Functional architecture of the retromer cargo-recognition complex
- PMID: 17891154
- PMCID: PMC2377034
- DOI: 10.1038/nature06216
Functional architecture of the retromer cargo-recognition complex
Abstract
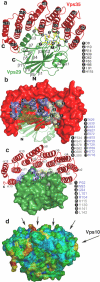
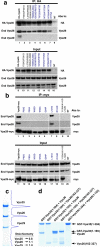
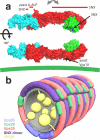
The retromer complex is required for the sorting of acid hydrolases to lysosomes, transcytosis of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor, Wnt gradient formation, iron transporter recycling and processing of the amyloid precursor protein. Human retromer consists of two smaller complexes: the cargo recognition VPS26-VPS29-VPS35 heterotrimer and a membrane-targeting heterodimer or homodimer of SNX1 and/or SNX2 (ref. 13). Here we report the crystal structure of a VPS29-VPS35 subcomplex showing how the metallophosphoesterase-fold subunit VPS29 (refs 14, 15) acts as a scaffold for the carboxy-terminal half of VPS35. VPS35 forms a horseshoe-shaped, right-handed, alpha-helical solenoid, the concave face of which completely covers the metal-binding site of VPS29, whereas the convex face exposes a series of hydrophobic interhelical grooves. Electron microscopy shows that the intact VPS26-VPS29-VPS35 complex is a stick-shaped, flexible structure, approximately 21 nm long. A hybrid structural model derived from crystal structures, electron microscopy, interaction studies and bioinformatics shows that the alpha-solenoid fold extends the full length of VPS35, and that VPS26 is bound at the opposite end from VPS29. This extended structure presents multiple binding sites for the SNX complex and receptor cargo, and appears capable of flexing to conform to curved vesicular membranes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interchangeable but essential functions of SNX1 and SNX2 in the association of retromer with endosomes and the trafficking of mannose 6-phosphate receptors.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Feb;27(3):1112-24. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00156-06. Epub 2006 Nov 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17101778 Free PMC article.
-
The retromer subunit Vps26 has an arrestin fold and binds Vps35 through its C-terminal domain.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006 Jun;13(6):540-8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1103. Epub 2006 May 28. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16732284 Free PMC article.
-
VPS29-VPS35 intermediate of retromer is stable and may be involved in the retromer complex assembly process.FEBS Lett. 2015 Jun 4;589(13):1430-6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.04.040. Epub 2015 May 1. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 25937119
-
Retromer.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008 Aug;20(4):427-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.03.009. Epub 2008 May 9. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18472259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updated Insight into the Physiological and Pathological Roles of the Retromer Complex.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 25;18(8):1601. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081601. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28757549 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The exomer cargo adaptor features a flexible hinge domain.Structure. 2013 Mar 5;21(3):486-92. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.01.003. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Structure. 2013. PMID: 23395181 Free PMC article.
-
PGC-1s in the Spotlight with Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 28;22(7):3487. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073487. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33800548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retromer forms low order oligomers on supported lipid bilayers.J Biol Chem. 2020 Aug 21;295(34):12305-12316. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013672. Epub 2020 Jul 10. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32651229 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of the ClpA unfoldase opens the axial gate of ClpP peptidase.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 7;285(19):14834-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.090498. Epub 2010 Mar 16. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20236930 Free PMC article.
-
A mutation in VPS35, encoding a subunit of the retromer complex, causes late-onset Parkinson disease.Am J Hum Genet. 2011 Jul 15;89(1):168-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.06.008. Am J Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 21763483 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

