabdomyosarcoma: An under reported entity.Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2022 Oct-Dec;65(4):864-868. doi: 10.4103/ijpm.ijpm_178_21. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36308195
-
Role of surgery in children with rhabdomyosarcoma.Med Pediatr Oncol. 2003 Jul;41(1):1-6. doi: 10.1002/mpo.10261. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12764734 Review.
-
Molecular biology of rhabdomyosarcoma.Clin Transl Oncol. 2007 Jul;9(7):415-9. doi: 10.1007/s12094-007-0079-3. Clin Transl Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17652054 Review.
Cited by
-
Wide-Excision Choice in Orbital Rhabdomyosarcoma on an 8-Year-Old Patient in a Low-Resource Setting: A Case Report.Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2024 Oct 25;15(1):762-768. doi: 10.1159/000541645. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39464314 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Circulating Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Tumor Monitoring in Pediatric Sarcomas: Recent Advances and Future Directions.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 16;14(10):1306. doi: 10.3390/biom14101306. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dependence of PAX3-FOXO1 chromatin occupancy on ETS1 at important disease-promoting genes exposes new targetable vulnerability in Fusion-Positive Rhabdomyosarcoma.Oncogene. 2024 Oct 24. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03201-2. Online ahead of print. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 39448867
-
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of prostate combined with prostatic abscess in an adult patient: a case report and literature review.Transl Androl Urol. 2024 Sep 30;13(9):2146-2152. doi: 10.21037/tau-24-117. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Transl Androl Urol. 2024. PMID: 39434757 Free PMC article.
-
Anlotinib treatment for rapidly progressing pediatric embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma in the maxillary gingiva: a case report.Diagn Pathol. 2024 Oct 8;19(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s13000-024-01555-5. Diagn Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39379998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crist WM, et al. Intergroup rhabdomyosarcoma study-IV: results for patients with nonmetastatic disease. Journal of Clinical Oncology 19, 3091–3102 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Crist W, et al. The Third Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study. J Clin Oncol 13, 610–630 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Arndt CA, et al. Vincristine, actinomycin, and cyclophosphamide compared with vincristine, actinomycin, and cyclophosphamide alternating with vincristine, topotecan, and cyclophosphamide for intermediate-risk rhabdomyosarcoma: children's oncology group study D9803. J Clin Oncol 27, 5182–5188 (2009). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

