Logic Pro User Guide for iPad
- What’s new in Logic Pro 1.1
-
- What is Logic Pro?
- Working areas
- Work with function buttons
- Work with numeric values
-
- Intro to tracks
- Create tracks
- Create tracks using drag and drop
- Choose the default region type for a software instrument track
- Select tracks
- Duplicate tracks
- Reorder tracks
- Rename tracks
- Change track icons
- Change track colors
- Use the tuner on an audio track
- Show the output track in the Tracks area
- Delete tracks
- Edit track parameters
- Start a Logic Pro subscription
- How to get help
-
- Intro to recording
-
- Before recording software instruments
- Record software instruments
- Record additional software instrument takes
- Record to multiple software instrument tracks
- Record multiple MIDI devices to multiple tracks
- Record software instruments and audio simultaneously
- Merge software instrument recordings
- Spot erase software instrument recordings
- Replace software instrument recordings
- Capture your most recent MIDI performance
- Use the metronome
- Use the count-in
-
- Intro to arranging
-
- Intro to regions
- Select regions
- Cut, copy, and paste regions
- Move regions
- Remove gaps between regions
- Delay region playback
- Trim regions
- Loop regions
- Repeat regions
- Mute regions
- Split and join regions
- Stretch regions
- Separate a MIDI region by note pitch
- Bounce regions in place
- Change the gain of audio regions
- Create regions in the Tracks area
- Convert a MIDI region to a Drummer region or a pattern region
- Rename regions
- Change the color of regions
- Delete regions
- Create fades on audio regions
- Access mixing functions using the Fader
-
- Intro to Step Sequencer
- Use Step Sequencer with Drum Machine Designer
- Record Step Sequencer patterns live
- Step record Step Sequencer patterns
- Load and save patterns
- Modify pattern playback
- Edit steps
- Edit rows
- Edit Step Sequencer pattern, row, and step settings in the inspector
- Customize Step Sequencer
-
- Effect plug-ins overview
-
- Instrument plug-ins overview
-
- ES2 overview
- Interface overview
-
- Modulation overview
-
- Vector Envelope overview
- Use Vector Envelope points
- Use Vector Envelope solo and sustain points
- Set Vector Envelope segment times
- Vector Envelope XY pad controls
- Vector Envelope Actions menu
- Vector Envelope loop controls
- Vector Envelope release phase behavior
- Vector Envelope point transition shapes
- Use Vector Envelope time scaling
- Use the Mod Pad
- Modulation source reference
- Via modulation source reference
-
- Sample Alchemy overview
- Interface overview
- Add source material
- Save a preset
- Edit mode
- Play modes
- Source overview
- Synthesis modes
- Granular controls
- Additive effects
- Additive effect controls
- Spectral effect
- Spectral effect controls
- Filter module
- Low and highpass filter
- Comb PM filter
- Downsampler filter
- FM filter
- Envelope generators
- Mod Matrix
- Modulation routing
- Motion mode
- Trim mode
- More menu
- Sampler
- Copyright
Adaptive Limiter in Logic Pro for iPad
Adaptive Limiter is a versatile tool for controlling the perceived loudness of sounds. It works by rounding and smoothing peaks in the signal, producing an effect similar to an analog amplifier being driven hard. Like an amplifier, it can slightly color the sound of the signal. You can use Adaptive Limiter to achieve maximum gain, without introducing unwanted distortion and clipping, which can occur when the signal exceeds 0 dBFS.
Adaptive Limiter is typically used on the final mix, where it can be placed after a compressor, such as Multipressor, and before a final gain control, resulting in a mix of maximum loudness. Adaptive Limiter can produce a louder-sounding mix than can be achieved by normalizing the signal.
To add Adaptive Limiter to your project, choose Dynamics > Adaptive Limiter in a channel strip Audio Effect plug-in menu or the Plug-ins area. See Intro to plug-ins. Also see Add, replace, reorder, and remove plug-ins in the Plug-ins area and Work with plug-ins in the Mixer.
Note: Adaptive Limiter adds latency when the Lookahead parameter is active. The effect is most commonly used for mixing and mastering previously recorded tracks, not while recording. You should bypass Adaptive Limiter while recording.
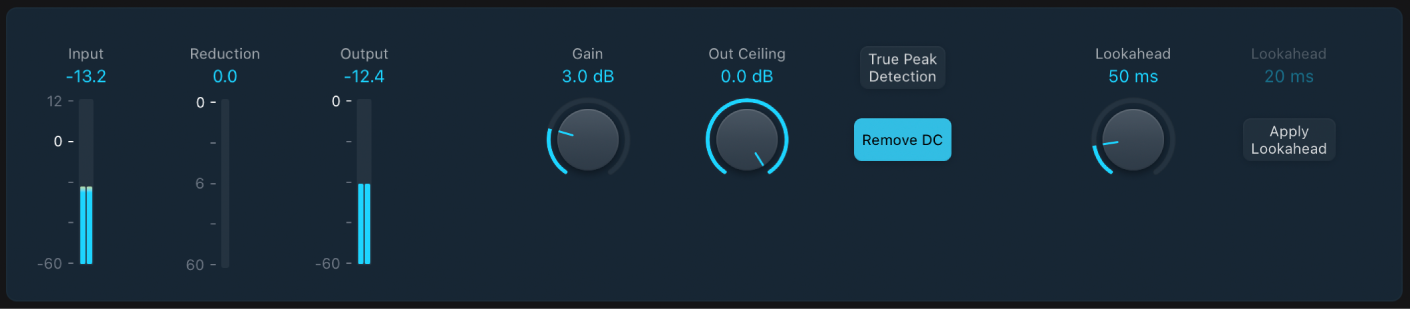
Adaptive Limiter parameters
Input meters: Show input levels in real time. The Margin field shows the peak input level.
 Reduction meter: Show the amount of gain reduction. The Margin field shows the peak reduction level.
Reduction meter: Show the amount of gain reduction. The Margin field shows the peak reduction level.Output meters: Show output levels of the limited signal. The Margin field shows the peak output level.
 Gain knob and field: Set the amount of gain after input scaling.
Gain knob and field: Set the amount of gain after input scaling. Out Ceiling knob and field: Set the maximum output level, or ceiling. The signal does not rise above this.
Out Ceiling knob and field: Set the maximum output level, or ceiling. The signal does not rise above this.TP Detection button: Turn on to detect inter-sample peaks (true peaks) in the signal.
Remove DC button: Turn on to activate a highpass filter that removes direct current (DC) from the signal. DC can be introduced by lower-quality audio hardware.
Lookahead knob and field: Set the playback buffer size (how far in the future the file is analyzed for peaks). Also see the Optimal Lookahead parameter. Values lower than the optimal buffer size are indicated in red.
Apply Lookahead button and field: Use the Apply Lookahead button to set the optimal playback buffer size. This changes the value shown in the Lookahead field.
Note: The Optimal Lookahead value is automatically determined and cannot be changed directly.
Download this guide: PDF