Constitutive localization of DR4 in lipid rafts is mandatory for TRAIL-induced apoptosis in B-cell hematologic malignancies
- PMID: 24136227
- PMCID: PMC3920963
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.389
Constitutive localization of DR4 in lipid rafts is mandatory for TRAIL-induced apoptosis in B-cell hematologic malignancies
Abstract
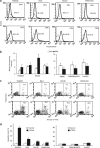
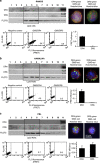
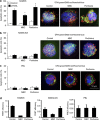
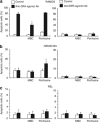
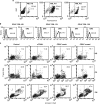
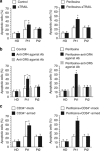
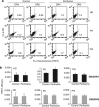
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) acts as an apoptosis inducer for cancer cells sparing non-tumor cell targets. However, several phase I/II clinical trials have shown limited benefits of this molecule. In the present work, we investigated whether cell susceptibility to TRAIL ligation could be due to the presence of TRAIL death receptors (DRs) 4 and 5 in membrane microdomains called lipid rafts. We performed a series of analyses, either by biochemical methods or fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) technique, on normal cells (i.e. lymphocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells), on a panel of human cancer B-cell lines as well as on CD19(+) lymphocytes from patients with B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia, treated with different TRAIL ligands, that is, recombinant soluble TRAIL, specific agonistic antibodies to DR4 and DR5, or CD34(+) TRAIL-armed cells. Irrespective to the expression levels of DRs, a molecular interaction between ganglioside GM3, abundant in lymphoid cells, and DR4 was detected. This association was negligible in all non-transformed cells and was strictly related to TRAIL susceptibility of cancer cells. Interestingly, lipid raft disruptor methyl-beta-cyclodextrin abrogated this susceptibility, whereas the chemotherapic drug perifosine, which induced the recruitment of TRAIL into lipid microdomains, improved TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Accordingly, in ex vivo samples from patients with B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the constitutive embedding of DR4 in lipid microdomains was associated per se with cell death susceptibility, whereas its exclusion was associated with TRAIL resistance. These results provide a key mechanism for TRAIL sensitivity in B-cell malignances: the association, within lipid microdomains, of DR4 but not DR5, with a specific ganglioside, that is the monosialoganglioside GM3. On these bases we suggest that lipid microdomains could exert a catalytic role for DR4-mediated cell death and that an ex vivo quantitative FRET analysis could be predictive of cancer cell sensitivity to TRAIL.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Death receptor 4 is preferentially recruited to lipid rafts in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells contributing to tumor necrosis related apoptosis inducing ligand-induced synergistic apoptotic responses.Leuk Lymphoma. 2011 Jul;52(7):1290-301. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2011.567317. Leuk Lymphoma. 2011. PMID: 21699383
-
Redistribution of DR4 and DR5 in lipid rafts accounts for the sensitivity to TRAIL in NSCLC cells.Int J Oncol. 2011 Dec;39(6):1577-86. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1129. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Int J Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21769428
-
Activated Cdc42-associated kinase 1 (Ack1) is required for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor recruitment to lipid rafts and induction of cell death.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 15;288(46):32922-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.481507. Epub 2013 Oct 1. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24085293 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting miRNAs associated with surface expression of death receptors to modulate TRAIL resistance in breast cancer.Cancer Lett. 2016 Dec 28;383(2):154-160. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.09.021. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27693456 Review.
-
Spatial dynamics of TRAIL death receptors in cancer cells.Drug Resist Updat. 2015 Mar;19:13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2015.02.001. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Drug Resist Updat. 2015. PMID: 25840763 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Death Receptor Signaling by S-Palmitoylation and Detergent-Resistant Membrane Micro Domains-Greasing the Gears of Extrinsic Cell Death Induction, Survival, and Inflammation.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 21;13(11):2513. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112513. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34063813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
4EGI-1 induces apoptosis and enhances radiotherapy sensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via DR5 induction on 4E-BP1 dephosphorylation.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 19;7(16):21728-41. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7824. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26942880 Free PMC article.
-
TRAIL-induced variation of cell signaling states provides nonheritable resistance to apoptosis.Life Sci Alliance. 2019 Nov 8;2(6):e201900554. doi: 10.26508/lsa.201900554. Print 2019 Dec. Life Sci Alliance. 2019. PMID: 31704709 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipids: key regulators of apoptosis and pivotal players in cancer drug resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Mar 12;15(3):4356-92. doi: 10.3390/ijms15034356. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24625663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of TRAIL Molecular Anatomy in Receptor Oligomerization and Signaling. Implications for Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Mar 29;11(4):444. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040444. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30934872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995;3:673–682. - PubMed
-
- Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue CJ, Moore A, Ashkenazi A. Activation of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand is independent of FADD but blocked by CrmA. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:12687–12690. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A. Targeting death and decoy receptors of the tumour-necrosis factor superfamily. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:420–430. - PubMed
-
- Falschlehner C, Emmerich CH, Gerlach B, Walczak H. TRAIL signalling: decisions between life and death. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39:1462–1475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

