SRAMP: prediction of mammalian N6-methyladenosine (m6A) sites based on sequence-derived features
- PMID: 26896799
- PMCID: PMC4889921
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw104
SRAMP: prediction of mammalian N6-methyladenosine (m6A) sites based on sequence-derived features
Abstract
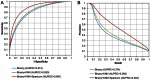
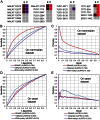
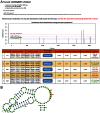
N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) is a prevalent RNA methylation modification involved in the regulation of degradation, subcellular localization, splicing and local conformation changes of RNA transcripts. High-throughput experiments have demonstrated that only a small fraction of the m(6)A consensus motifs in mammalian transcriptomes are modified. Therefore, accurate identification of RNA m(6)A sites becomes emergently important. For the above purpose, here a computational predictor of mammalian m(6)A site named SRAMP is established. To depict the sequence context around m(6)A sites, SRAMP combines three random forest classifiers that exploit the positional nucleotide sequence pattern, the K-nearest neighbor information and the position-independent nucleotide pair spectrum features, respectively. SRAMP uses either genomic sequences or cDNA sequences as its input. With either kind of input sequence, SRAMP achieves competitive performance in both cross-validation tests and rigorous independent benchmarking tests. Analyses of the informative features and overrepresented rules extracted from the random forest classifiers demonstrate that nucleotide usage preferences at the distal positions, in addition to those at the proximal positions, contribute to the classification. As a public prediction server, SRAMP is freely available at http://www.cuilab.cn/sramp/.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
WHISTLE: a high-accuracy map of the human N6-methyladenosine (m6A) epitranscriptome predicted using a machine learning approach.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Apr 23;47(7):e41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz074. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30993345 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive review and assessment of computational methods for predicting RNA post-transcriptional modification sites from RNA sequences.Brief Bioinform. 2020 Sep 25;21(5):1676-1696. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz112. Brief Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 31714956 Review.
-
RNAMethPre: A Web Server for the Prediction and Query of mRNA m6A Sites.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 10;11(10):e0162707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162707. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27723837 Free PMC article.
-
WHISTLE: A Functionally Annotated High-Accuracy Map of Human m6A Epitranscriptome.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2284:519-529. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1307-8_28. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33835461
-
Predicting N6-Methyladenosine Sites in Multiple Tissues of Mammals through Ensemble Deep Learning.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 7;23(24):15490. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415490. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
m6A-TSHub: Unveiling the Context-specific m6A Methylation and m6A-affecting Mutations in 23 Human Tissues.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023 Aug;21(4):678-694. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2022.09.001. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36096444 Free PMC article.
-
Geographic encoding of transcripts enabled high-accuracy and isoform-aware deep learning of RNA methylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Oct 14;50(18):10290-10310. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac830. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36155798 Free PMC article.
-
Kdm4a is an activity downregulated barrier to generate engrams for memory separation.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 13;15(1):5887. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50218-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39003305 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of m6A Modifiers and RNA Modifications in Uterine Fibroids.Endocrinology. 2024 Jul 1;165(8):bqae074. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae074. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38946397 Free PMC article.
-
m6A demethylase FTO regulate CTNNB1 to promote adipogenesis of chicken preadipocyte.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2022 Dec 2;13(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s40104-022-00795-z. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36461116 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

