
Replicator controls in Motion
The parameters in the Replicator Inspector give you complete control over every aspect of the pattern created by the selected replicator. This includes the shape upon which the pattern is built and the shape’s related parameters, such as the size of the pattern, how the elements are arranged in the pattern, and so on.
Some parameters in the Replicator Inspector depend on the settings of other parameters. All combinations of parameters are described below:
Shape: A pop-up menu to set the overall shape of the onscreen replicator pattern. The default setting is Rectangle. Choose any of up to ten shape styles from the menu to alter the distribution of the pattern elements.

The Shape pop-up menu contains the following items:
Line: Elements are positioned on a line. In the Inspector, you can set a specific number of points on the line—one element is positioned at every point (including the end points of the line).
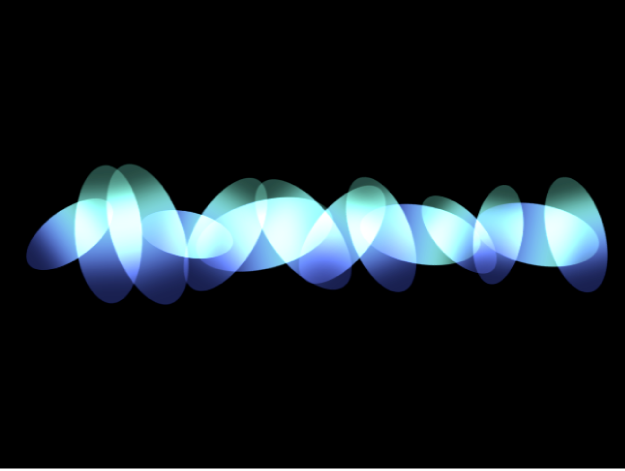
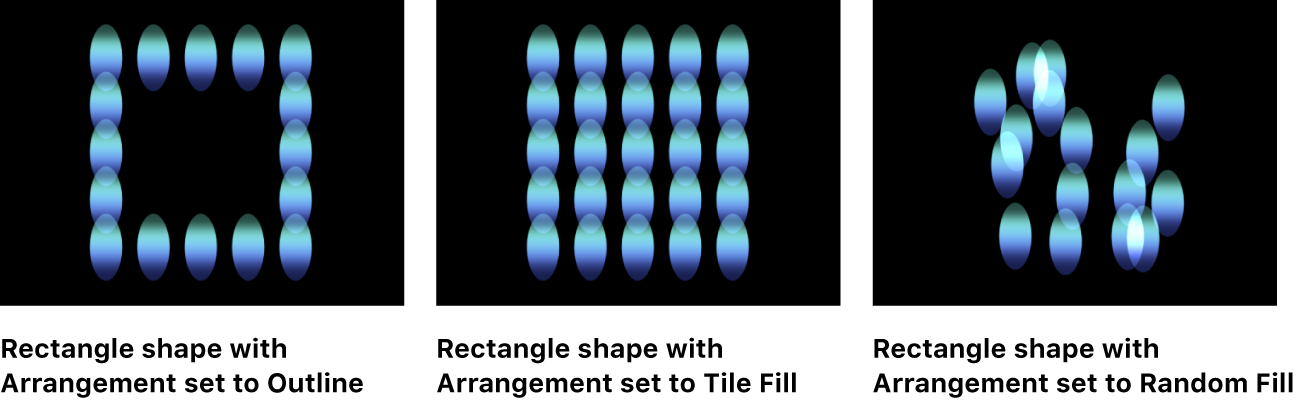
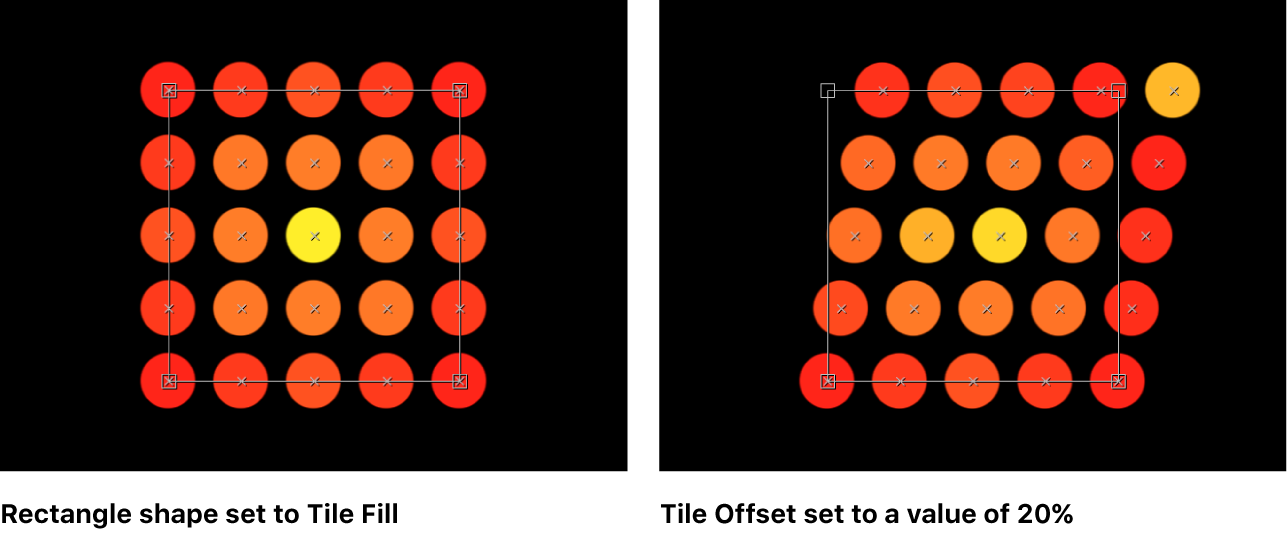
Rectangle: Elements are positioned in a rectangle along the replicator outline, or in a tile or random fill pattern. When Rectangle is selected, the Arrangement parameter becomes available (described below).
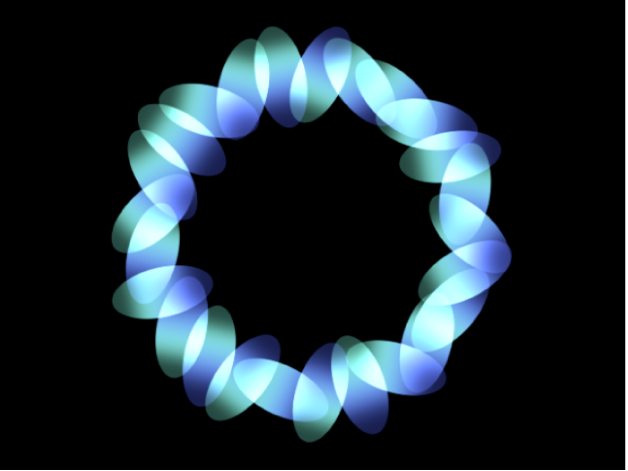
Circle: Elements are positioned in a circle along the replicator outline, or in a tile or random fill pattern. When Circle is selected, the Arrangement parameter becomes available. In the following image, the circle’s Arrangement is set to Outline.
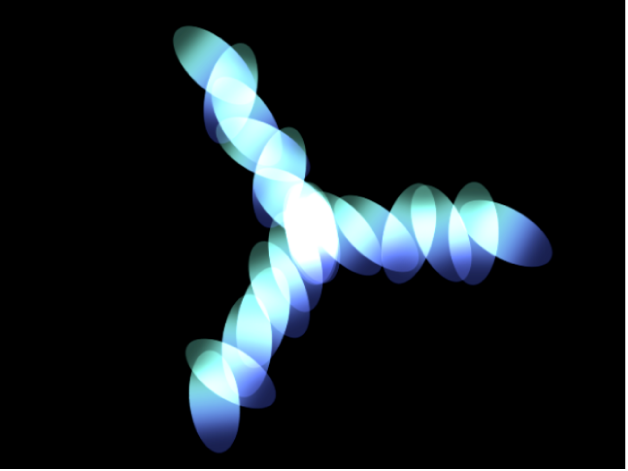
Burst: Elements are positioned in a flare pattern.
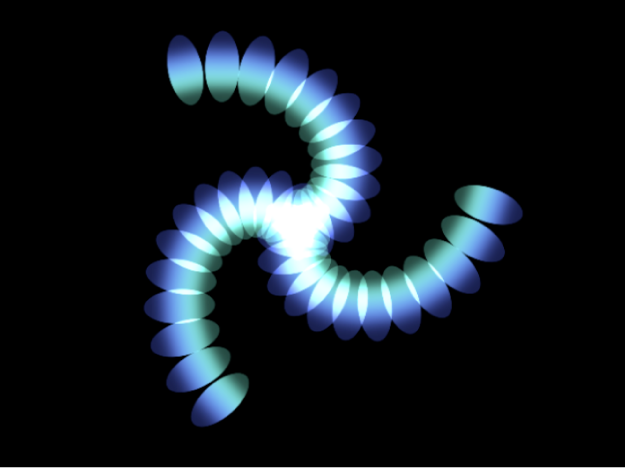
Spiral: Elements are positioned in a spiral pattern.
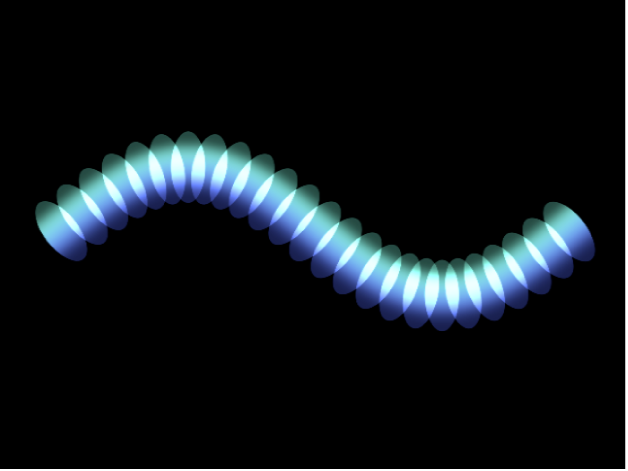
Wave: Elements are positioned on a waveform.
Geometry: Elements are positioned along the edge of a shape, defined by a spline object used as the shape source. See Create a custom replicator shape in Motion.
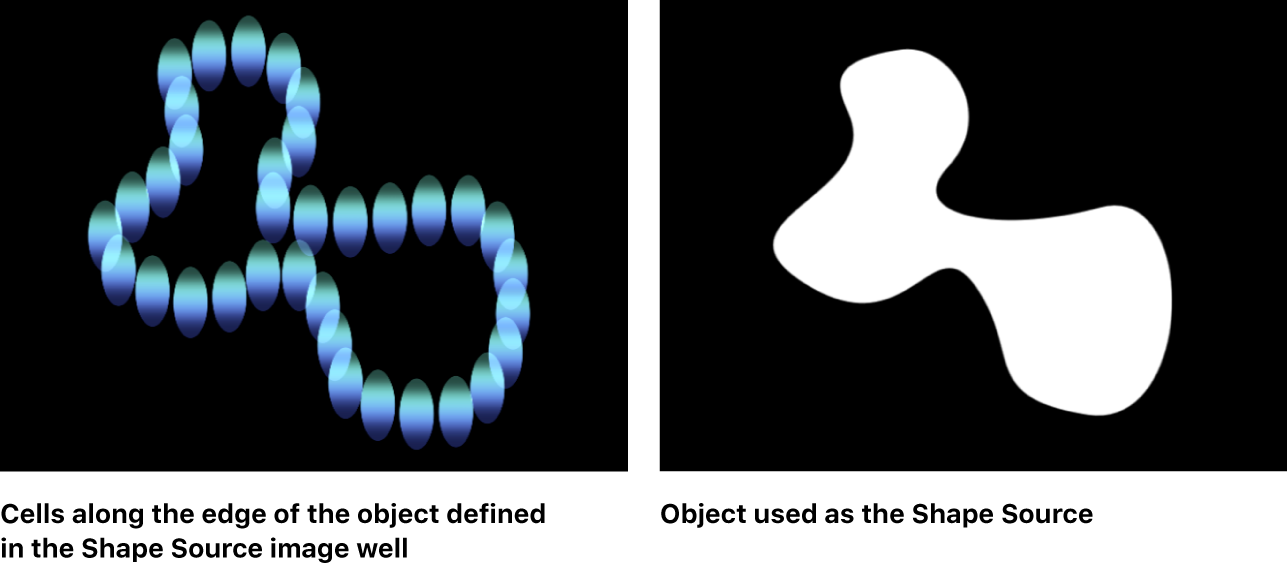
For information on using the Geometry shape, see Replicator cell controls in Motion.
Image: Elements appear within an area defined by an image or along its border, depending on the Arrangement setting. The image may have an alpha channel; if so, the shape of the alpha channel can also be used to define the pattern. See Create a custom replicator shape in Motion.
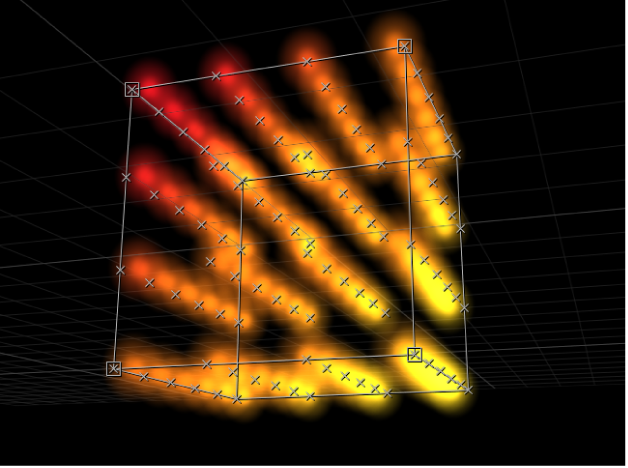
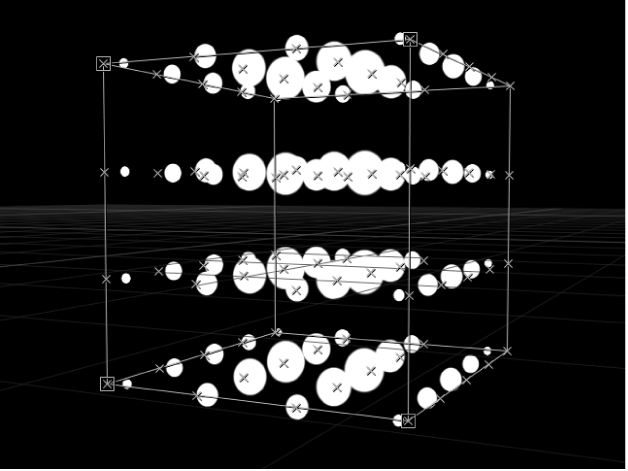
Box: This option is available when the 3D checkbox (described below) is selected in the Replicator Inspector. Elements are positioned in a three-dimensional cube along the replicator outline, or on its surface in a tile or random fill pattern. Using the onscreen controls (with the Adjust Item tool selected in the canvas toolbar), you can specify the size and location of the rectangle. Drag the front horizontal outline edge to adjust height; drag the front vertical edge to adjust width; drag a back edge to adjust depth; drag a front corner to simultaneously adjust the width and height. To reposition the replicator, drag in the replicator (but not on an edge or corner point). In the following image, the box’s Arrangement is set to Tile.
Sphere: This option is available when the 3D checkbox (described below) is selected in the Replicator Inspector. Elements are positioned in a three-dimensional sphere along the replicator outline, or on its surface in a tile or random fill pattern. Using the onscreen controls (with the Adjust Item tool selected in the canvas toolbar), you can specify the radius and location of the circle. Drag the outline of the sphere to adjust its radius; drag in the sphere to reposition it in the canvas.
Arrangement: A pop-up menu (available when the Shape pop-up menu is set to Rectangle, Circle, Image, Box, or Sphere) to specify the layout of the elements in the selected shape. There are three menu options:
Outline: Elements are positioned along the edge of the shape.

Tile Fill: Elements are positioned in a tiled pattern of rows and columns in the circle, rectangle, image, box, or sphere pattern. You can specify the number of columns and rows, as well as the tile offset. This is the default setting.
Random Fill: Elements are positioned randomly within the circle, sphere, rectangle, or box pattern.
Size/Radius: A slider (available when Shape is set to Rectangle or Box) to set the size of the rectangle or cube shape. Click the disclosure triangle to display separate Width, Height, and Depth (for the Box shape) parameters. When Circle is the selected shape, this parameter becomes Radius.
Note: For projects using the default camera settings and a default Z position for the replicator, Height is measured in pixels, and Width is measured in square pixels, to ensure that a numerically square shape looks square when Correct for Aspect Ratio is enabled (in the View pop-up menu).
Shape Source: An image well (available only when Shape is set to Geometry) to specify a shape object as the source for the replicator pattern. To set the shape source for the replicator, drag a shape from the Layers list or Timeline into the Shape Source well.
Image Source: An image well (available when the Shape parameter is set to Image) to specify an image object as the source for the replicator shape. To set the image source, drag an image from the Layers list or Timeline into the Image Source well.
Emission Alpha Cutoff: A slider (available when the Image Source object contains an alpha channel) to set the minimum opacity value necessary to create an element at that point on the source image. For example, when set to 25%, elements appear only at points where the alpha value of the image is equal to or greater than 25% opacity. The lower the Emission Alpha Cutoff value, the more cells appear. For this parameter to be effective, the alpha channel must have areas of varying transparency.

Start Point: Value sliders (available when Shape is set to Line or Wave) to define, in X and Y coordinates, the first point of the line or wave on which the elements are positioned. Click the disclosure triangle to modify the Z position (depth) of the start point. You can adjust these values in the canvas using the onscreen controls (with the Adjust Item tool selected in the canvas toolbar).
End Point: Value sliders (available when Shape is set to Line or Wave) to define, in X and Y coordinates, the end point of the line or wave on which the elements are positioned. Click the disclosure triangle to modify the Z position (depth) of the end point. You can adjust these values in the canvas using the onscreen controls (with the Adjust Item tool selected in the canvas toolbar).
Amplitude: A slider (available only when Shape is set to Wave) to define half the distance from the highest point to the lowest point in the wave. Higher values result in more extreme waves.
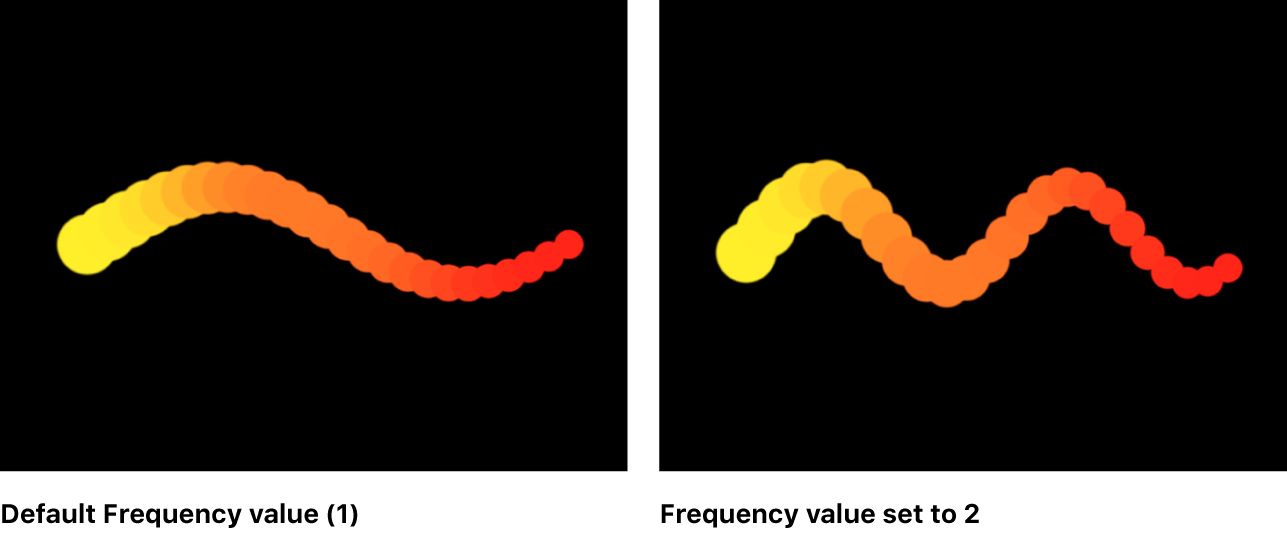
Frequency: A slider (available only when Shape is set to Wave) to define the number of waves. The default is value is 1.
Phase: A dial (available only when Shape is set to Wave) to define the degree of offset of the waves from the start and end points of the path. When set to 0 degrees (default), the wave begins and ends at half the distance from the highest point to the lowest point in the wave. When set to 90 degrees, the wave begins and ends at the highest point in the wave. When set to –90 degrees, the wave begins at the lowest point in the wave. When set to 180 degrees, the waves are the same as at 0 degrees, but are inverted.
Damping: A slider (available only when Shape is set to Wave) to set the diminishing oscillation of the wave. Positive damping values diminish the wave forward (from left to right); negative values diminish the wave backward (from right to left).

Points: A slider that does the following:
When Shape is set to Rectangle, Circle, Image, Box, or Sphere, and Arrangement is set to Outline or Random Fill, specifies the number of evenly distributed element points along the edge of the shape.
When Shape is set to Line or Wave, specifies the number of evenly distributed element points on the line or wave.
When Shape is set to Geometry, specifies the number of evenly distributed element points around the shape.
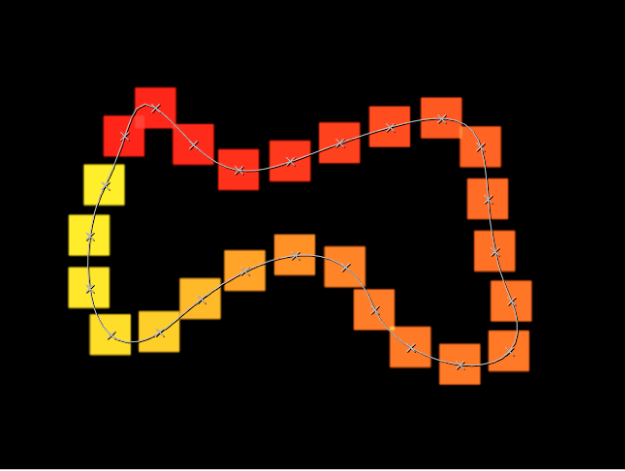
When the Adjust Item tool is selected in the canvas toolbar, these points are visible in the canvas.
Offset: A slider that does the following:
When Shape is set to Line or Wave, moves the elements along the line or wave.
When Shape is set to Rectangle, Circle, Image, Box, or Sphere, and Arrangement is set to Outline, moves the elements along the edge of the shape.
When Shape is set to Geometry, moves the position of the elements along the edge of the shape.
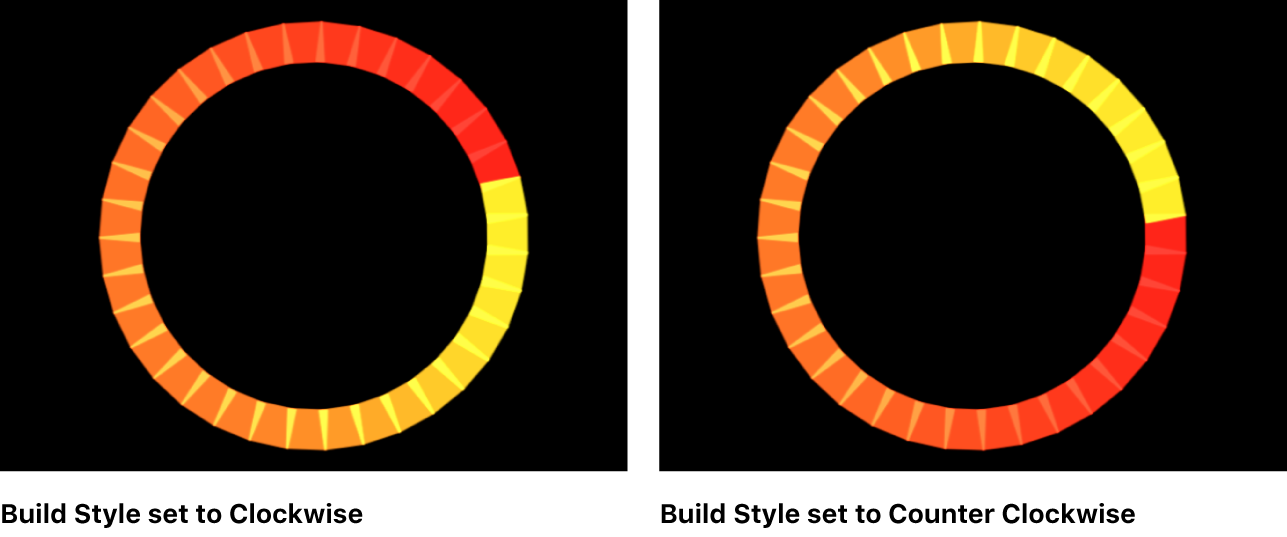
Build Style: A pop-up menu and related controls to specify how elements are built over the replicator shape. When Shape is set to Rectangle, Circle, or Image, and Arrangement is set to Outline; or when Shape is set to Geometry, the pop-up menu contains the following options:
Clockwise: Places the elements along the shape in a clockwise direction.
Counter Clockwise: Places the elements along the shape in a counterclockwise direction.
When Shape is set to Rectangle or Image, and Arrangement is set to Tile Fill, and Origin is set to Upper Left, Upper Right, Lower Left, or Lower Right, the Build Style pop-up menu contains the following options:
Across: Builds the elements across the pattern in the direction implied by the Origin parameter.
By Row: Builds the elements over the pattern by row.
By Column: Builds the elements over the pattern by column.
When Shape is set to Box, and Arrangement is set to Tile Fill, and Origin is set to Front Upper Left, Front Upper Right, Front Lower Left, Front Lower Right, Back Upper Left, Back Upper Right, Back Lower Left, or Back Lower Right, the Build Style pop-up menu contains the following options:
Across: Builds the elements across the pattern in the direction implied by the Origin parameter.
By Row, Column, Rank: Builds the elements over the pattern by row, column, then rank starting from the Origin.
By Column, Row, Rank: Builds the elements over the pattern by column, row, then rank starting from the Origin.
By Row, Rank, Column: Builds the elements over the pattern by row, rank, then column starting from the Origin.
By Column, Rank, Row: Builds the elements over the pattern by column, rank, then row starting from the Origin.
By Rank, Row, Column: Builds the elements over the pattern by rank, row, then column starting from the Origin.
By Rank, Column, Row: Builds the elements over the pattern by rank, column, then row starting from the Origin.
Radius: A slider (available when Shape is set to Burst, Spiral, Circle, or Sphere) to set the size of the selected shape.
Twists: A slider (available only when Shape is set to Spiral) to set the number of turns in a spiral. The default value is 0.25. When Number of Arms is set to one, a single spiral is created.
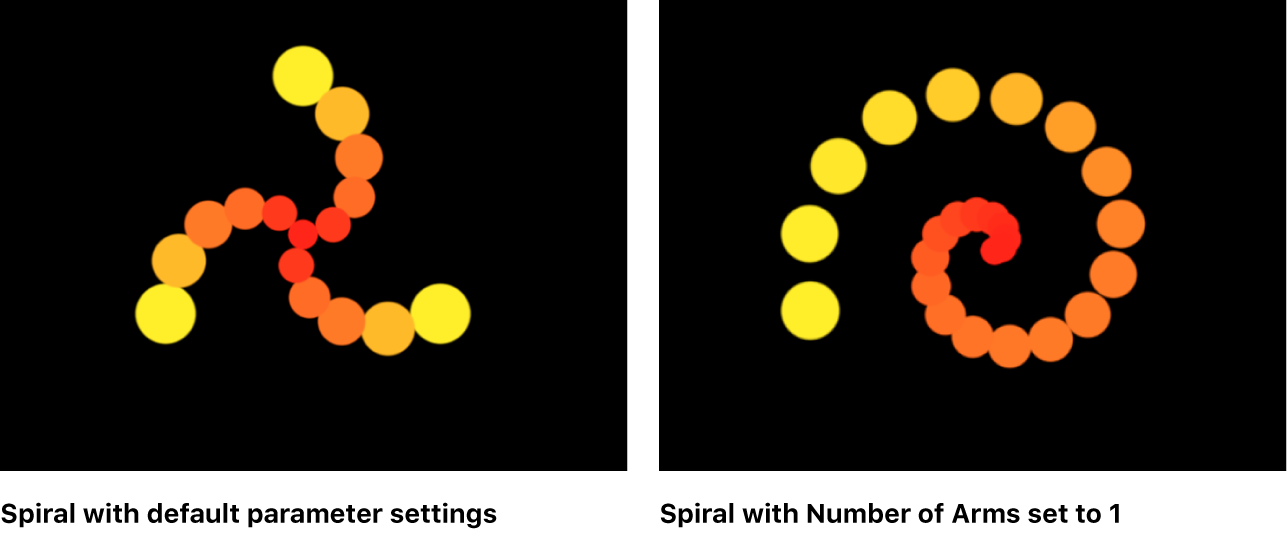

Number of Arms: A slider (available only when Shape is set to Burst or Spiral) to set the number of branches on which the elements are positioned. The default value is 3.
Points Per Arm: A slider (available only when Shape is set to Burst or Spiral) to set the number of element points on each branch of the burst or spiral. When the Adjust Item tool is selected in the canvas toolbar, the points are visible in the canvas.
Columns: A slider (available when Shape is set to Rectangle, Circle, or Image, and Arrangement is set to Tile Fill; or when Shape is set to Box or Sphere and Arrangement is set to Outline or Tile Fill) to specify the number of vertical columns on a grid over the selected replicator. In irregular shapes (nonrectangular), points that fall outside the shape are ignored.
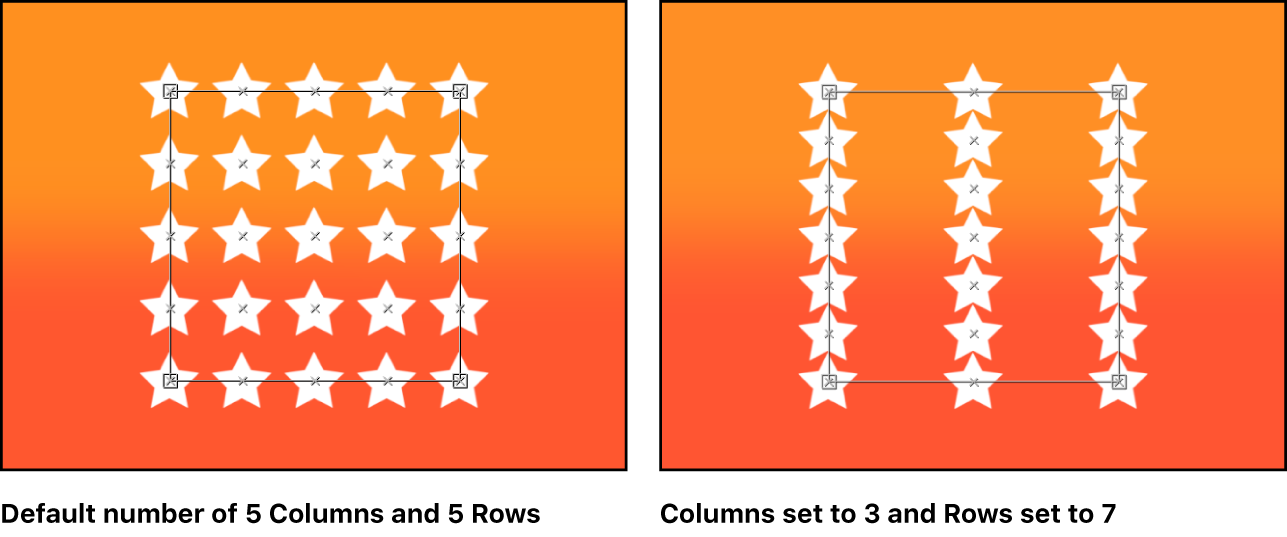
Rows: A slider (available when Arrangement is set to Tile Fill) to set the number of horizontal rows on a grid over the selected replicator. In irregular shapes (nonrectangular), points that fall outside the shape are ignored. This control is also available for Box and Sphere when Arrangement is set to Outline or Tile Fill.
Ranks: A slider (available when Shape is set to Box and Arrangement is set to Tile Fill or Outline; or when Shape is set to Sphere and Arrangement is set to Tile Fill) to specify the number of points in Z space (depth) on a grid over the selected replicator. In irregular shapes (nonrectangular), points that fall outside the shape are ignored.
Tile Offset: A slider (available when Shape is set to Rectangle, Circle, Image, Box, or Sphere, and Arrangement is set to Tile Fill) to specify the amount (in percentage points) that the elements are offset from the pattern. Values from 0 to 100% offset the rows toward the right, and values from 0 to –100% offset the rows toward the left. A value of 50 or –50% creates a brickwork pattern.
Origin: A pop-up menu to specify how the elements traverse across the pattern from a point of origin. For example, when set to Left, the elements sweep across the pattern from left to right. When set to Upper Right, the elements traverse from the upper-right corner point of the shape to the lower-right corner.
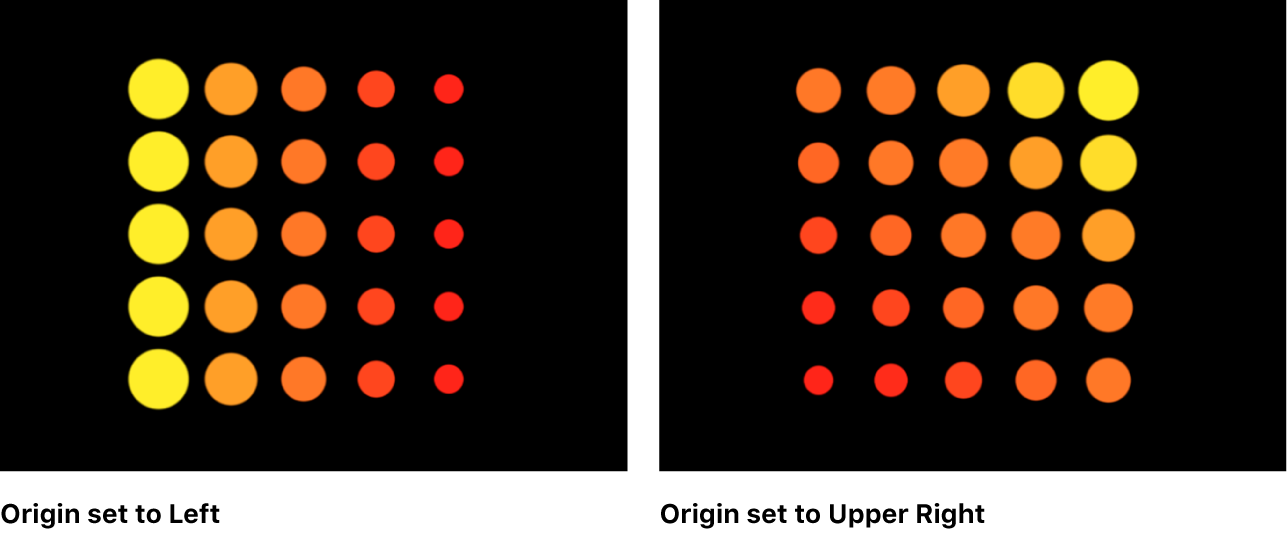
When Shape is set to Rectangle, Circle, Image, Box, or Sphere, and Arrangement is set to Tile Fill or Random Fill the Origin pop-up menu contains the following options:
Upper Left: Elements originate in the upper-left corner of the pattern and end in the lower-right corner.
Upper Right: Elements originate in the upper-right corner of the pattern and end in the lower-left corner.
Lower Left: Elements originate in the lower-left corner of the pattern and end in the upper-right corner.
Lower Right: Elements originate in the lower-right corner of the pattern and end in the upper-left corner.
Center: Elements originate in the center of the pattern and move outward. This is the default Origin option.
Left: Elements originate at the left side of the pattern and end at the right side.
Right: Elements originate at the right side of the pattern and end at the left side.
Top: Elements originate at the top of the pattern and end at the bottom.
Bottom: Elements originate at the bottom of the pattern and end at the top.
When Shape is set to Circle or Sphere, and Arrangement is set to Tile Fill or Random Fill, the Origin pop-up menu contains the following options:
Center: Elements originate in the center of the pattern and build outward. This is the default Origin option.
Edge: Elements originate along the edge of the pattern and build inward.
When Shape is set to Box, and Arrangement is set to Tile Fill or Random Fill, the Origin pop-up menu contains the following options:
Front Upper Left: Elements originate in the front upper-left corner of the pattern and end in the back lower right.
Front Upper Right: Elements originate in the front upper-right corner of the pattern and end in the back lower left.
Front Lower Left: Elements originate in the front lower-left corner of the pattern and end in the back upper right.
Front Lower Right: Elements originate in the front lower-right corner of the pattern and end in the back upper left.
Back Upper Left: Elements originate in the back upper-left corner of the pattern and end in the front lower right.
Back Upper Right: Elements originate in the back upper-right corner of the pattern and end in the front lower left.
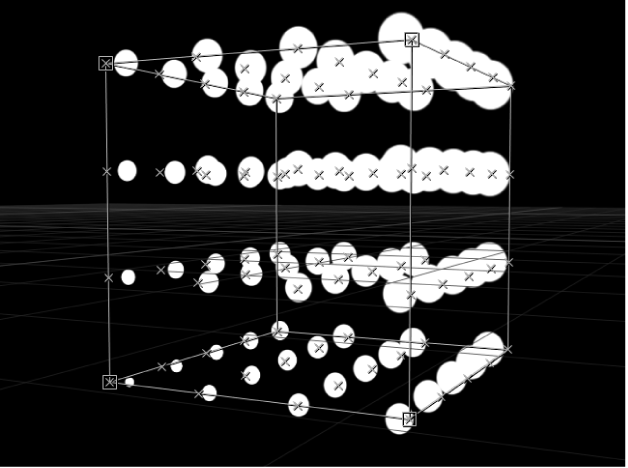
Back Lower Left: Elements originate in the back lower-left corner of the pattern and end in the front upper-right.
Back Lower Right: Elements originate in the back lower-right corner of the pattern and end in the front upper-left.
Left: Elements originate at the left side of the pattern and end at the right side. The pattern is identical on each row.
Right: Elements originate at the right side of the pattern and end at the left side. The pattern is identical on each row.
Top: Elements originate at the top of the pattern and end at the bottom. The pattern is identical on each rank.
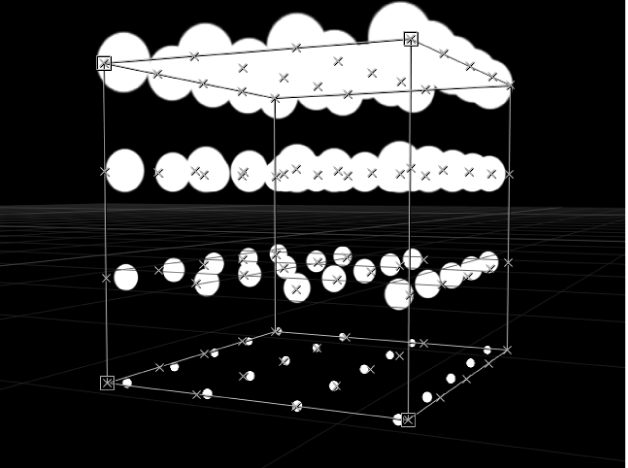
Bottom: Elements originate at the bottom of the pattern and end at the top. The pattern is identical on each rank.
Front: Elements originate at the front of the pattern and end at the back. The pattern is identical on each column.
Back: Elements originate at the back of the pattern and end at the front. The pattern is identical on each column.
Center: Elements originate in the center of the pattern and move outward. This is the default Origin option.
X Axis: Elements originate along the X axis of the pattern and move outward.
Y Axis: Elements originate along the Y axis of the pattern and move outward.
Z Axis: Elements originate along the Z axis of the pattern and move outward.
Note: The Origin pop-up menu also determines where the Sequence Replicator behavior starts its animation. For more information on the Sequence Replicator behavior, see Apply the Sequence Replicator behavior in Motion.
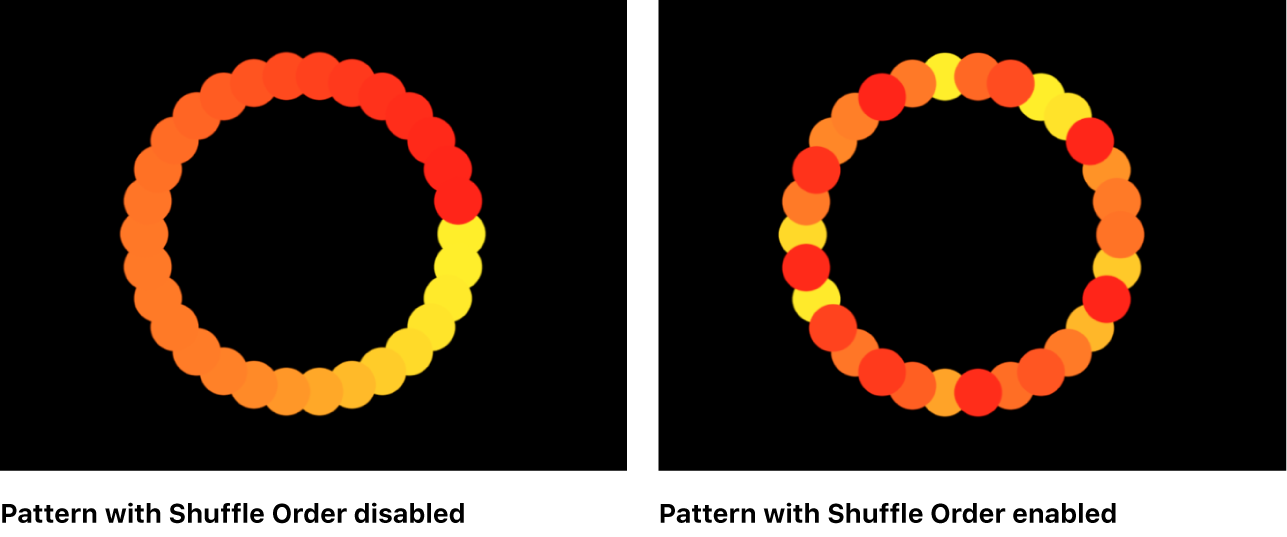
Shuffle Order: A checkbox that, when selected, rearranges the order in which the elements appear.
Replicate Seed: A random seed generator button and field (available when Shape is set to Rectangle, Circle, Image, Box, or Sphere, and Arrangement is set to Random Fill) to modify the Random Fill pattern. Click the button to right of the seed value set a new random seed number.
Although the result of the Random Fill option from the Arrangement pop-up menu seems random, it’s deterministic. This means that the random variation in the pattern is created based on the number shown. Unless this seed number is changed, a replicator with the same parameter settings and source object always appears the same. If you don’t like the current random fill, you can change the seed number by typing a new number or clicking Generate. This changes the random calculations performed for that pattern. This parameter is also used to randomize the Shuffle Order parameter.
3D: A checkbox that, when selected, enables the Box and Sphere options in the Shape pop-up menu.
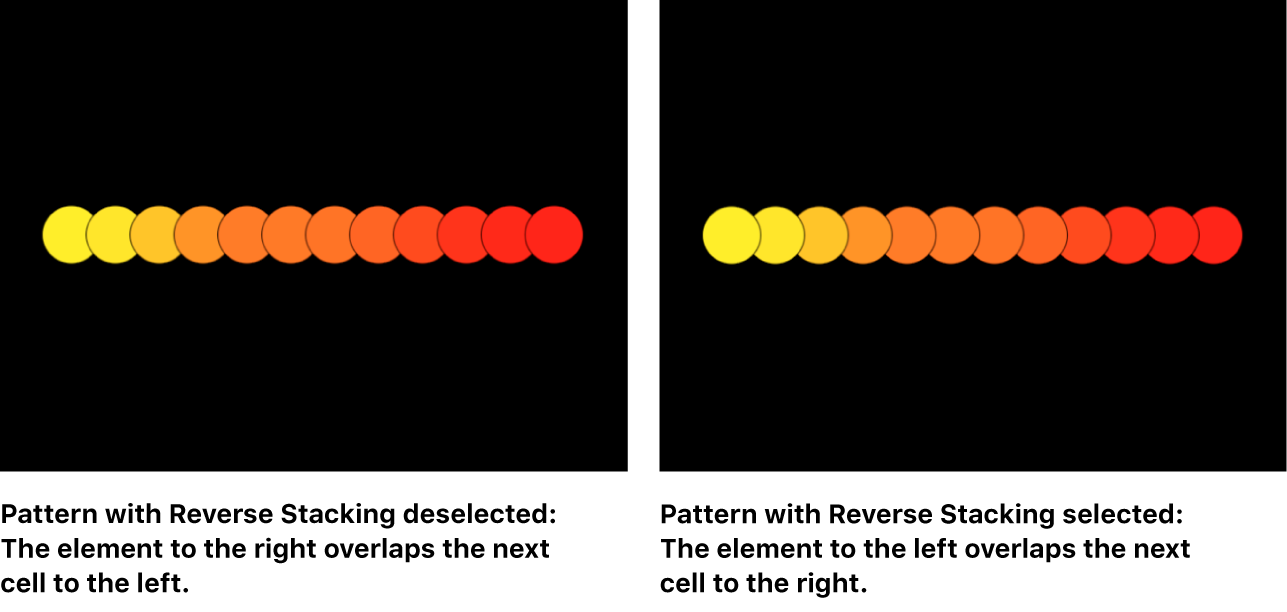
Reverse Stacking: A checkbox that, when selected, inverts the order in which elements are stacked. To see the effect of this parameter, elements must be overlapping.
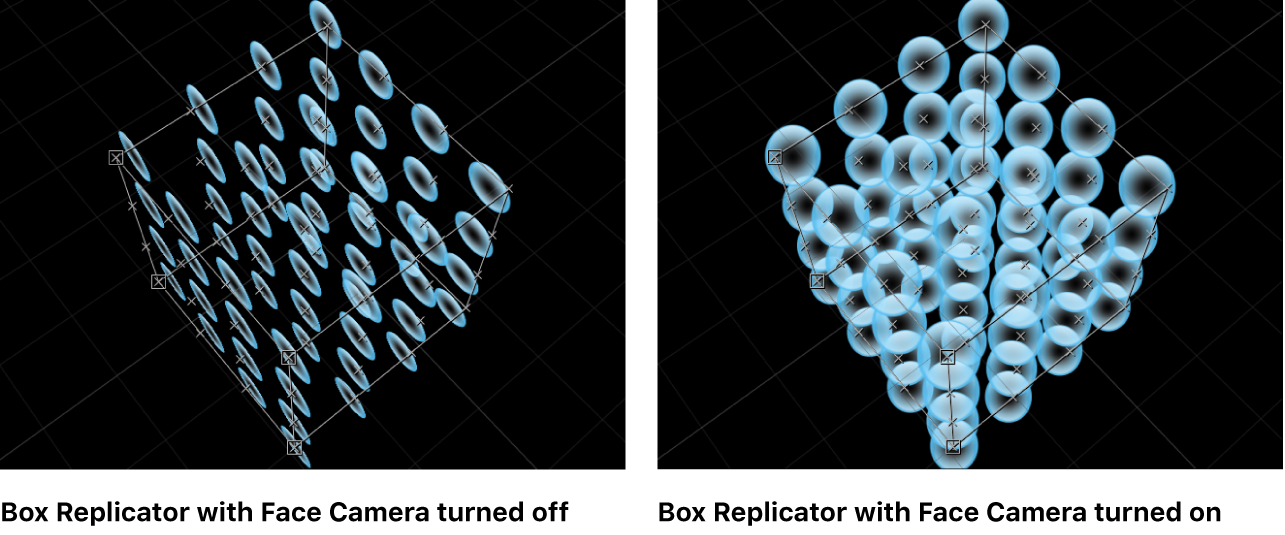
Face Camera: A checkbox (available when the 3D checkbox is selected) that forces pattern elements to face the camera when the camera or the replicator is rotated. When Face Camera is deselected, the elements face forward in the replicator pattern and appear flat (unless the source layer or pattern elements are rotated in 3D space). Because Motion does not support 3D objects (other than 3D text), this option is key to giving 2D layers the appearance of 3D as the camera is animated.
Note: Because replicator pattern elements are 2D (flat) objects (unless 3D text is used as the replicator source), the pattern elements are not visible when you use the orthogonal reference camera views, such as Left, Right, and Top (unless the source layer or pattern elements are rotated in 3D space). This is because orthogonal views are at right angles (perpendicular) to the elements. For more information on using cameras, see Intro to 3D cameras in Motion.
Download this guide: PDF