The C. elegans H3K27 demethylase UTX-1 is essential for normal development, independent of its enzymatic activity
- PMID: 22570628
- PMCID: PMC3342935
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002647
The C. elegans H3K27 demethylase UTX-1 is essential for normal development, independent of its enzymatic activity
Abstract
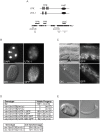
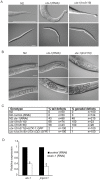
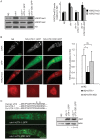
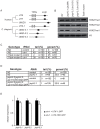
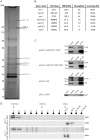
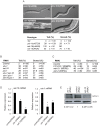
Epigenetic modifications influence gene expression and provide a unique mechanism for fine-tuning cellular differentiation and development in multicellular organisms. Here we report on the biological functions of UTX-1, the Caenorhabditis elegans homologue of mammalian UTX, a histone demethylase specific for H3K27me2/3. We demonstrate that utx-1 is an essential gene that is required for correct embryonic and postembryonic development. Consistent with its homology to UTX, UTX-1 regulates global levels of H3K27me2/3 in C. elegans. Surprisingly, we found that the catalytic activity is not required for the developmental function of this protein. Biochemical analysis identified UTX-1 as a component of a complex that includes SET-16(MLL), and genetic analysis indicates that the defects associated with loss of UTX-1 are likely mediated by compromised SET-16/UTX-1 complex activity. Taken together, these results demonstrate that UTX-1 is required for many aspects of nematode development; but, unexpectedly, this function is independent of its enzymatic activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
H3K27 modifiers regulate lifespan in C. elegans in a context-dependent manner.BMC Biol. 2021 Mar 25;19(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12915-021-00984-8. BMC Biol. 2021. PMID: 33766022 Free PMC article.
-
UTX and UTY demonstrate histone demethylase-independent function in mouse embryonic development.PLoS Genet. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002964. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002964. Epub 2012 Sep 27. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23028370 Free PMC article.
-
H3K27me3 demethylase UTX regulates the differentiation of a subset of bipolar cells in the mouse retina.Genes Cells. 2020 Jun;25(6):402-412. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12767. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Genes Cells. 2020. PMID: 32215989
-
JMJD3 as an epigenetic regulator in development and disease.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;67:148-57. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26193001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysine Demethylase KDM6A in Differentiation, Development, and Cancer.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Sep 28;40(20):e00341-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00341-20. Print 2020 Sep 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32817139 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The neuron-specific IIS/FOXO transcriptome in aged animals reveals regulatory mechanisms of cognitive aging.Elife. 2024 Jun 26;13:RP95621. doi: 10.7554/eLife.95621. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38922671 Free PMC article.
-
Pluripotent cells will not dosage compensate.Worm. 2014 May 8;3:e29051. doi: 10.4161/worm.29051. eCollection 2014. Worm. 2014. PMID: 25254152 Free PMC article.
-
The histone H3-K27 demethylase Utx regulates HOX gene expression in Drosophila in a temporally restricted manner.Development. 2013 Aug;140(16):3478-85. doi: 10.1242/dev.097204. Development. 2013. PMID: 23900545 Free PMC article.
-
KDM6 demethylase independent loss of histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation during early embryonic development.PLoS Genet. 2014 Aug 7;10(8):e1004507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004507. eCollection 2014 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25101834 Free PMC article.
-
UTX Mutations in Human Cancer.Cancer Cell. 2019 Feb 11;35(2):168-176. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.01.001. Cancer Cell. 2019. PMID: 30753822 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Strahl BD, Allis CD. The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature. 2000;403:41–45. - PubMed
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128:693–705. - PubMed
-
- Berger SL. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature. 2007;447:407–412. - PubMed
-
- Tsukada Y, Fang J, Erdjument-Bromage H, Warren ME, Borchers CH, et al. Histone demethylation by a family of JmjC domain-containing proteins. Nature. 2006;439:811–816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

