Structural basis of nucleic-acid recognition and double-strand unwinding by the essential neuronal protein Pur-alpha
- PMID: 26744780
- PMCID: PMC4764581
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.11297
Structural basis of nucleic-acid recognition and double-strand unwinding by the essential neuronal protein Pur-alpha
Abstract
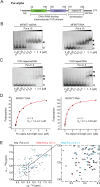
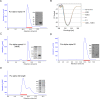
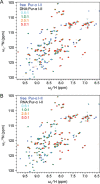
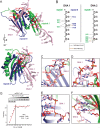
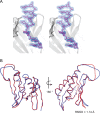
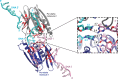
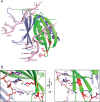
The neuronal DNA-/RNA-binding protein Pur-alpha is a transcription regulator and core factor for mRNA localization. Pur-alpha-deficient mice die after birth with pleiotropic neuronal defects. Here, we report the crystal structure of the DNA-/RNA-binding domain of Pur-alpha in complex with ssDNA. It reveals base-specific recognition and offers a molecular explanation for the effect of point mutations in the 5q31.3 microdeletion syndrome. Consistent with the crystal structure, biochemical and NMR data indicate that Pur-alpha binds DNA and RNA in the same way, suggesting binding modes for tri- and hexanucleotide-repeat RNAs in two neurodegenerative RNAopathies. Additionally, structure-based in vitro experiments resolved the molecular mechanism of Pur-alpha's unwindase activity. Complementing in vivo analyses in Drosophila demonstrated the importance of a highly conserved phenylalanine for Pur-alpha's unwinding and neuroprotective function. By uncovering the molecular mechanisms of nucleic-acid binding, this study contributes to understanding the cellular role of Pur-alpha and its implications in neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: 5q31.3 microdeletion syndrome; d. melanogaster; e. coli; ALS; DNA unwinding; DNA-/RNA-protein interaction; FXTAS; X-ray crystallography; biochemistry; biophysics; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PURA, the gene encoding Pur-alpha, member of an ancient nucleic acid-binding protein family with mammalian neurological functions.Gene. 2018 Feb 15;643:133-143. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.12.004. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29221753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
X-ray structure of Pur-alpha reveals a Whirly-like fold and an unusual nucleic-acid binding surface.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Nov 3;106(44):18521-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907990106. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19846792 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Pur-α binds to trinucleotide-repeat containing cellular RNAs and translocates to the early oocyte.RNA Biol. 2012 May;9(5):633-43. doi: 10.4161/rna.19760. Epub 2012 May 1. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22614836
-
Functional role of a conformationally flexible homopurine/homopyrimidine domain of the androgen receptor gene promoter interacting with Sp1 and a pyrimidine single strand DNA-binding protein.Mol Endocrinol. 1997 Jan;11(1):3-15. doi: 10.1210/mend.11.1.9868. Mol Endocrinol. 1997. PMID: 8994183
-
The pur protein family: genetic and structural features in development and disease.J Cell Physiol. 2013 May;228(5):930-7. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24237. J Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23018800 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A 25 Mainland Chinese cohort of patients with PURA-related neurodevelopmental disorders: clinical delineation and genotype-phenotype correlations.Eur J Hum Genet. 2023 Jan;31(1):112-121. doi: 10.1038/s41431-022-01217-4. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Eur J Hum Genet. 2023. PMID: 36376392 Free PMC article.
-
PURA, the gene encoding Pur-alpha, member of an ancient nucleic acid-binding protein family with mammalian neurological functions.Gene. 2018 Feb 15;643:133-143. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.12.004. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29221753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CGG Repeat Expansion, and Elevated Fmr1 Transcription and Mitochondrial Copy Number in a New Fragile X PM Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Model.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 30;8:482. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00482. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32695777 Free PMC article.
-
PURA syndrome-causing mutations impair PUR-domain integrity and affect P-body association.Elife. 2024 Apr 24;13:RP93561. doi: 10.7554/eLife.93561. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38655849 Free PMC article.
-
RNA toxicity and foci formation in microsatellite expansion diseases.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2017 Jun;44:17-29. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2017.01.005. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2017. PMID: 28208060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung L-W, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH. PHENIX: a comprehensive python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography. 2010;66:213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

