Structural characterization of a novel Chlamydia pneumoniae type III secretion-associated protein, Cpn0803
- PMID: 22272312
- PMCID: PMC3260263
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030220
Structural characterization of a novel Chlamydia pneumoniae type III secretion-associated protein, Cpn0803
Abstract
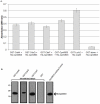
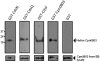
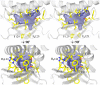
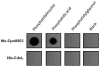
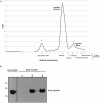
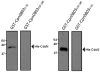
Type III secretion (T3S) is an essential virulence factor used by gram-negative pathogenic bacteria to deliver effector proteins into the host cell to establish and maintain an intracellular infection. Chlamydia is known to use T3S to facilitate invasion of host cells but many proteins in the system remain uncharacterized. The C. trachomatis protein CT584 has previously been implicated in T3S. Thus, we analyzed the CT584 ortholog in C. pneumoniae (Cpn0803) and found that it associates with known T3S proteins including the needle-filament protein (CdsF), the ATPase (CdsN), and the C-ring protein (CdsQ). Using membrane lipid strips, Cpn0803 interacted with phosphatidic acid and phosphatidylinositol, suggesting that Cpn0803 may associate with host cells. Crystallographic analysis revealed a unique structure of Cpn0803 with a hydrophobic pocket buried within the dimerization interface that may be important for binding small molecules. Also, the binding domains on Cpn0803 for CdsN, CdsQ, and CdsF were identified using Pepscan epitope mapping. Collectively, these data suggest that Cpn0803 plays a role in T3S.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

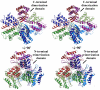

Similar articles
-
Chlamydia pneumoniae CopD translocator protein plays a critical role in type III secretion (T3S) and infection.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 24;9(6):e99315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099315. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24959658 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the putative type III secretion ATPase CdsN (Cpn0707) of Chlamydophila pneumoniae.J Bacteriol. 2008 Oct;190(20):6580-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.00761-08. Epub 2008 Aug 15. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18708502 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydia Outer Protein (Cop) B from Chlamydia pneumoniae possesses characteristic features of a type III secretion (T3S) translocator protein.BMC Microbiol. 2015 Aug 14;15:163. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0498-1. BMC Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26272448 Free PMC article.
-
[Effector proteins of Clamidia].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2009 Nov-Dec;43(6):963-83. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2009. PMID: 20088373 Review. Russian.
-
Protein export according to schedule: architecture, assembly, and regulation of type III secretion systems from plant- and animal-pathogenic bacteria.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Jun;76(2):262-310. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.05017-11. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22688814 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the Mode of Action of Aurodox, a Type III Secretion System Inhibitor from Streptomyces goldiniensis.Infect Immun. 2019 Jan 24;87(2):e00595-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00595-18. Print 2019 Feb. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 30455200 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of CT584 from Chlamydia trachomatis refined to 3.05 Å resolution.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2013 Nov;69(Pt 11):1196-201. doi: 10.1107/S1744309113027371. Epub 2013 Oct 26. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2013. PMID: 24192348 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of CPAF mutants: new functions, new questions (the ins and outs of a chlamydial protease).Pathog Dis. 2014 Aug;71(3):287-91. doi: 10.1111/2049-632X.12194. Pathog Dis. 2014. PMID: 24942261 Free PMC article.
-
A working model for the type III secretion mechanism in Chlamydia.Microbes Infect. 2016 Feb;18(2):84-92. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2015.10.006. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Microbes Infect. 2016. PMID: 26515030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chlamydia pneumoniae CopD translocator protein plays a critical role in type III secretion (T3S) and infection.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 24;9(6):e99315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099315. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24959658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scidmore M, Hackstadt T. Mammalian 14-3-3beta associates with the Chlamydia trachomatis inclusion via its interaction with IncG. Mol Microbiol. 2008;39:1638–1650. - PubMed
-
- Galan J, Collmer A. Type III secretion machines: bacterial devices for protein delivery into host cells. Science. 1999;284:1322–1328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

