Structure of CT584 from Chlamydia trachomatis refined to 3.05 Å resolution
- PMID: 24192348
- PMCID: PMC3818032
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309113027371
Structure of CT584 from Chlamydia trachomatis refined to 3.05 Å resolution
Abstract
Chlamydia trachomatis is a major cause of various diseases, including blinding trachoma and pelvic inflammatory disease, and is the leading reported sexually transmitted bacterial infection worldwide. All pathogenic Chlamydiae spp. utilize a supramolecular syringe, or type III secretion system (T3SS), to inject proteins into their obligate host in order to propagate infection. Here, the structure of CT584, a T3SS-associated protein, that has been refined to a resolution of 3.05 Å is reported. The CT584 structure is a hexamer comprised of a trimer of dimers. The structure shares a high degree of similarity to the recently reported structure of an orthologous protein, Cpn0803, from Chlamydia pneumoniae, which highlights the highly conserved nature of this protein across these chlamydial species, despite different tissue tropism and disease pathology.
Keywords: CT584; Chlamydia trachomatis; type III secretion system.
Figures
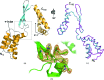

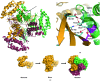
Similar articles
-
Biophysical characterization of Chlamydia trachomatis CT584 supports its potential role as a type III secretion needle tip protein.Biochemistry. 2009 Nov 3;48(43):10353-61. doi: 10.1021/bi901200y. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19769366 Free PMC article.
-
Structural characterization of a novel Chlamydia pneumoniae type III secretion-associated protein, Cpn0803.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030220. Epub 2012 Jan 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22272312 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel type III secretion chaperone-substrate complexes of Chlamydia trachomatis.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56292. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056292. Epub 2013 Feb 19. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23431368 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved type III secretion system exerts important roles in Chlamydia trachomatis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Aug 15;7(9):5404-14. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25337183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type III Secretion in Chlamydia.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2023 Sep 26;87(3):e0003423. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00034-23. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37358451 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aspects of Phage-Based Vaccines for Protein and Epitope Immunization.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Feb 14;11(2):436. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020436. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunogenicity and Protective Capacity of a Virus-like Particle Vaccine against Chlamydia trachomatis Type 3 Secretion System Tip Protein, CT584.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jan 12;10(1):111. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10010111. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35062772 Free PMC article.
-
Global mapping of the Chlamydia trachomatis conventional secreted effector - host interactome reveals CebN interacts with nucleoporins and Rae1 to impede STAT1 nuclear translocation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 25:2024.04.25.587017. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.25.587017. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38712050 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A working model for the type III secretion mechanism in Chlamydia.Microbes Infect. 2016 Feb;18(2):84-92. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2015.10.006. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Microbes Infect. 2016. PMID: 26515030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural insights into the architecture and membrane interactions of the conserved COMMD proteins.Elife. 2018 Aug 1;7:e35898. doi: 10.7554/eLife.35898. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30067224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, P. D. et al. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221. - PubMed
-
- Adams, P. D., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., Hung, L.-W., Ioerger, T. R., McCoy, A. J., Moriarty, N. W., Read, R. J., Sacchettini, J. C., Sauter, N. K. & Terwilliger, T. C. (2002). Acta Cryst. D58, 1948–1954. - PubMed
-
- Barlow, D. J. & Thornton, J. M. (1988). J. Mol. Biol. 201, 601–619. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

