MainStage User Guide
- Welcome
-
- Overview of Edit mode
-
- Select patches and sets in the Patch List
- Copy, paste, and delete patches
- Reorder and move patches in the Patch List
- Add and rename patches
- Create a patch from several patches
-
- Overview of the Patch Settings Inspector
- Select patch settings in the Patch Library
- Set the time signature for patches
- Change the tempo when you select a patch
- Set program change and bank numbers
- Defer patch changes
- Instantly silence the previous patch
- Change patch icons
- Transpose the pitch of incoming notes for a patch
- Change the tuning for a patch
- Add text notes to a patch
-
- Overview of channel strips
- Add a channel strip
- Change a channel strip setting
- Configure channel strip components
- Show signal flow channel strips
- Hide the metronome channel strip
- Create an alias of a channel strip
- Add a patch bus
- Set channel strip pan or balance positions
- Set channel strip volume levels
- Mute and solo channel strips
- Use multiple instrument outputs
- Use external MIDI instruments
- Reorganize channel strips
- Delete channel strips
-
- Overview of the Channel Strip Inspector
- Choose channel strip settings
- Rename channel strips
- Change channel strip colors
- Change channel strip icons
- Use feedback protection with channel strips
- Set keyboard input for a software instrument channel strip
- Transpose individual software instruments
- Filter MIDI messages
- Scale channel strip velocity
- Set channel strips to ignore Hermode tuning
- Override concert- and set-level key ranges
- Add text notes to a channel strip in the Channel Strip Inspector
- Route audio via send effects
-
- Screen Control Inspector overview
- Replace parameter labels
- Choose custom colors for screen controls
- Change background or grouped screen control appearance
- Set screen controls to show the hardware value
- Set parameter change behavior for screen controls
- Set hardware matching behavior for screen controls
- Reset and compare changes to a patch
- Override concert- and set-level mappings
-
- Overview of mapping screen controls
- Map to channel strip and plug-in parameters
- Map screen controls to actions
- Map a screen control to multiple parameters
- Use screen controls to display PDF document pages
- Edit the saved value for a mapped parameter
- Set drum pads or buttons to use note velocity
- Map screen controls to all channel strips in a patch
- Undo screen control parameter mappings
- Remove screen control mappings
- Work with graphs
- Create controller transforms
- Share patches and sets between concerts
- Record the audio output of a concert
-
- Overview of concerts
- Create a concert
- Open and close concerts
- Save concerts
- How saving affects parameter values
- Clean up concerts
- Consolidate assets in a concert
- Rename the current concert
-
- Overview of the Concert Settings Inspector
- Set MIDI Routing to channel strips
- Transpose incoming note pitch for a concert
- Define the program change message source
- Send unused program changes to channel strips
- Set the time signature for a concert
- Change the tuning for a concert
- Set the pan law for a concert
- Add text notes to a concert
- Control the metronome
- Silence MIDI notes
- Mute audio output
-
- Layout mode overview
-
- Screen control parameter editing overview
- Lift and stamp screen control parameters
- Reset screen control parameters
- Common screen control parameters
- Keyboard screen control parameters
- MIDI activity screen control parameters
- Drum pad screen control parameters
- Waveform screen control parameters
- Selector screen control parameters
- Text screen control parameters
- Background screen control parameters
- How MainStage passes through MIDI messages
- Export and import layouts
- Change the aspect ratio of a layout
-
- Before performing live
- Use Perform mode
- Screen controls in performance
- Tempo changes during performance
- Tips for performing with keyboard controllers
- Tips for performing with guitars and other instruments
- Tune guitars and other instruments with the Tuner
- The Playback plug-in in performance
- Record your performances
- After the performance
- Tips for complex hardware setups
-
- Overview of keyboard shortcuts and command sets
-
- Concerts and layouts keyboard shortcuts
- Patches and sets (Edit mode) keyboard shortcuts
- Editing keyboard shortcuts
- Actions keyboard shortcuts
- Parameter mapping (Edit mode) keyboard shortcuts
- Channel strips (Edit mode) keyboard shortcuts
- Screen controls (Layout mode) keyboard shortcuts
- Perform in Full Screen keyboard shortcuts
- Window and view keyboard shortcuts
- Help and support keyboard shortcuts
-
-
- Use MIDI plug-ins
-
- Arpeggiator overview
- Arpeggiator control parameters
- Note order parameters overview
- Note order variations
- Note order inversions
- Arpeggiator pattern parameters overview
- Use Live mode
- Use Grid mode
- Arpeggiator options parameters
- Arpeggiator keyboard parameters
- Use keyboard parameters
- Assign controllers
- Modifier controls
- Note Repeater controls
- Randomizer controls
-
- Use Scripter
- Use the Script Editor
- Scripter API overview
- MIDI processing functions overview
- HandleMIDI function
- ProcessMIDI function
- GetParameter function
- SetParameter function
- ParameterChanged function
- Reset function
- JavaScript objects overview
- Use the JavaScript Event object
- Use the JavaScript TimingInfo object
- Use the Trace object
- Use the MIDI event beatPos property
- Use the JavaScript MIDI object
- Create Scripter controls
- Transposer controls
-
-
- Alchemy overview
- Alchemy interface overview
- Alchemy Name bar
- Alchemy file locations
-
- Alchemy source overview
- Source master controls
- Import browser
- Source subpage controls
- Source filter controls
- Source filter use tips
- Source elements overview
- Additive element controls
- Additive element effects
- Spectral element controls
- Spectral element effects
- Pitch correction controls
- Formant filter controls
- Granular element controls
- Sampler element controls
- VA element controls
- Wide unison mode
- Source modulations
- Morph controls
- Alchemy master voice section
- Alchemy Extended parameters
-
- Playback plug-in overview
- Add a Playback plug-in
- Playback interface
- Use the Playback waveform display
- Playback transport and function buttons
- Playback information display
- Playback Sync, Snap To, and Play From parameters
- Use the Playback group functions
- Use the Playback Action menu and File field
- Use markers with the Playback plug-in
-
- Sample Alchemy overview
- Interface overview
- Add source material
- Edit mode
- Play modes
- Source overview
- Synthesis modes
- Granular controls
- Additive effects
- Additive effect controls
- Spectral effect
- Spectral effect controls
- Filter module
- Lowpass, bandpass, and highpass filters
- Comb PM filter
- Downsampler filter
- FM filter
- Envelope generators
- Mod Matrix
- Modulation routing
- Motion mode
- Trim mode
- More menu
-
- Sculpture overview
- Sculpture interface
- Global parameters
- Amplitude envelope parameters
- Use the Waveshaper
- Filter parameters
- Output parameters
- Define MIDI controllers
- Extended parameters
-
- Studio Piano
- Copyright

Use Ultrabeat oscillator 2 model mode in MainStage
This oscillator 2 mode employs a method of synthesis known as component modeling. This tone generation technique mimics the physical properties of an object, such as a guitar string. Further objects are used to stimulate the string, emulating the way that it is played: plucked, bowed, and so on. Although the term string is used, model mode enables you to create sounds that don’t sound like traditional stringed instruments.
The string is the element that is responsible for the basic tone. Ultrabeat offers parameters that enable you to adjust its material—what it’s made of, in other words.
The exciters make the string vibrate (move) in different ways. The string itself doesn’t make a sound unless it is stimulated, or excited.
The signal of the vibrating string is sent to the filter, amplifier, and so on, in the Synthesizer section.
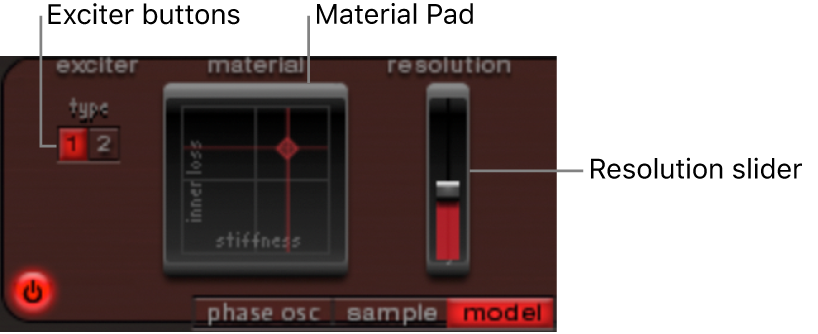
Model mode parameters
Exciter buttons: Select one of the two contrasting exciters. Each offers different sound characteristics.
Note: In this context, an exciter is the agent or triggering device used to initiate the vibration of the string. Don’t confuse it with the effect plug-in of the same name.
Material Pad: Determines the basic tone of the string with the string Stiffness and damping (Inner Loss) parameters.
Inner Loss: Emulates damping of the string, as caused by the string material—steel, glass, nylon, or wood. These are frequency-dependent losses that cause the sound to become more mellow during the decay phase.
Stiffness: Sets the rigidity of the string. In reality, this is determined by the string material and diameter—or, to be more precise, by its geometrical moment of inertia. Stiffer strings exhibit an inharmonic vibration, where overtones are not integer multiples of the base frequency. Rather, they have higher frequencies, which can make upper or lower notes sound somewhat out of tune with each other.
Resolution slider: Determine the precision of the calculation. High values produce extra harmonics. Low values produce fewer harmonics, or inharmonic spectra.
Use the Ultrabeat Material Pad
The combination of the Inner Loss and Stiffness parameter positions determines the string material and, therefore, the general timbre of your sound. In general synthesizer terms, use of these parameters could be viewed as being similar to the waveform selector/generator in the oscillator section. The default pitch of the string is C3 (middle C).
In MainStage, you can simultaneously adjust the Inner Loss and Stiffness parameter positions by dragging the ball (which correlates to the x and y coordinates) in the Material Pad.
Low Stiffness values, combined with low Inner Loss values, lead to metallic sounds.
Increase the Stiffness to make the sound more bell-like, or glass-like. Extreme Stiffness values turn the string into a solid metal rod.
Increase the Inner Loss value while maintaining a low Stiffness level to emulate nylon or catgut strings.
High Stiffness values, combined with high Inner Loss values, simulate wood-like materials.
Note: Option-click the ball to reset all string parameters to their default values.