Ahora estás siguiendo a
Error al seguir a usuario.
Este usuario no permite que los usuarios lo sigan.
Ya estás siguiendo a este usuario.
Tu plan de membresía solo permite 0 seguimientos. Mejora tu membresía aquí.
Dejaste de seguir correctamente a
Error al dejar de seguir al usuario.
Has recomendado exitosamente a
Error al recomendar al usuario.
Algo salió mal. Por favor, actualiza la página e intenta de nuevo.
Email verificado correctamente.

Gajendra V.
@gajendrav9
0,0
0
0,0
0,0
0%
Translation work
$10 USD / hora
・
India (2:08 a. m.)
・
Se unió el diciembre 24, 2024
$10 USD / hora
・
1. Language Proficiency:
Bilingual or Multilingual: A professional translator is fluent in at least two lan
Cultural Understanding: Beyond mere language skills, a translator must have a
2. Types of Translation:
Written Translation: This is the most common
Interpretation: This is oral translation and can be simultaneous (at the same time as the speake
Specialized Translation: Many translators specialize in particular fields, such as legal translation, medical translation, or technical translation, requiring specific knowledge of terminology in those areas.
3. Skills and Competencies:
Accuracy: Translators must convey the original message as precisely as possible without altering the meaning.
Attention to Detail: Every word, phrase, and nuance counts in a translation, especially in technical or legal contexts.
Research Skills: Translators often need to research terms, idiomatic expressions, or concepts that are unfamiliar to ensure accuracy.
Writing Skills: A professional translator is also a strong writer in the target language, ensuring that the translation reads naturally and fluently.
4. Tools and Technology:
Many professional translators use CAT (Computer-Assisted Translation) tools like SDL Trados, MemoQ, or Wordfast. These tools help streamline the process by storing translations in databases and providing consistency across large projects.
Machine Translation (MT): While MT tools like Google Translate are helpful, professional translators often refine machine-generated translations to improve accuracy, tone, and meaning.
5. Professional Standards:
Translators often adhere to professional codes of conduct, which include confidentiality, impartiality, and integrity.
Many professional translators belong to organizations such as the American Translators Association (ATA), International Federation of Translators (FIT), or Institute of Translation and Interpreting (ITI).
6. Certifications:
Some translators pursue certifications to enhance their credibility and marketability. Certifications like the ATA certification (for translators working into English) or the Certified Translator status in various countries can increase trust with clients.
7. Career Opportunities:
Freelance Work: Many translators are self-employed and work with various clients, including translation agencies, businesses, and individual clients.
In-house Positions: So
Specialization: Translators often find niche areas where they excel, such as in legal, medical, or scientific translations.
Overall, being a professional translator requires a combination of linguistic skills, cultural knowledge, and technical proficiency to deliver high-quality translations that meet clients’
Verificaciones
Portafolio
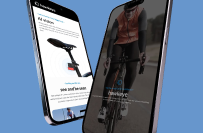
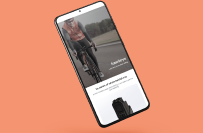
Portafolio
This file is translated English to A
This file is translated English to A
Cambios guardados
¡No hay comentarios para ver aquí!
Educación
B.sc
2020 - 2023
•
3 años

India
2020 - 2023
•
3 años
¡Invitación enviada correctamente!
¡Gracias! Te hemos enviado un enlace para reclamar tu crédito gratuito.
Algo salió mal al enviar tu correo electrónico. Por favor, intenta de nuevo.
Cargando visualización previa
Permiso concedido para Geolocalización.
Tu sesión de acceso ha expirado y has sido desconectado. Por favor, inica sesión nuevamente.