The pydeck library is a set of Python bindings for making spatial visualizations with deck.gl, optimized for a Jupyter environment. To get started, see the documentation.
To install pydeck, see the instructions here.
For interactive demos, click the binder logo below:
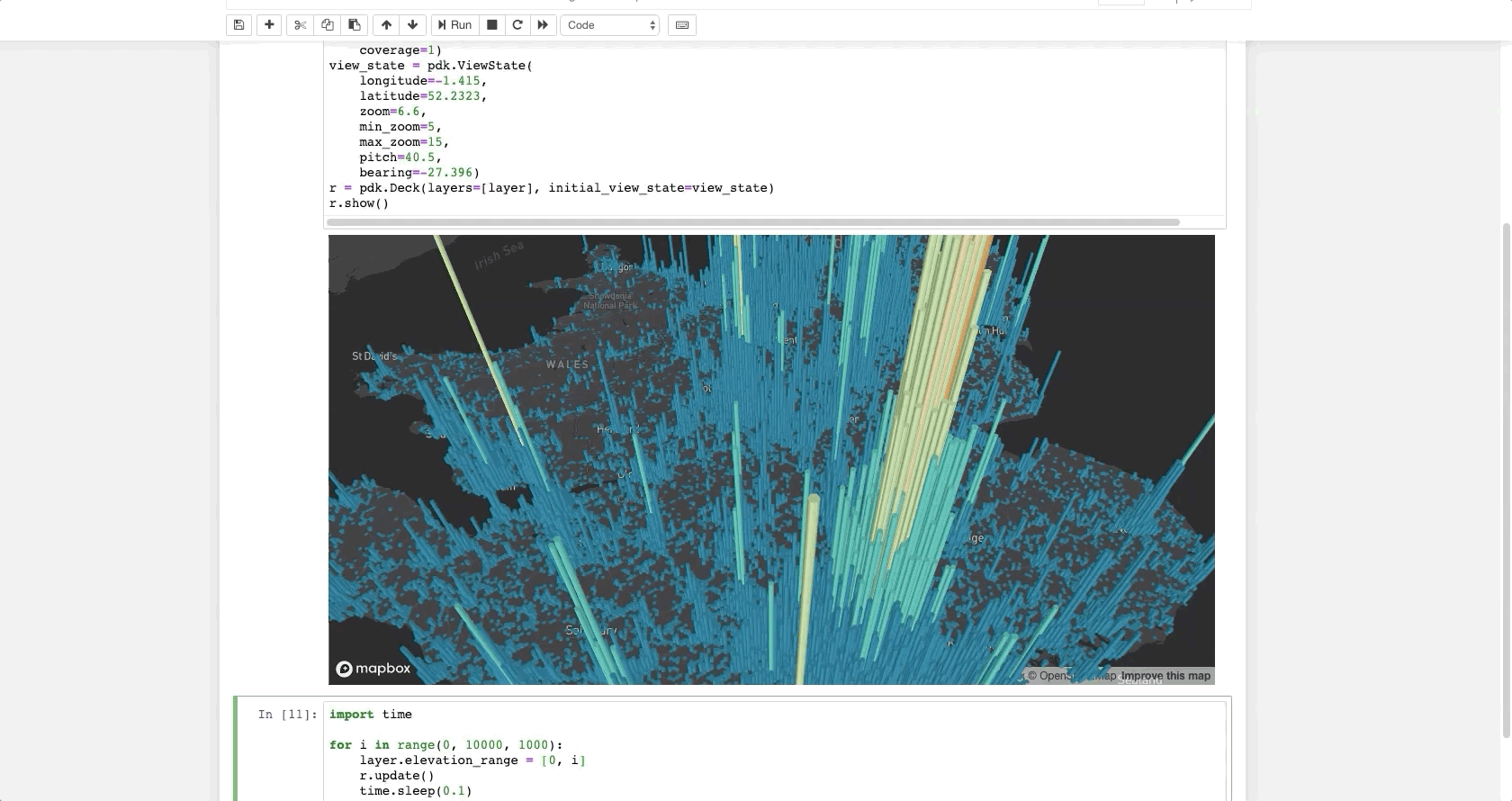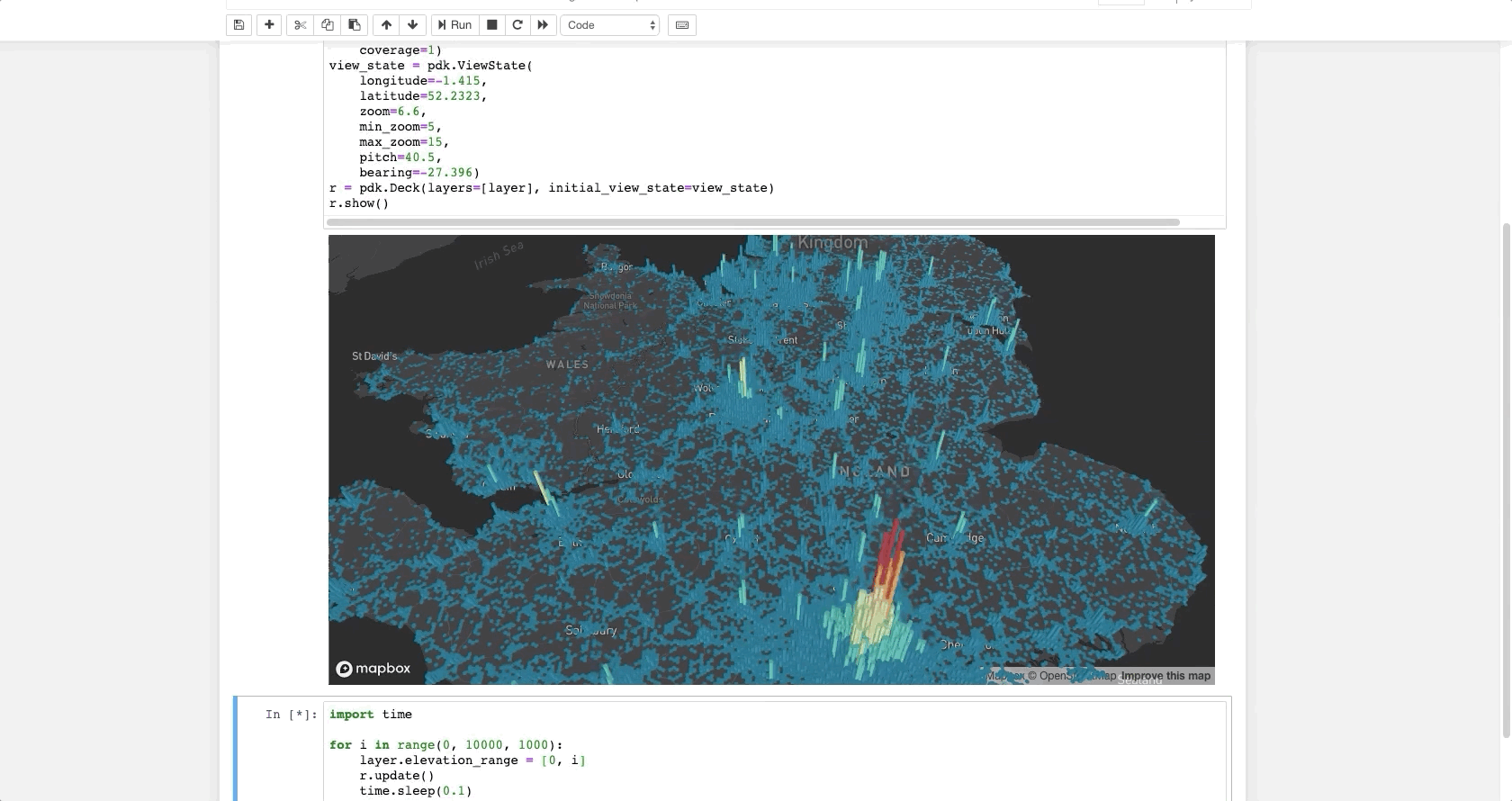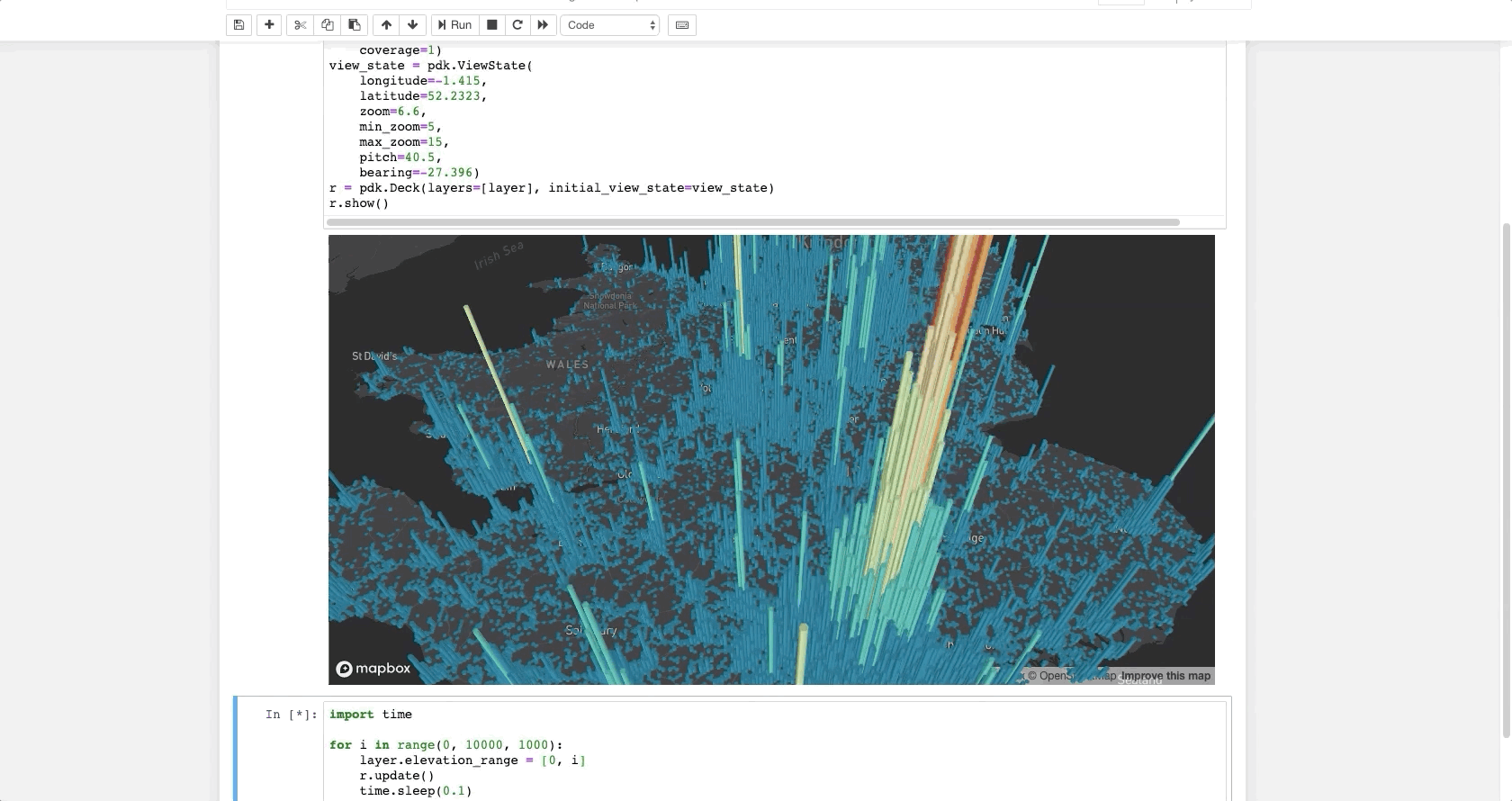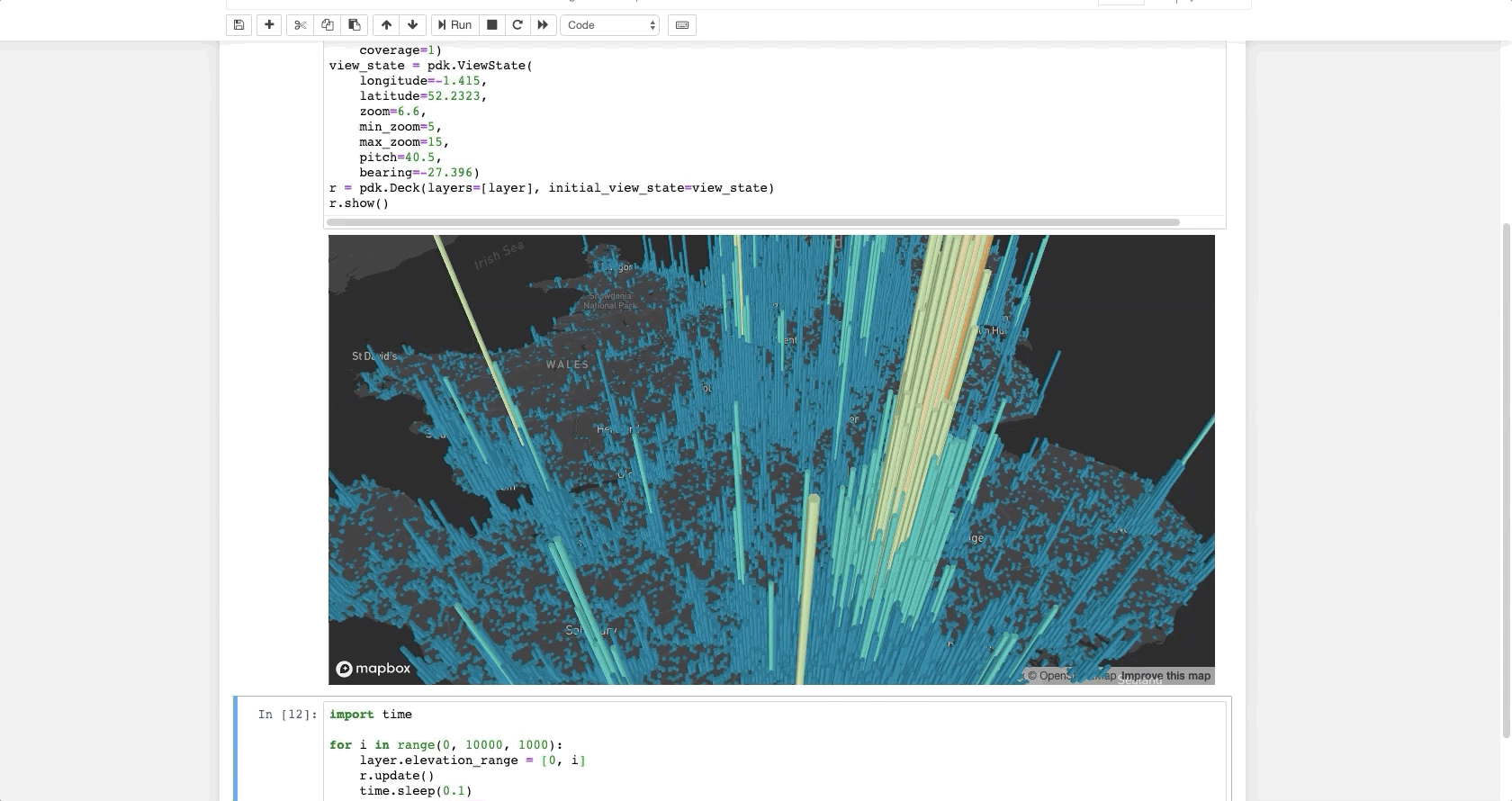
The following code renders a visualization similar to the one above in a Jupyter notebook:
import pydeck as pdk
# 2014 locations of car accidents in the UK
UK_ACCIDENTS_DATA = ('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/uber-common/'
'deck.gl-data/master/examples/3d-heatmap/heatmap-data.csv')
# Define a layer to display on a map
layer = pdk.Layer(
'HexagonLayer',
UK_ACCIDENTS_DATA,
get_position=['lng', 'lat'],
auto_highlight=True,
elevation_scale=50,
pickable=True,
elevation_range=[0, 3000],
extruded=True,
coverage=1)
# Set the viewport location
view_state = pdk.ViewState(
longitude=-1.415,
latitude=52.2323,
zoom=6,
min_zoom=5,
max_zoom=15,
pitch=40.5,
bearing=-27.36)
# Render
r = pdk.Deck(layers=[layer], initial_view_state=view_state)
r.to_html('demo.html')If you're developing outside a Jupyter environment, you can run:
r.to_html('demo.html', notebook_display=False)See the gallery for more examples.
If you encounter an issue, file it in the deck.gl issues page and include your browser's console output, if any.
If you'd like to contribute to pydeck, please follow the deck.gl contribution guidelines and the pydeck development installation instructions.