Highly multiplexed single-cell analysis of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded cancer tissue
- PMID: 23818604
- PMCID: PMC3718135
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1300136110
Highly multiplexed single-cell analysis of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded cancer tissue
Abstract
Limitations on the number of unique protein and DNA molecules that can be characterized microscopically in a single tissue specimen impede advances in understanding the biological basis of health and disease. Here we present a multiplexed fluorescence microscopy method (MxIF) for quantitative, single-cell, and subcellular characterization of multiple analytes in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Chemical inactivation of fluorescent dyes after each image acquisition round allows reuse of common dyes in iterative staining and imaging cycles. The mild inactivation chemistry is compatible with total and phosphoprotein detection, as well as DNA FISH. Accurate computational registration of sequential images is achieved by aligning nuclear counterstain-derived fiducial points. Individual cells, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, tumor, and stromal regions are segmented to achieve cellular and subcellular quantification of multiplexed targets. In a comparison of pathologist scoring of diaminobenzidine staining of serial sections and automated MxIF scoring of a single section, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, estrogen receptor, p53, and androgen receptor staining by diaminobenzidine and MxIF methods yielded similar results. Single-cell staining patterns of 61 protein antigens by MxIF in 747 colorectal cancer subjects reveals extensive tumor heterogeneity, and cluster analysis of divergent signaling through ERK1/2, S6 kinase 1, and 4E binding protein 1 provides insights into the spatial organization of mechanistic target of rapamycin and MAPK signal transduction. Our results suggest MxIF should be broadly applicable to problems in the fields of basic biological research, drug discovery and development, and clinical diagnostics.
Keywords: cancer diagnostics; high-content cellular analysis; image analysis; mTOR; multiplexing.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: All authors affiliated with GE Global Research Center, Niskayuna, NY, 12309 are current employees of General Electric Company.
Figures

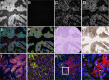
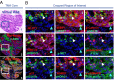
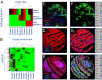
Comment in
-
Imaging cycler microscopy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 14;111(2):E215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319017111. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24398531 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Schubert et al.: Regarding critique of highly multiplexed technologies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 14;111(2):E216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319622111. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24571024 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Reply to Schubert et al.: Regarding critique of highly multiplexed technologies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 14;111(2):E216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319622111. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24571024 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Strategies for improving the immunohistochemical staining of various intranuclear prognostic markers in formalin-paraffin sections: androgen receptor, estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, p53 protein, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, and Ki-67 antigen revealed by antigen retrieval techniques.Hum Pathol. 1994 Mar;25(3):263-70. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90198-8. Hum Pathol. 1994. PMID: 7512074
-
Multiplexed Barcoding Image Analysis for Immunoprofiling and Spatial Mapping Characterization in the Single-Cell Analysis of Paraffin Tissue Samples.J Vis Exp. 2023 Apr 7;(194). doi: 10.3791/64758. J Vis Exp. 2023. PMID: 37092851
-
Microtomy: Cutting Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Sections.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1897:269-278. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8935-5_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30539451 Review.
-
Multiplex Immunofluorescence Assays.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2055:467-495. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9773-2_22. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31502166 Review.
Cited by
-
Neoadjuvant toripalimab plus axitinib for clear cell renal cell carcinoma with inferior vena cava tumor thrombus: NEOTAX, a phase 2 study.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Oct 4;9(1):264. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01990-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39362847 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Systems immune monitoring in cancer therapy.Eur J Cancer. 2016 Jul;61:77-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.03.085. Epub 2016 May 4. Eur J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27155446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Multiplexed Immunofluorescence Imaging to Chromogenic Immunohistochemistry of Skin Biomarkers in Response to Monkeypox Virus Infection.Viruses. 2020 Jul 23;12(8):787. doi: 10.3390/v12080787. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32717786 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplex immunohistochemistry reveals cochlear macrophage heterogeneity and local auditory nerve inflammation in cisplatin-induced hearing loss.Front Neurol. 2022 Oct 20;13:1015014. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1015014. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36341090 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in toponomics drug discovery: Imaging cycler microscopy correctly predicts a therapy method of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Cytometry A. 2015 Aug;87(8):696-703. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.22671. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Cytometry A. 2015. PMID: 25869332 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

