The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Psoriasis: IL-17A and Beyond
- PMID: 30127781
- PMCID: PMC6088173
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01682
The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Psoriasis: IL-17A and Beyond
Abstract
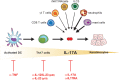
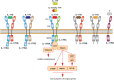
Psoriasis is a frequent chronic inflammatory skin disease, nowadays considered a major global health problem. Several new drugs, targeting the IL-23/IL-17A pathway, have been recently licensed or are in clinical development. These therapies represent a major improvement of the way in which psoriasis is managed, since they show an unprecedented efficacy on skin symptoms of psoriasis. This has been made possible, thanks to an increasingly more accurate pathogenic view of psoriasis. Today, the belief that Th17 cells mediate psoriasis is moving to the concept of psoriasis as an IL-17A-driven disease. New questions arise at the horizon, given that IL-17A is part of a newly described family of cytokines, which has five distinct homologous: IL-17B, IL-17C, IL-17D, IL-17E, also known as IL-25 and IL-17F. IL-17 family cytokines elicit similar effects in target cells, but simultaneously trigger different and sometimes opposite functions in a tissue-specific manner. This is complicated by the fact that IL-17 cytokines show a high capacity of synergisms with other inflammatory stimuli. In this review, we will summarize the current knowledge around the cytokines belonging to the IL-17 family in relation to skin inflammation in general and psoriasis in particular, and discuss possible clinical implications. A comprehensive understanding of the different roles played by the IL-17 cytokines is crucial to appreciate current and developing therapies and to allow an effective pathogenesis- and mechanisms-driven drug design.
Keywords: IL-17 family; IL-17A; IL-17E; IL-25; Th17 cells; comorbidities; interleukin; psoriasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-17 family cytokines in protective immunity against infections: role of hematopoietic cell-derived and non-hematopoietic cell-derived interleukin-17s.Microbiol Immunol. 2018 Jan;62(1):1-13. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12560. Microbiol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29205464 Review.
-
Revisiting the interleukin 17 family of cytokines in psoriasis: pathogenesis and potential targets for innovative therapies.Front Immunol. 2023 May 22;14:1186455. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1186455. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37283755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-17 inhibitors for psoriasis.Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2018 Sep;37(3):148-157. doi: 10.12788/j.sder.2018.051. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2018. PMID: 30215631 Review.
-
Interleukin 17A: toward a new understanding of psoriasis pathogenesis.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Jul;71(1):141-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.12.036. Epub 2014 Mar 18. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24655820 Review.
-
The role of IL-17 in psoriasis.J Dermatolog Treat. 2015 Feb;26(1):41-4. doi: 10.3109/09546634.2013.879093. Epub 2014 Feb 20. J Dermatolog Treat. 2015. PMID: 24552504 Review.
Cited by
-
Sprayable inflammasome-inhibiting lipid nanorods in a polymeric scaffold for psoriasis therapy.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 19;15(1):9035. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53396-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39426974 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Curcumin on the IL-17A-Mediated p53-Fibrinolytic System: Mouse Proteomics and Integrated Human Fibrosis scRNAseq Insights.Inflammation. 2024 Oct 19. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02167-3. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 39424752
-
Distinguishing between help and harm: Helper T cell subsets and immune-related adverse events.J Clin Invest. 2024 Oct 15;134(20):e184310. doi: 10.1172/JCI184310. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39403930 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Psoriasis and Pseudohernia of the Abdominal Wall at the Site of Herpes Zoster-Wolf's Isotopic Response.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024 Sep 23;17:2111-2115. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S482555. eCollection 2024. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 39345989 Free PMC article.
-
Senescence Rejuvenation through Reduction in Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Generation by Polygonum cuspidatum Extract: In Vitro Evidence.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 14;13(9):1110. doi: 10.3390/antiox13091110. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334769 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. World Psoriasis wdocument EB133.R2, Agenda Item 6.2. May 30. (2013). http://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/EB133/B133_R2-en.pdf
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

