MainStage User Guide
- Welcome
-
- Overview of Edit mode
-
- Select patches and sets in the Patch List
- Copy, paste, and delete patches
- Reorder and move patches in the Patch List
- Add and rename patches
- Create a patch from several patches
-
- Overview of the Patch Settings Inspector
- Select patch settings in the Patch Library
- Set the time signature for patches
- Change the tempo when you select a patch
- Set program change and bank numbers
- Defer patch changes
- Instantly silence the previous patch
- Change patch icons
- Transpose the pitch of incoming notes for a patch
- Change the tuning for a patch
- Add text notes to a patch
-
- Overview of channel strips
- Add a channel strip
- Change a channel strip setting
- Configure channel strip components
- Show signal flow channel strips
- Hide the metronome channel strip
- Create an alias of a channel strip
- Add a patch bus
- Set channel strip pan or balance positions
- Set channel strip volume levels
- Mute and solo channel strips
- Use multiple instrument outputs
- Use external MIDI instruments
- Reorganize channel strips
- Delete channel strips
-
- Overview of the Channel Strip Inspector
- Choose channel strip settings
- Rename channel strips
- Change channel strip colors
- Change channel strip icons
- Use feedback protection with channel strips
- Set keyboard input for a software instrument channel strip
- Transpose individual software instruments
- Filter MIDI messages
- Scale channel strip velocity
- Set channel strips to ignore Hermode tuning
- Override concert- and set-level key ranges
- Add text notes to a channel strip in the Channel Strip Inspector
- Route audio via send effects
-
- Screen Control Inspector overview
- Replace parameter labels
- Choose custom colors for screen controls
- Change background or grouped screen control appearance
- Set screen controls to show the hardware value
- Set parameter change behavior for screen controls
- Set hardware matching behavior for screen controls
- Reset and compare changes to a patch
- Override concert- and set-level mappings
-
- Overview of mapping screen controls
- Map to channel strip and plug-in parameters
- Map screen controls to actions
- Map a screen control to multiple parameters
- Use screen controls to display PDF document pages
- Edit the saved value for a mapped parameter
- Set drum pads or buttons to use note velocity
- Map screen controls to all channel strips in a patch
- Undo screen control parameter mappings
- Remove screen control mappings
- Work with graphs
- Create controller transforms
- Share patches and sets between concerts
- Record the audio output of a concert
-
- Overview of concerts
- Create a concert
- Open and close concerts
- Save concerts
- How saving affects parameter values
- Clean up concerts
- Consolidate assets in a concert
- Rename the current concert
-
- Overview of the Concert Settings Inspector
- Set MIDI Routing to channel strips
- Transpose incoming note pitch for a concert
- Define the program change message source
- Send unused program changes to channel strips
- Set the time signature for a concert
- Change the tuning for a concert
- Set the pan law for a concert
- Add text notes to a concert
- Control the metronome
- Silence MIDI notes
- Mute audio output
-
- Layout mode overview
-
- Screen control parameter editing overview
- Lift and stamp screen control parameters
- Reset screen control parameters
- Common screen control parameters
- Keyboard screen control parameters
- MIDI activity screen control parameters
- Drum pad screen control parameters
- Waveform screen control parameters
- Selector screen control parameters
- Text screen control parameters
- Background screen control parameters
- How MainStage passes through MIDI messages
- Export and import layouts
- Change the aspect ratio of a layout
-
- Before performing live
- Use Perform mode
- Screen controls in performance
- Tempo changes during performance
- Tips for performing with keyboard controllers
- Tips for performing with guitars and other instruments
- Tune guitars and other instruments with the Tuner
- The Playback plug-in in performance
- Record your performances
- After the performance
- Tips for complex hardware setups
-
- Overview of keyboard shortcuts and command sets
-
- Concerts and layouts keyboard shortcuts
- Patches and sets (Edit mode) keyboard shortcuts
- Editing keyboard shortcuts
- Actions keyboard shortcuts
- Parameter mapping (Edit mode) keyboard shortcuts
- Channel strips (Edit mode) keyboard shortcuts
- Screen controls (Layout mode) keyboard shortcuts
- Perform in Full Screen keyboard shortcuts
- Window and view keyboard shortcuts
- Help and support keyboard shortcuts
-
-
- Use MIDI plug-ins
-
- Arpeggiator overview
- Arpeggiator control parameters
- Note order parameters overview
- Note order variations
- Note order inversions
- Arpeggiator pattern parameters overview
- Use Live mode
- Use Grid mode
- Arpeggiator options parameters
- Arpeggiator keyboard parameters
- Use keyboard parameters
- Assign controllers
- Modifier controls
- Note Repeater controls
- Randomizer controls
-
- Use Scripter
- Use the Script Editor
- Scripter API overview
- MIDI processing functions overview
- HandleMIDI function
- ProcessMIDI function
- GetParameter function
- SetParameter function
- ParameterChanged function
- Reset function
- JavaScript objects overview
- Use the JavaScript Event object
- Use the JavaScript TimingInfo object
- Use the Trace object
- Use the MIDI event beatPos property
- Use the JavaScript MIDI object
- Create Scripter controls
- Transposer controls
-
-
- Alchemy overview
- Alchemy interface overview
- Alchemy Name bar
- Alchemy file locations
-
- Alchemy source overview
- Source master controls
- Import browser
- Source subpage controls
- Source filter controls
- Source filter use tips
- Source elements overview
- Additive element controls
- Additive element effects
- Spectral element controls
- Spectral element effects
- Pitch correction controls
- Formant filter controls
- Granular element controls
- Sampler element controls
- VA element controls
- Wide unison mode
- Source modulations
- Morph controls
- Alchemy master voice section
- Alchemy Extended parameters
-
- Playback plug-in overview
- Add a Playback plug-in
- Playback interface
- Use the Playback waveform display
- Playback transport and function buttons
- Playback information display
- Playback Sync, Snap To, and Play From parameters
- Use the Playback group functions
- Use the Playback Action menu and File field
- Use markers with the Playback plug-in
-
- Sample Alchemy overview
- Interface overview
- Add source material
- Edit mode
- Play modes
- Source overview
- Synthesis modes
- Granular controls
- Additive effects
- Additive effect controls
- Spectral effect
- Spectral effect controls
- Filter module
- Lowpass, bandpass, and highpass filters
- Comb PM filter
- Downsampler filter
- FM filter
- Envelope generators
- Mod Matrix
- Modulation routing
- Motion mode
- Trim mode
- More menu
-
- Sculpture overview
- Sculpture interface
- Global parameters
- Amplitude envelope parameters
- Use the Waveshaper
- Filter parameters
- Output parameters
- Define MIDI controllers
- Extended parameters
-
- Studio Piano
- Copyright

Program a slap bass sound in Sculpture in MainStage
You’re actually dealing with two different articulations here. The low notes originate when the thumb literally slaps the strings on the upper part of the fingerboard. The high notes are produced when the strings are strongly plucked or popped with the fingers. This is achieved by hooking a finger under the string, pulling it away from the instrument, then allowing it to slap back onto the fingerboard. In conjunction, these articulation methods make up the typically aggressive and overtone-rich slap bass sound.
Emulate a slap bass sound in Sculpture
In MainStage, load the E-Bass Fingered Basic EQ1 setting.
Turn off the Body EQ.
Also turn off Object 2 and Object 3 for now.
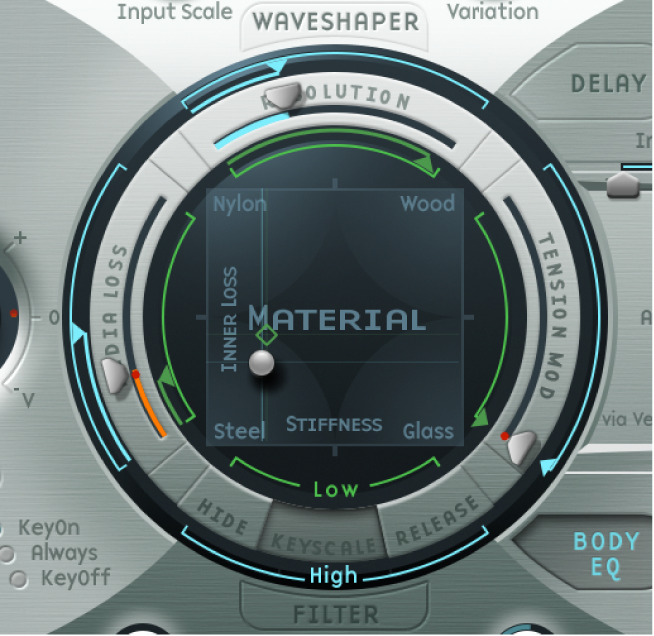
Because the basic sound of a slap bass is brighter than a standard fingered bass, you need to adjust some Material Pad settings.
Return the Low Keyscale parameter to its initial value by Option-clicking the small green triangle (found below the main Resolution slider).
Drag the ball down a little, and the sound becomes more wiry. The ball should now be directly above the word “Steel” on the horizontal axis.
From the models at your disposal, Strike is the most suitable for simulating a thumb physically striking the strings from above. This model is not, however, as appropriate for the slapped (popped) strings. It makes the most sense to choose the Pick model for this purpose.
To be safe, turn the Level knob to −25 dB.
Choose the Pick model for Object 1.
Drag Object 1 to position 0.90 in the Pickup display. This position corresponds to a playing position above or on the fingerboard.
Note: Given its universal concept, Sculpture does not react exactly like a bass, where one would tend to play in the middle of the string on the upper part of the fingerboard. Try moving Object 1 to this position and see how it sounds. You’ll find that the sound is a little too smooth.
Set the parameters for object 1 in Sculpture
In MainStage, set Timbre to a value of 0.38, which corresponds to a rapid attack.
Timbre determines the angle of the obstacle to the string.
Set the Strength parameter to 0.53.
Set the Variation parameter to −0.69.
This defines the softer material that constitutes the fleshy part on the side of your slapping thumb. Put more technically, Variation defines the type and degree of reflection.
Choose Bound in the Object 2 Type pop-up menu to emulate the typical bright rattling that is created when the string strikes the fingerboard.
Bound limits the antinode of the string in exactly the same way as the fingerboard on a real electric bass.
Adjust object 2 parameters in Sculpture
In MainStage, set Timbre to 0.39.
This corresponds to a fingerboard that runs almost parallel to the string.
Set the Strength parameter to 0.33.
Note: Try some higher values as well. You’ll see that the sound becomes softer and softer until it’s completely dampened by the obstacle.
Set Variation to 0.64. Despite the overtone-rich reflection, the string can still vibrate freely.
Note: Try some negative values—you’ll see that the reflections can no longer develop in an unhindered fashion.
Set the Level knob to −3 dB. The Bound obstacle has made the sound softer.
Notice that the sound is still too smooth for a real slap bass, so try using the Body EQ again. Turn on the Body EQ, and adjust the parameters as follows: Low 0.25, Mid 0.43, High 0.51, and drag the Mid Frequency slider to 0.59.
Save this sound as Slap Bass Basic#1.