COMMD1 disrupts HIF-1alpha/beta dimerization and inhibits human tumor cell invasion
- PMID: 20458141
- PMCID: PMC2877941
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI40583
COMMD1 disrupts HIF-1alpha/beta dimerization and inhibits human tumor cell invasion
Abstract
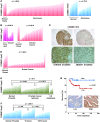
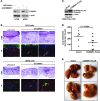
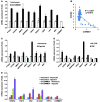
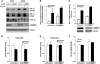
The gene encoding COMM domain-containing 1 (COMMD1) is a prototypical member of the COMMD gene family that has been shown to inhibit both NF-kappaB- and HIF-mediated gene expression. NF-kappaB and HIF are transcription factors that have been shown to play a role in promoting tumor growth, survival, and invasion. In this study, we demonstrate that COMMD1 expression is frequently suppressed in human cancer and that decreased COMMD1 expression correlates with a more invasive tumor phenotype. We found that direct repression of COMMD1 in human cell lines led to increased tumor invasion in a chick xenograft model, while increased COMMD1 expression in mouse melanoma cells led to decreased lung metastasis in a mouse model. Decreased COMMD1 expression also correlated with increased expression of genes known to promote cancer cell invasiveness, including direct targets of HIF. Mechanistically, our studies show that COMMD1 inhibits HIF-mediated gene expression by binding directly to the amino terminus of HIF-1alpha, preventing its dimerization with HIF-1beta and subsequent DNA binding and transcriptional activation. Altogether, our findings demonstrate a role for COMMD1 in tumor invasion and provide a detailed mechanism of how this factor regulates the HIF pathway in cancer cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
COMMD1 Promotes pVHL and O2-Independent Proteolysis of HIF-1alpha via HSP90/70.PLoS One. 2009 Oct 5;4(10):e7332. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007332. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19802386 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear-cytosolic transport of COMMD1 regulates NF-kappaB and HIF-1 activity.Traffic. 2009 May;10(5):514-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00892.x. Epub 2009 Feb 11. Traffic. 2009. PMID: 19220812
-
Characterization of COMMD protein-protein interactions in NF-kappaB signalling.Biochem J. 2006 Aug 15;398(1):63-71. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051664. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16573520 Free PMC article.
-
HSCARG regulates NF-kappaB activation by promoting the ubiquitination of RelA or COMMD1.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 3;284(27):17998-8006. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809752200. Epub 2009 May 11. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19433587 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB suppresses HIF-1α response by competing for P300 binding.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Jan 28;404(4):997-1003. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.12.098. Epub 2010 Dec 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21187066
Cited by
-
COMMD1 Exemplifies the Power of Inbred Dogs to Dissect Genetic Causes of Rare Copper-Related Disorders.Animals (Basel). 2021 Feb 25;11(3):601. doi: 10.3390/ani11030601. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the COMMD4-H2B protein complex in lung cancer.Br J Cancer. 2023 Dec;129(12):2014-2024. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02476-8. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Br J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37914802 Free PMC article.
-
The Copper Metabolism MURR1 domain protein 1 (COMMD1) modulates the aggregation of misfolded protein species in a client-specific manner.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 1;9(4):e92408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092408. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24691167 Free PMC article.
-
Defining COMMD4 as an anti-cancer therapeutic target and prognostic factor in non-small cell lung cancer.Br J Cancer. 2020 Aug;123(4):591-603. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-0899-2. Epub 2020 May 22. Br J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32439936 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the architecture and membrane interactions of the conserved COMMD proteins.Elife. 2018 Aug 1;7:e35898. doi: 10.7554/eLife.35898. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30067224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van de Sluis B, Rothuizen J, Pearson PL, van Oost BA, Wijmenga C. Identification of a new copper metabolism gene by positional cloning in a purebred dog population. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11(2):165–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

