Logic Pro User Guide for iPad
- What’s new in Logic Pro 1.1
-
- What is Logic Pro?
- Working areas
- Work with function buttons
- Work with numeric values
-
- Intro to tracks
- Create tracks
- Create tracks using drag and drop
- Choose the default region type for a software instrument track
- Select tracks
- Duplicate tracks
- Reorder tracks
- Rename tracks
- Change track icons
- Change track colors
- Use the tuner on an audio track
- Show the output track in the Tracks area
- Delete tracks
- Edit track parameters
- Start a Logic Pro subscription
- How to get help
-
- Intro to recording
-
- Before recording software instruments
- Record software instruments
- Record additional software instrument takes
- Record to multiple software instrument tracks
- Record multiple MIDI devices to multiple tracks
- Record software instruments and audio simultaneously
- Merge software instrument recordings
- Spot erase software instrument recordings
- Replace software instrument recordings
- Capture your most recent MIDI performance
- Use the metronome
- Use the count-in
-
- Intro to arranging
-
- Intro to regions
- Select regions
- Cut, copy, and paste regions
- Move regions
- Remove gaps between regions
- Delay region playback
- Trim regions
- Loop regions
- Repeat regions
- Mute regions
- Split and join regions
- Stretch regions
- Separate a MIDI region by note pitch
- Bounce regions in place
- Change the gain of audio regions
- Create regions in the Tracks area
- Convert a MIDI region to a Drummer region or a pattern region
- Rename regions
- Change the color of regions
- Delete regions
- Create fades on audio regions
- Access mixing functions using the Fader
-
- Intro to Step Sequencer
- Use Step Sequencer with Drum Machine Designer
- Record Step Sequencer patterns live
- Step record Step Sequencer patterns
- Load and save patterns
- Modify pattern playback
- Edit steps
- Edit rows
- Edit Step Sequencer pattern, row, and step settings in the inspector
- Customize Step Sequencer
-
- Effect plug-ins overview
-
- Instrument plug-ins overview
-
- ES2 overview
- Interface overview
-
- Modulation overview
-
- Vector Envelope overview
- Use Vector Envelope points
- Use Vector Envelope solo and sustain points
- Set Vector Envelope segment times
- Vector Envelope XY pad controls
- Vector Envelope Actions menu
- Vector Envelope loop controls
- Vector Envelope release phase behavior
- Vector Envelope point transition shapes
- Use Vector Envelope time scaling
- Use the Mod Pad
- Modulation source reference
- Via modulation source reference
-
- Sample Alchemy overview
- Interface overview
- Add source material
- Save a preset
- Edit mode
- Play modes
- Source overview
- Synthesis modes
- Granular controls
- Additive effects
- Additive effect controls
- Spectral effect
- Spectral effect controls
- Filter module
- Low and highpass filter
- Comb PM filter
- Downsampler filter
- FM filter
- Envelope generators
- Mod Matrix
- Modulation routing
- Motion mode
- Trim mode
- More menu
- Sampler
- Copyright
EVOC 20 PS global parameters in Logic Pro for iPad
The global parameters determine the keyboard mode and number of voices used by EVOC 20 PS.
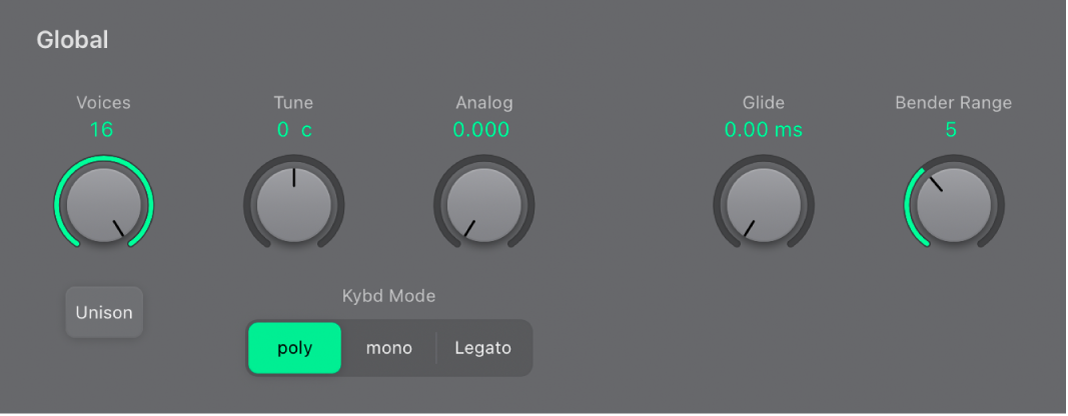
Global parameters
Voices knob and field: Set the maximum number of voices in the numeric field (only when Poly is turned on).
Unison button: Turn Unison mode on or off.
In Unison/Poly mode—where both the Unison and Poly buttons are active—each voice is doubled. This cuts polyphony in half (to a maximum of eight voices, shown in the Voices field). The doubled voices are detuned by the amount defined with the Analog knob.
In Unison/Mono mode—where both the Unison and Mono or Legato buttons are active—up to 16 voices can be stacked and played monophonically. The Voices field displays the number of stacked voices that are heard.
Important: Stacking voices in Unison/Mono mode increases the output volume. To avoid overloading the instrument channel strip output, set a low Level slider value and gradually increase it.
Tune knob and field: Set the overall tuning in cents. One hundred cents equals one semitone step.
Analog knob and field: Set the amount of random pitch detuning. Analog simulates the instability of analog circuitry found in vintage vocoders by randomly altering the pitch of each note. This behavior is much like that of polyphonic analog synthesizers.
Kybd Mode switch: Determine the keyboard mode.
Poly: When on, you can set the maximum number of voices with the Voices knob. (When Mono or Legato is on, only a single voice is heard.)
Mono: When on, Glide is always active and the envelopes are retriggered by every note played (multi trigger behavior).
Legato: When on, Glide is active only on tied notes. Envelopes are not retriggered when tied notes are played (single trigger behavior).
Glide knob and field: Determine the time it takes for the pitch to slide from one note to another—portamento.
Bender Range knob and field: Determine the pitch bend modulation range, in semitone steps.
Download this guide: PDF