Interaction with dopamine D2 receptor enhances expression of transient receptor potential channel 1 at the cell surface
- PMID: 18261457
- PMCID: PMC2312457
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.01.011
Interaction with dopamine D2 receptor enhances expression of transient receptor potential channel 1 at the cell surface
Abstract
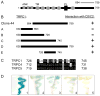
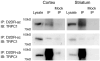
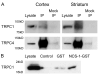
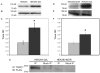
Receptor signaling is mediated by direct protein interaction with various types of cytoskeletal, adapter, effector, and additional receptor molecules. In brain tissue and in cultured neurons, activation of dopamine D2 receptors (D2Rs) has been found to impact cellular calcium signaling. Using a yeast two-hybrid approach, we have uncovered a direct physical interaction between the D2R and the transient receptor potential channel (TRPC) subtypes 1, 4 and 5. The TRPC/D2R interaction was further validated by GST-pulldown assays and coimmunoprecipitation from mammalian brain. Ultrastructural analysis of TRPC1 and D2R expression indicates colocalization of the two proteins within the cell body and dendrites of cortical neurons. In cultured cells, expression of D2Rs was found to increase expression of TRPC1 at the cell surface by 50%. These findings shed new light on the constituents of the D2R signalplex, and support the involvement of D2Rs in cellular calcium signaling pathways via a novel link to TRPC channels.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dopamine D2 receptors regulate the action potential threshold by modulating T-type calcium channels in stellate cells of the medial entorhinal cortex.J Physiol. 2019 Jul;597(13):3363-3387. doi: 10.1113/JP277976. Epub 2019 May 28. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31049961
-
Signaling by dopamine regulates D2 receptors trafficking at the membrane.Cell Cycle. 2008 Jul 15;7(14):2241-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.14.6307. Epub 2008 May 15. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18635969
-
Regulation of type 1 IP₃ receptor expression by dopamine D2-like receptors via AP-1 and NFATc4 activation.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Aug;71:264-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.03.036. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23597509
-
TRPC1 as a negative regulator for TRPC4 and TRPC5 channels.Pflugers Arch. 2019 Aug;471(8):1045-1053. doi: 10.1007/s00424-019-02289-w. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 31222490 Review.
-
A proteomic approach to receptor signaling: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications derived from discovery of the dopamine D2 receptor signalplex.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Oct 31;572(2-3):83-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.06.059. Epub 2007 Jul 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17662712 Review.
Cited by
-
Morphine-induced trafficking of a mu-opioid receptor interacting protein in rat locus coeruleus neurons.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014 Apr 3;50:53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.12.003. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24333843 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic and functional analysis of NCS-1 binding proteins reveals novel signaling pathways required for inner ear development in zebrafish.BMC Neurosci. 2009 Mar 25;10:27. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-10-27. BMC Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19320994 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of GPR177 (Wntless/Evi/Sprinter), a highly conserved Wnt-transport protein, in rat tissues, zebrafish embryos, and cultured human cells.Dev Dyn. 2010 Sep;239(9):2426-34. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22369. Dev Dyn. 2010. PMID: 20652957 Free PMC article.
-
A synergistic approach towards understanding the functional significance of dopamine receptor interactions.J Mol Signal. 2013 Dec 5;8(1):13. doi: 10.1186/1750-2187-8-13. J Mol Signal. 2013. PMID: 24308343 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between the Polysialylated Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule and the Transient Receptor Potential Canonical Channels 1, 4, and 5 Induce Entry of Ca2+ into Neurons.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 2;23(17):10027. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710027. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertorello AM, Hopfield JF, Aperia A, Greengard P. Inhibition by dopamine of (Na(+)+K+)ATPase activity in neostriatal neurons through D1 and D2 dopamine receptor synergism. Nature. 1990;347:386–8. - PubMed
-
- Goldman-Rakic PS. The cortical dopamine system: role in memory and cognition. Adv Pharmacol. 1998;42:707–11. - PubMed
-
- Schultz W. Getting formal with dopamine and reward. Neuron. 2002;36:241–63. - PubMed
-
- Missale C, Nash SR, Robinson SW, Jaber M, Caron MG. Dopamine receptors: from structure to function. Physiol Rev. 1998;78:189–225. - PubMed
-
- Civelli O, Bunzow JR, Grandy DK. Molecular diversity of the dopamine receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;33:281–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

