Endosomal sorting of Notch receptors through COMMD9-dependent pathways modulates Notch signaling
- PMID: 26553930
- PMCID: PMC4639872
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201505108
Endosomal sorting of Notch receptors through COMMD9-dependent pathways modulates Notch signaling
Abstract
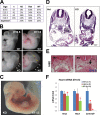
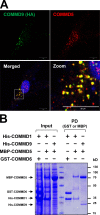
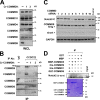
Notch family members are transmembrane receptors that mediate essential developmental programs. Upon ligand binding, a proteolytic event releases the intracellular domain of Notch, which translocates to the nucleus to regulate gene transcription. In addition, Notch trafficking across the endolysosomal system is critical in its regulation. In this study we report that Notch recycling to the cell surface is dependent on the COMMD-CCDC22-CCDC93 (CCC) complex, a recently identified regulator of endosomal trafficking. Disruption in this system leads to intracellular accumulation of Notch2 and concomitant reduction in Notch signaling. Interestingly, among the 10 copper metabolism MURR1 domain containing (COMMD) family members that can associate with the CCC complex, only COMMD9 and its binding partner, COMMD5, have substantial effects on Notch. Furthermore, Commd9 deletion in mice leads to embryonic lethality and complex cardiovascular alterations that bear hallmarks of Notch deficiency. Altogether, these studies highlight that the CCC complex controls Notch activation by modulating its intracellular trafficking and demonstrate cargo-specific effects for members of the COMMD protein family.
© 2015 Li et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The COMMD Family Regulates Plasma LDL Levels and Attenuates Atherosclerosis Through Stabilizing the CCC Complex in Endosomal LDLR Trafficking.Circ Res. 2018 Jun 8;122(12):1648-1660. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.312004. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Circ Res. 2018. PMID: 29545368
-
Endosomal PI(3)P regulation by the COMMD/CCDC22/CCDC93 (CCC) complex controls membrane protein recycling.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 19;10(1):4271. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12221-6. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31537807 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of murine copper homeostasis by members of the COMMD protein family.Dis Model Mech. 2021 Jan 1;14(1):dmm045963. doi: 10.1242/dmm.045963. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Dis Model Mech. 2021. PMID: 33262129 Free PMC article.
-
Towards a molecular understanding of endosomal trafficking by Retromer and Retriever.Traffic. 2019 Jul;20(7):465-478. doi: 10.1111/tra.12649. Traffic. 2019. PMID: 30993794 Review.
-
Endocytic Trafficking of the Notch Receptor.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1066:99-122. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-89512-3_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30030824 Review.
Cited by
-
COMMD proteins function and their regulating roles in tumors.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 23;13:1067234. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1067234. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36776284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COMMD10 Is Essential for Neural Plate Development during Embryogenesis.J Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 16;11(1):13. doi: 10.3390/jdb11010013. J Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36976102 Free PMC article.
-
News on the molecular regulation and function of hepatic low-density lipoprotein receptor and LDLR-related protein 1.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2017 Jun;28(3):241-247. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000411. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2017. PMID: 28301372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial Sensing by Intestinal Myeloid Cells Controls Carcinogenesis and Epithelial Differentiation.Cell Rep. 2018 Aug 28;24(9):2342-2355. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.066. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30157428 Free PMC article.
-
Endosomal receptor trafficking: Retromer and beyond.Traffic. 2018 Aug;19(8):578-590. doi: 10.1111/tra.12574. Epub 2018 May 21. Traffic. 2018. PMID: 29667289 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baladrón V., Ruiz-Hidalgo M.J., Nueda M.L., Díaz-Guerra M.J., García-Ramírez J.J., Bonvini E., Gubina E., and Laborda J.. 2005. dlk acts as a negative regulator of Notch1 activation through interactions with specific EGF-like repeats. Exp. Cell Res. 303:343–359. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.10.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

