Tumor Interferon Signaling Regulates a Multigenic Resistance Program to Immune Checkpoint Blockade
- PMID: 27912061
- PMCID: PMC5385895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.022
Tumor Interferon Signaling Regulates a Multigenic Resistance Program to Immune Checkpoint Blockade
Abstract
Therapeutic blocking of the PD1 pathway results in significant tumor responses, but resistance is common. We demonstrate that prolonged interferon signaling orchestrates PDL1-dependent and PDL1-independent resistance to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) and to combinations such as radiation plus anti-CTLA4. Persistent type II interferon signaling allows tumors to acquire STAT1-related epigenomic changes and augments expression of interferon-stimulated genes and ligands for multiple T cell inhibitory receptors. Both type I and II interferons maintain this resistance program. Crippling the program genetically or pharmacologically interferes with multiple inhibitory pathways and expands distinct T cell populations with improved function despite expressing markers of severe exhaustion. Consequently, tumors resistant to multi-agent ICB are rendered responsive to ICB monotherapy. Finally, we observe that biomarkers for interferon-driven resistance associate with clinical progression after anti-PD1 therapy. Thus, the duration of tumor interferon signaling augments adaptive resistance and inhibition of the interferon response bypasses requirements for combinatorial ICB therapies.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
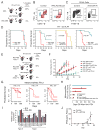
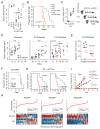
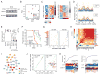



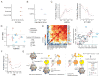
Comment in
-
Too Much of a Good Thing? Chronic IFN Fuels Resistance to Cancer Immunotherapy.Immunity. 2016 Dec 20;45(6):1181-1183. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.12.004. Immunity. 2016. PMID: 28002724
-
IFN Signaling and ICB Resistance: Time is on Tumor's Side.Trends Cancer. 2017 Mar;3(3):161-163. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Trends Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28718428 Review.
Similar articles
-
Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer.Nature. 2015 Apr 16;520(7547):373-7. doi: 10.1038/nature14292. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25754329 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing Functions of Interferon Coordinate Adaptive and Innate Immune Responses to Cancer Immune Checkpoint Blockade.Cell. 2019 Aug 8;178(4):933-948.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.07.019. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31398344 Free PMC article.
-
Radiotherapy complements immune checkpoint blockade.Cancer Cell. 2015 Apr 13;27(4):437-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.03.015. Cancer Cell. 2015. PMID: 25873170
-
The Era of Checkpoint Blockade in Lung Cancer: Taking the Brakes Off the Immune System.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017 Aug;14(8):1248-1260. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201702-152FR. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017. PMID: 28613923 Review.
-
Combining forces: the promise and peril of synergistic immune checkpoint blockade and targeted therapy in metastatic melanoma.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017 Mar;36(1):43-50. doi: 10.1007/s10555-017-9656-2. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017. PMID: 28181070 Review.
Cited by
-
AVL-armed oncolytic vaccinia virus promotes viral replication and boosts antitumor immunity via increasing ROS levels in pancreatic cancer.Mol Ther Oncol. 2024 Sep 17;32(4):200878. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200878. eCollection 2024 Dec 19. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39431173 Free PMC article.
-
IFNγ-Induced Bcl3, PD-L1 and IL-8 Signaling in Ovarian Cancer: Mechanisms and Clinical Significance.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 27;16(15):2676. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152676. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galectin-1-driven T cell exclusion in the tumor endothelium promotes immunotherapy resistance.J Clin Invest. 2019 Dec 2;129(12):5553-5567. doi: 10.1172/JCI129025. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 31710313 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity of Type I Interferon-Mediated Responses in Cancer Therapy: From Anti-tumor Immunity to Resistance.Front Oncol. 2018 Aug 21;8:322. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00322. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30186768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lymph node colonization induces tumor-immune tolerance to promote distant metastasis.Cell. 2022 May 26;185(11):1924-1942.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.019. Epub 2022 May 6. Cell. 2022. PMID: 35525247 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

