ConSurf 2005: the projection of evolutionary conservation scores of residues on protein structures
- PMID: 15980475
- PMCID: PMC1160131
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki370
ConSurf 2005: the projection of evolutionary conservation scores of residues on protein structures
Abstract
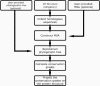
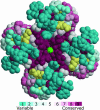
Key amino acid positions that are important for maintaining the 3D structure of a protein and/or its function(s), e.g. catalytic activity, binding to ligand, DNA or other proteins, are often under strong evolutionary constraints. Thus, the biological importance of a residue often correlates with its level of evolutionary conservation within the protein family. ConSurf (http://consurf.tau.ac.il/) is a web-based tool that automatically calculates evolutionary conservation scores and maps them on protein structures via a user-friendly interface. Structurally and functionally important regions in the protein typically appear as patches of evolutionarily conserved residues that are spatially close to each other. We present here version 3.0 of ConSurf. This new version includes an empirical Bayesian method for scoring conservation, which is more accurate than the maximum-likelihood method that was used in the earlier release. Various additional steps in the calculation can now be controlled by a number of advanced options, thus further improving the accuracy of the calculation. Moreover, ConSurf version 3.0 also includes a measure of confidence for the inferred amino acid conservation scores.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The ConSurf-HSSP database: the mapping of evolutionary conservation among homologs onto PDB structures.Proteins. 2005 Feb 15;58(3):610-7. doi: 10.1002/prot.20305. Proteins. 2005. PMID: 15614759
-
ConSurf 2010: calculating evolutionary conservation in sequence and structure of proteins and nucleic acids.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jul;38(Web Server issue):W529-33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq399. Epub 2010 May 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20478830 Free PMC article.
-
ConSurf: identification of functional regions in proteins by surface-mapping of phylogenetic information.Bioinformatics. 2003 Jan;19(1):163-4. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/19.1.163. Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 12499312
-
Scoring residue conservation.Proteins. 2002 Aug 1;48(2):227-41. doi: 10.1002/prot.10146. Proteins. 2002. PMID: 12112692 Review.
-
Wenxiang 3.0: Evolutionary Visualization of α, π, and 3/10 Helices.Evol Bioinform Online. 2022 May 31;18:11769343221101014. doi: 10.1177/11769343221101014. eCollection 2022. Evol Bioinform Online. 2022. PMID: 35668741 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Solution NMR structure of Alr2454 from Nostoc sp. PCC 7120, the first structural representative of Pfam domain family PF11267.J Struct Funct Genomics. 2012 Sep;13(3):171-6. doi: 10.1007/s10969-012-9135-5. Epub 2012 May 17. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22592539 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function analysis of the extracellular domain of the pneumococcal cell division site positioning protein MapZ.Nat Commun. 2016 Jun 27;7:12071. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12071. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27346279 Free PMC article.
-
Dimerization of a 5-kDa domain defines the architecture of the 5-MDa gammaproteobacterial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.Sci Adv. 2024 Feb 9;10(6):eadj6358. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj6358. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38324697 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function relationship of the mammarenavirus envelope glycoprotein.Virol Sin. 2016 Oct;31(5):380-394. doi: 10.1007/s12250-016-3815-4. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Virol Sin. 2016. PMID: 27562602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Italian cohort study identifies four new pathologic mutations in the ARSA gene.J Mol Neurosci. 2013 Jun;50(2):284-90. doi: 10.1007/s12031-013-0006-8. Epub 2013 Apr 5. J Mol Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23559313
References
-
- Glaser F., Pupko T., Paz I., Bell R.E., Bechor-Shental D., Martz E., Ben-Tal N. ConSurf: identification of functional regions in proteins by surface-mapping of phylogenetic information. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:163–164. - PubMed
-
- Mayrose I., Graur D., Ben-Tal N., Pupko T. Comparison of site-specific rate-inference methods for protein sequences: empirical Bayesian methods are superior. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004;21:1781–1791. - PubMed
-
- Pupko T., Bell R.E., Mayrose I., Glaser F., Ben-Tal N. Rate4Site: an algorithmic tool for the identification of functional regions in proteins by surface mapping of evolutionary determinants within their homologues. Bioinformatics. 2002;18:S71–S77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

