Motion User Guide
- Welcome
-
- Intro to basic compositing
-
- Intro to transforming layers
-
- Intro to transforming layers in the canvas
- Transform layer properties in the canvas
- Transform tools
- Change layer position, scale, or rotation
- Move a layer’s anchor point
- Add a drop shadow to a layer
- Distort or shear a layer
- Crop a layer
- Modify shape or mask points
- Transform text glyphs and other object attributes
- Align layers in the canvas
- Transform layers in the HUD
- Transform 2D layers in 3D space
-
- Intro to behaviors
- Behaviors versus keyframes
-
- Intro to behavior types
-
- Intro to Parameter behaviors
- Audio behavior
- Average behavior
- Clamp behavior
- Custom behavior
- Add a Custom behavior
- Exponential behavior
- Link behavior
- Logarithmic behavior
- MIDI behavior
- Add a MIDI behavior
- Negate behavior
- Oscillate behavior
- Create a decaying oscillation
- Overshoot behavior
- Quantize behavior
- Ramp behavior
- Randomize behavior
- Rate behavior
- Reverse behavior
- Stop behavior
- Track behavior
- Wriggle behavior
-
- Intro to Simulation behaviors
- Align to Motion behavior
- Attracted To behavior
- Attractor behavior
- Drag behavior
- Drift Attracted To behavior
- Drift Attractor behavior
- Edge Collision behavior
- Gravity behavior
- Orbit Around behavior
- Random Motion behavior
- Repel behavior
- Repel From behavior
- Rotational Drag behavior
- Spring behavior
- Vortex behavior
- Wind behavior
- Additional behaviors
-
- Intro to using generators
- Add a generator
-
- Intro to image generators
- Caustics generator
- Cellular generator
- Checkerboard generator
- Clouds generator
- Color Solid generator
- Concentric Polka Dots generator
- Concentric Shapes generator
- Gradient generator
- Grid generator
- Japanese Pattern generator
- Lens Flare generator
- Manga Lines generator
- Membrane generator
- Noise generator
- One Color Ray generator
- Op Art 1 generator
- Op Art 2 generator
- Op Art 3 generator
- Overlapping Circles generator
- Radial Bars generator
- Soft Gradient generator
- Spirals generator
- Spiral Drawing generator
- Use Spiral Drawing onscreen controls
- Star generator
- Stripes generator
- Sunburst generator
- Truchet Tiles generator
- Two Color Ray generator
- Save a modified generator
-
- Intro to filters
- Browse and preview filters
- Apply or remove filters
-
- Intro to filter types
-
- Intro to Color filters
- Brightness filter
- Channel Mixer filter
- Color Adjustments filter
- Color Balance filter
- Example: Color-balance two layers
- Color Curves filter
- Use the Color Curves filter
- Color Reduce filter
- Color Wheels filter
- Use the Color Wheels filter
- Colorize filter
- Contrast filter
- Custom LUT filter
- Use the Custom LUT filter
- Gamma filter
- Gradient Colorize filter
- HDR Tools filter
- Hue/Saturation filter
- Hue/Saturation Curves filter
- Use the Hue/Saturation Curves filter
- Levels filter
- Negative filter
- OpenEXR Tone Map filter
- Sepia filter
- Threshold filter
- Tint filter
-
- Intro to Distortion filters
- Black Hole filter
- Bulge filter
- Bump Map filter
- Disc Warp filter
- Droplet filter
- Earthquake filter
- Fisheye filter
- Flop filter
- Fun House filter
- Glass Block filter
- Glass Distortion
- Insect Eye filter
- Mirror filter
- Page Curl filter
- Poke filter
- Polar filter
- Refraction filter
- Ring Lens filter
- Ripple filter
- Scrape filter
- Sliced Scale filter
- Use the Sliced Scale filter
- Sphere filter
- Starburst filter
- Stripes filter
- Target filter
- Tiny Planet filter
- Twirl filter
- Underwater filter
- Wave filter
-
- Intro to Stylize filters
- Add Noise filter
- Bad Film filter
- Bad TV filter
- Circle Screen filter
- Circles filter
- Color Emboss filter
- Comic filter
- Crystallize filter
- Edges filter
- Extrude filter
- Fill filter
- Halftone filter
- Hatched Screen filter
- Highpass filter
- Indent filter
- Line Art filter
- Line Screen filter
- MinMax filter
- Noise Dissolve filter
- Pixellate filter
- Posterize filter
- Relief filter
- Slit Scan filter
- Slit Tunnel filter
- Texture Screen filter
- Vignette filter
- Wavy Screen filter
- About filters and color processing
- Publish filter controls to Final Cut Pro
- Using filters on alpha channels
- Filter performance
- Save custom filters
-
- Intro to 3D objects
- Add a 3D object
- Move and rotate a 3D object
- Reposition a 3D object’s anchor point
- Exchange a 3D object file
- 3D object intersection and layer order
- Using cameras and lights with 3D objects
- Save custom 3D objects
- Guidelines for working with 3D objects
- Working with imported 3D objects
-
- Intro to 360-degree video
- 360-degree projects
- Create 360-degree projects
- Add 360-degree video to a project
- Create a tiny planet effect
- Reorient 360-degree media
- Creating 360-degree templates for Final Cut Pro
- 360-degree-aware filters and generators
- Export and share 360-degree projects
- Guidelines for better 360-degree projects
-
- Intro to settings and shortcuts
-
- Intro to Keyboard shortcuts
- Use function keys
- General keyboard shortcuts
- Audio list keyboard shortcuts
-
- Tools keyboard shortcuts
- Transform tool keyboard shortcuts
- Select/Transform tool keyboard shortcuts
- Crop tool keyboard shortcuts
- Edit Points tool keyboard shortcuts
- Edit shape tools keyboard shortcuts
- Pan and Zoom tools keyboard shortcuts
- Shape tools keyboard shortcuts
- Bezier tool keyboard shortcuts
- B-Spline tool keyboard shortcuts
- Paint Stroke tool keyboard shortcuts
- Text tool keyboard shortcuts
- Shape mask tools keyboard shortcuts
- Bezier Mask tool keyboard shortcuts
- B-Spline Mask tool keyboard shortcuts
- Transport control keyboard shortcuts
- View option keyboard shortcuts
- HUD keyboard shortcuts
- Inspector keyboard shortcuts
- Keyframe Editor keyboard shortcuts
- Layers keyboard shortcuts
- Library keyboard shortcuts
- Media list keyboard shortcuts
- Timeline keyboard shortcuts
- Keyframing keyboard shortcuts
- Shape and Mask keyboard shortcuts
- 3D keyboard shortcuts
- Miscellaneous keyboard shortcuts
- Touch Bar shortcuts
- Move assets to another computer
- Work with GPUs
- Glossary
- Copyright

Project Properties Inspector controls in Motion
When the Project object is selected in the Layers list, the Properties Inspector is divided into several control groups: General, Rendering, Motion Blur, Reflections, and Description.
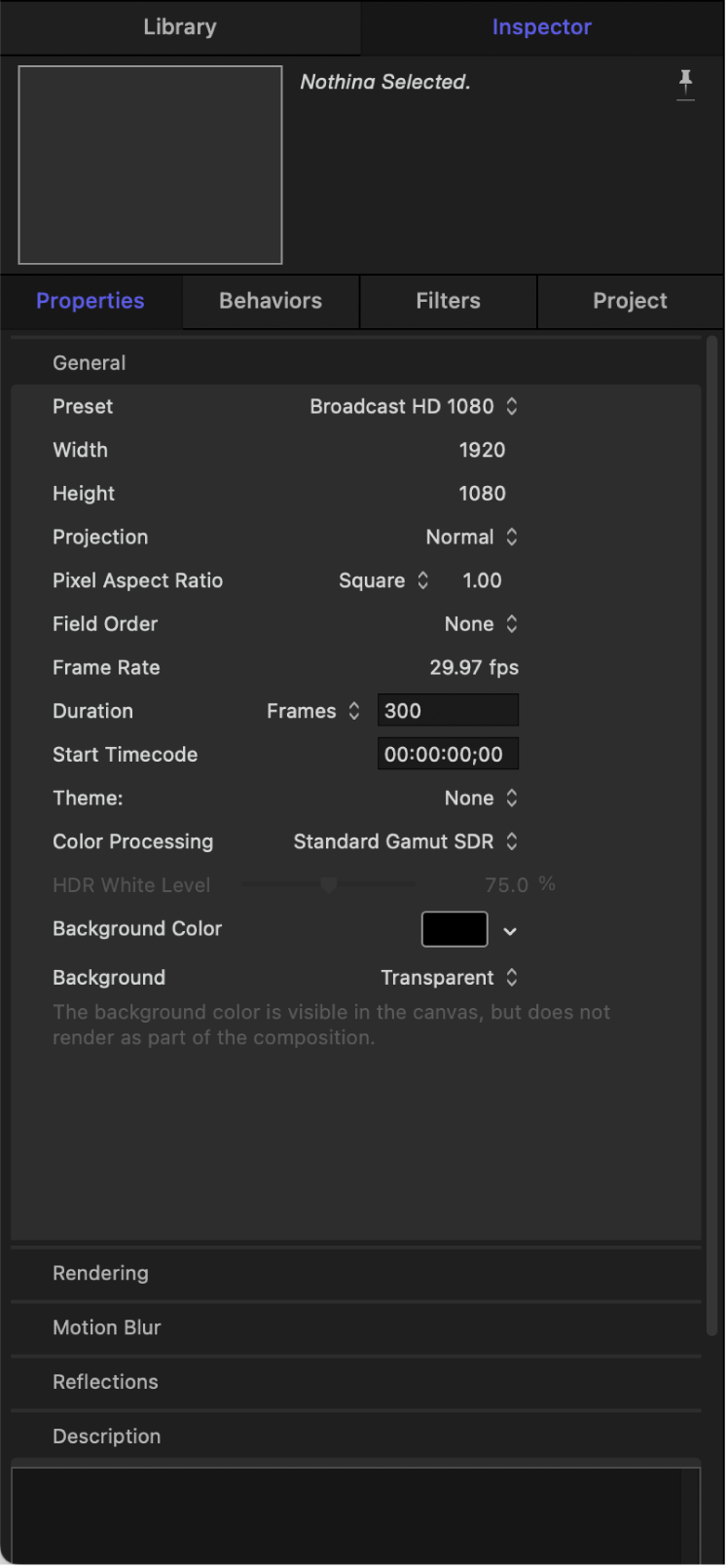
General controls
Use the controls in the General group to set or modify your project’s basic attributes.
Preset: A pop-up menu to choose a common video format to base your preset on. After choosing a preset, you can adjust the other parameters in the Properties Inspector to customize your format settings. For more information about managing Motion project presets, see Create and modify project presets in Motion.
Width and Height: A value slider to define the size of the canvas and the default output resolution of your project. Drag left or right over the values to decrease or increase them. Frame size is usually defined by the video format you plan on outputting to. For example, Broadcast HD video is 1920 x 1080, whereas 4K Ultra HD video has a frame size of 3840 x 2160.
Projection: A pop-up menu to set the project’s projection to Normal (flat video) or to 360° Monoscopic (spherical video). If you are using 360° video, ensure Projection is set to 360° Monoscopic.
When a normal project is changed to a 360° project, existing root-level 2D groups are converted to 3D groups; you can navigate the project in 360° (the 360° Look Around and 360° Overview options are available in the Camera menu in the canvas); and the project is exported using the 360° Overview camera.
When you create a new 360° project (by choosing a 360° Video option in the Preset pop-up menu in the Project Browser), 360° Monoscopic is the default Projection setting. See Intro to 360° video in Motion.
Pixel Aspect Ratio: A pop-up menu to set whether the project is created using square or nonsquare pixels. Computer displays, film, and high-definition video use square pixels, while standard-definition video uses nonsquare pixels. Choose Square for projects intended for the web, high-definition projects, and film, or choose a nonsquare pixel ratio corresponding to each international standard-definition broadcast format. A value slider to the right of this pop-up menu displays the numerical aspect ratio, in case you need to change the dimensions manually.
Field Order: A pop-up menu to set field order if the project uses interlaced video. Project field order should match the field order of the device being used to output the resulting QuickTime file to video. When working with progressive-scan video or film, choose None.
Frame Rate: A display field to see the project frame rate (in frames per second). Frame rate should match that of the format you output to. For example, film is 24 fps, PAL video is 25 fps, and NTSC video is 29.97 fps.
Important: Frame rates cannot be changed for existing projects.
Duration: A value field to modify the project’s Timeline duration. Use the adjacent pop-up menu to define the duration units (Frames, Timecode, or Seconds).
Override FCP Duration: A checkbox (available only in Final Cut Transition templates) that, when selected, overrides the default transition duration (as defined in the Editing pane of Final Cut Pro Settings). See Intro to Final Cut Pro for Mac templates in Motion.
Start Timecode: A value field to set the starting timecode displayed in the project.
Theme: A pop-up menu to assign a theme to the project.
Designed for 4K: A checkbox available only in Final Cut Effect, Transition, Generator, or Title template projects that adds a metadata flag so that Final Cut Pro users can quickly find 4K templates (and filter out all non-4K templates). See Set template resolution in Motion.
Color Processing: A pop-up menu to set the project’s working color space to Standard Gamut SDR (linear RGB with Rec. 709 color primaries), Wide Gamut HDR (linear RGB with Rec. 2020 color primaries), or Automatic (no native color space). See About color space and Manage automatic color processing in Motion.
Tip: Use Automatic color processing when you’re mixing SDR and HDR elements in a single project or when you’re creating effect, generator, transition, or title templates for Final Cut Pro. When applied to the timeline, the template automatically conforms to the color space of the Final Cut Pro project.
HDR White Level: A slider (available only when Color Processing in Project Properties is set to Automatic) to adjust the brightness of SDR elements when converted to different color spaces (usually from SDR to HDR). SDR elements include text, shapes, particles, and other graphics created in Motion, as well as SDR images and clips. If SDR elements appear too dim at the default value (75%), increase the white level value to better integrate the SDR elements into the HDR scene. See Manage automatic color processing in Motion and Color parameters in the Properties Inspector.
Tip: When creating templates in Motion for use in HDR Final Cut Pro projects, publish the HDR White Level slider to allow the brightness of graphics and any SDR media to be adjusted when the effect, transition, generator, or title is added to the Final Cut Pro timeline. See Intro to Final Cut Pro templates in Motion and Publish the HDR White Level slider in a template.
Override FCP Color Space: A checkbox to ensure that an effect, transition, generator, or title template retains the same appearance when applied to the Final Cut Pro timeline, regardless of the Final Cut Pro library’s color processing setting.
Note: This checkbox is available only in Final Cut template projects and when the Color Processing parameter (in Project Properties) is set to Standard Gamut SDR or Wide Gamut HDR. For more information on creating templates, see Intro to Final Cut Pro templates in Motion.
Background Color: A color control to set the background color of the canvas.
Background: A pop-up menu to define whether the Background Color is rendered as part of the alpha channel. Regardless of the selection, the Background Color is visible in the canvas. Choose from these three options:
Transparent: The background color does not render as part of the alpha channel.
Solid: The background color creates a solid alpha channel.
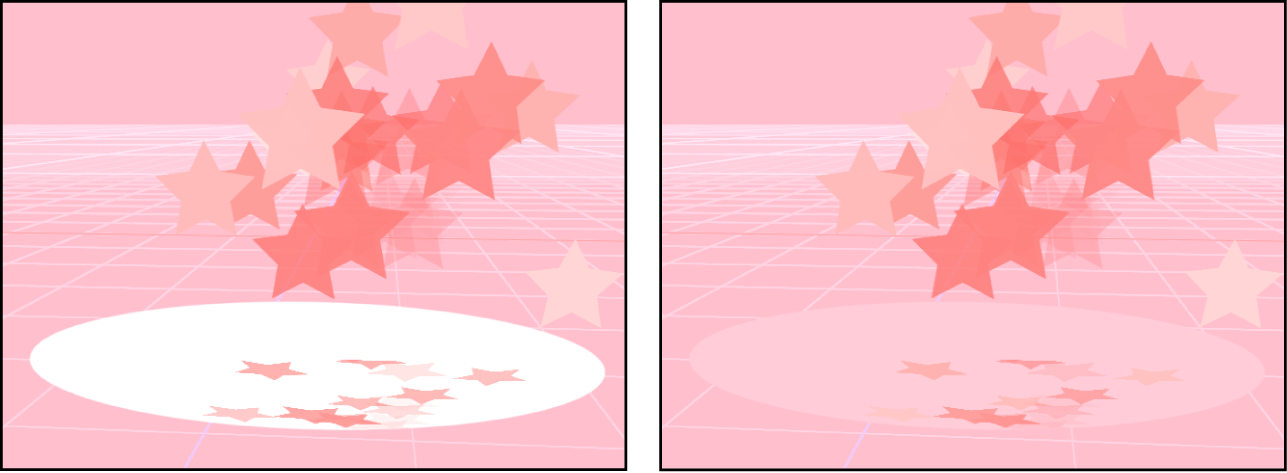
Environment: The background color creates a solid alpha channel and interacts with 3D projects, including blend modes and reflections. In the following images of the canvas, Reflection is turned on for the elliptical shape (in the shape’s Properties Inspector). In the left image, the elliptical shape retains its original white color because Background is set to Solid. In the right image, the pink background is reflected in the elliptical shape because Background is set to Environment.
Rendering, Motion Blur, and Reflections controls
Below the General section of the Properties Inspector are three groups of controls that can affect how your project looks when exported: Rendering, Motion Blur, and Reflections.
The Rendering controls determine how scaled-down media and 3D objects appear in your project. The Rendering section of the Properties Inspector has two controls:
Image Downscaling: A pop-up menu that sets the filtering operation for media that is sized down. Choose from these two options:
Smooth: The standard filtering operation for scaled-down images. Significant scaling may result in blurred images.
Sharp: May preserve some image sharpness in significantly scaled-down images. For example, choose Sharp when scaling down 4K footage for use in a Broadcast HD 1080 project, to retain more image detail and prevent image softening.
3D Object Environment: A value slider that controls the environment intensity for 3D objects. See Modify a 3D object’s inherent size and orientation in Motion.
The Motion Blur controls simulate the effect a camera’s mechanical shutter has on a frame of film or video when the camera or its subject is moving. In Motion, motion blur affects objects in your project that are animated using behaviors or keyframes, creating more natural-looking motion in your project, even though the animation is artificial. As with a camera, faster objects have more blur; slower objects have less blur.

The Motion Blur section of the Properties Inspector has two settings:
Samples: A slider to set the number of subframes rendered per frame, where one frame represents 360 degrees. Higher Samples values result in a higher-quality motion-blur effect, but are more processor-intensive. The default Samples value is 8. The maximum possible value is 256.
Shutter Angle: A slider to define the size of the motion blur that appears for animated objects. Increasing the shutter angle increases the number of frames over which the shutter is open.
The following image shows a shape keyframed to move quickly across the canvas horizontally.
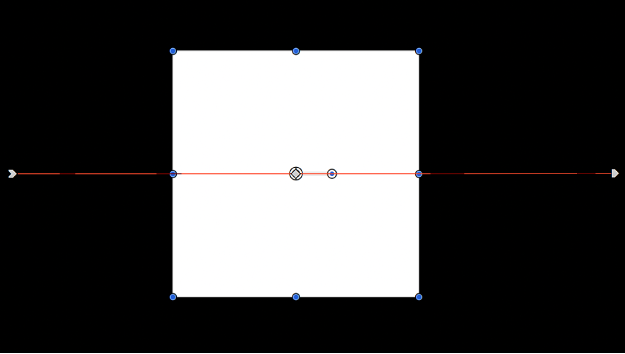
In the next image, Motion Blur is enabled and Samples is set to the default value of 8.

Note: When using larger Shutter Angle values, it may be necessary to increase the Samples value to eliminate unwanted artifacts.
In the above image, the Shutter Angle is set to the default of 360 degrees, which represents 1 frame. In the following image, Shutter Angle is set to 1100 degrees.

The Reflections section of the Properties Inspector has one parameter:
Maximum Bounces: A slider to limit the number of recursive reflections that can occur when two or more shiny objects reflect one another. This parameter is intended to prevent an endless repetition of reflective bounces.
For more information about reflections, see Cast a reflection in Motion.
Description field
At the bottom of the Properties Inspector is a field where you can enter a brief description of the project, including significant characteristics of the project preset, such as frame size and frame rate.
Download this guide: Apple Books | PDF