Logic Pro User Guide for iPad
- What’s new in Logic Pro 1.1
-
- What is Logic Pro?
- Working areas
- Work with function buttons
- Work with numeric values
-
- Intro to tracks
- Create tracks
- Create tracks using drag and drop
- Choose the default region type for a software instrument track
- Select tracks
- Duplicate tracks
- Reorder tracks
- Rename tracks
- Change track icons
- Change track colors
- Use the tuner on an audio track
- Show the output track in the Tracks area
- Delete tracks
- Edit track parameters
- Start a Logic Pro subscription
- How to get help
-
- Intro to recording
-
- Before recording software instruments
- Record software instruments
- Record additional software instrument takes
- Record to multiple software instrument tracks
- Record multiple MIDI devices to multiple tracks
- Record software instruments and audio simultaneously
- Merge software instrument recordings
- Spot erase software instrument recordings
- Replace software instrument recordings
- Capture your most recent MIDI performance
- Use the metronome
- Use the count-in
-
- Intro to arranging
-
- Intro to regions
- Select regions
- Cut, copy, and paste regions
- Move regions
- Remove gaps between regions
- Delay region playback
- Trim regions
- Loop regions
- Repeat regions
- Mute regions
- Split and join regions
- Stretch regions
- Separate a MIDI region by note pitch
- Bounce regions in place
- Change the gain of audio regions
- Create regions in the Tracks area
- Convert a MIDI region to a Drummer region or a pattern region
- Rename regions
- Change the color of regions
- Delete regions
- Create fades on audio regions
- Access mixing functions using the Fader
-
- Intro to Step Sequencer
- Use Step Sequencer with Drum Machine Designer
- Record Step Sequencer patterns live
- Step record Step Sequencer patterns
- Load and save patterns
- Modify pattern playback
- Edit steps
- Edit rows
- Edit Step Sequencer pattern, row, and step settings in the inspector
- Customize Step Sequencer
-
- Effect plug-ins overview
-
- Instrument plug-ins overview
-
- ES2 overview
- Interface overview
-
- Modulation overview
-
- Vector Envelope overview
- Use Vector Envelope points
- Use Vector Envelope solo and sustain points
- Set Vector Envelope segment times
- Vector Envelope XY pad controls
- Vector Envelope Actions menu
- Vector Envelope loop controls
- Vector Envelope release phase behavior
- Vector Envelope point transition shapes
- Use Vector Envelope time scaling
- Use the Mod Pad
- Modulation source reference
- Via modulation source reference
-
- Sample Alchemy overview
- Interface overview
- Add source material
- Save a preset
- Edit mode
- Play modes
- Source overview
- Synthesis modes
- Granular controls
- Additive effects
- Additive effect controls
- Spectral effect
- Spectral effect controls
- Filter module
- Low and highpass filter
- Comb PM filter
- Downsampler filter
- FM filter
- Envelope generators
- Mod Matrix
- Modulation routing
- Motion mode
- Trim mode
- More menu
- Sampler
- Copyright
Noise Gate in Logic Pro for iPad
Noise Gate is commonly used to suppress unwanted noise that is audible when the audio signal is at a low level. You can use it to remove background noise, crosstalk from other signal sources, and low-level hum.
Noise Gate works by allowing signals above the threshold level to pass unimpeded, while reducing signals below the threshold level. This effectively removes lower-level parts of the signal, while allowing the desired parts of the audio to pass.
In Ducker mode, the source signal is reduced in level. Ducking is a common technique used in radio and television broadcasting. When the DJ or announcer speaks while music is playing, the music level is automatically reduced. When the announcement has finished, the music is automatically raised to its original volume level.
To add Noise Gate to your project, choose Dynamics > Noise Gate in a channel strip Audio Effect plug-in menu or the Plug-ins area. See Intro to plug-ins. Also see Add, replace, reorder, and remove plug-ins in the Plug-ins area and Work with plug-ins in the Mixer.
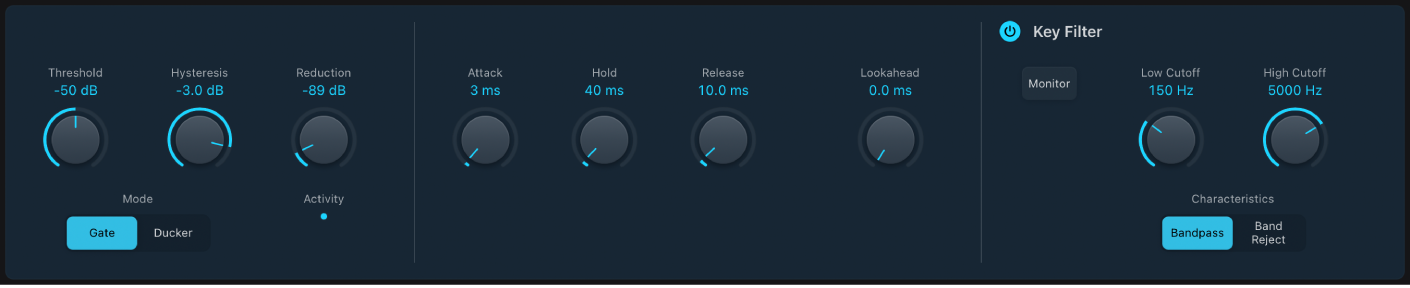
Noise Gate parameters
 Threshold knob and field: Set the threshold level. Signals that fall below the threshold are reduced in level.
Threshold knob and field: Set the threshold level. Signals that fall below the threshold are reduced in level.Hysteresis knob and field: Set the difference (in decibels) between the threshold values that open and close the gate. This prevents the gate from rapidly opening and closing when the input signal level is close to the threshold level.
Mode buttons: Set the operating mode: Gate or Ducker. See Use Noise Gate.
 Reduction knob and field: Set the amount of signal reduction.
Reduction knob and field: Set the amount of signal reduction.Activity indicators: Show current gate state.
Attack knob and field: Set the time it takes to fully open the gate after the signal exceeds the threshold.
Hold knob and field: Set the time the gate remains open after the signal falls below the threshold.
Release knob and field: Set the time it takes to reach maximum attenuation after the signal falls below the threshold.
Lookahead knob and field: Control how far ahead Noise Gate analyzes the incoming signal, allowing the effect to respond more quickly to peak levels.
Key Filter button: Turn on to enable the sidechain filter, allowing you to adjust the Low Cutoff and High Cutoff parameters.
Monitor button: Turn on to hear the side chain signal, including the effect of the Low Cut and High Cut filters (if enabled).
Low Cutoff knob and field: Set the lower cutoff frequency for the side chain signal.
Note: When no external side chain is selected, the input signal is used as the side chain control signal.
High Cutoff knob and field: Set the upper cutoff frequency for the side chain signal.
Characteristics buttons: Choose a Bandpass or Band Reject filter type.
Download this guide: PDF