Accounting reconciliation plays a fundamental role in ensuring that financial statements are reliable, detecting errors, preventing fraud and maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements. Businesses that prioritise effective reconciliation practices put themselves in a strong position to make informed decisions, mitigate risks and maintain the financial health necessary for long-term success.
According to a survey conducted by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE), financial statement fraud constituted 9% of all reported fraud cases in 2022. This highlights the significance of accurate accounting reconciliation in detecting and preventing fraudulent activities within an organisation. By reconciling financial records, such as bank statements, invoices and receipts, businesses can identify discrepancies and irregularities and protect themselves against potential fraud.
We'll cover best practices and strategies that organisations can use to streamline their reconciliation processes, minimise errors and establish a solid foundation for financial management.
What's in this article?
- What is reconciliation in accounting?
- Types of accounting reconciliation
- Why accounting reconciliation matters for businesses
- Accounting reconciliation best practices
- Accounting reconciliation with Stripe
What is reconciliation in accounting?
In accounting, reconciliation refers to the process of comparing two sets of records or financial information, such as bank statements, general ledger accounts or other relevant records, to ensure their accuracy and consistency.
The primary objective of reconciliation is to identify and resolve any discrepancies between the two sets of records. This helps preserve the integrity of financial statements and identifies errors or fraudulent activities.
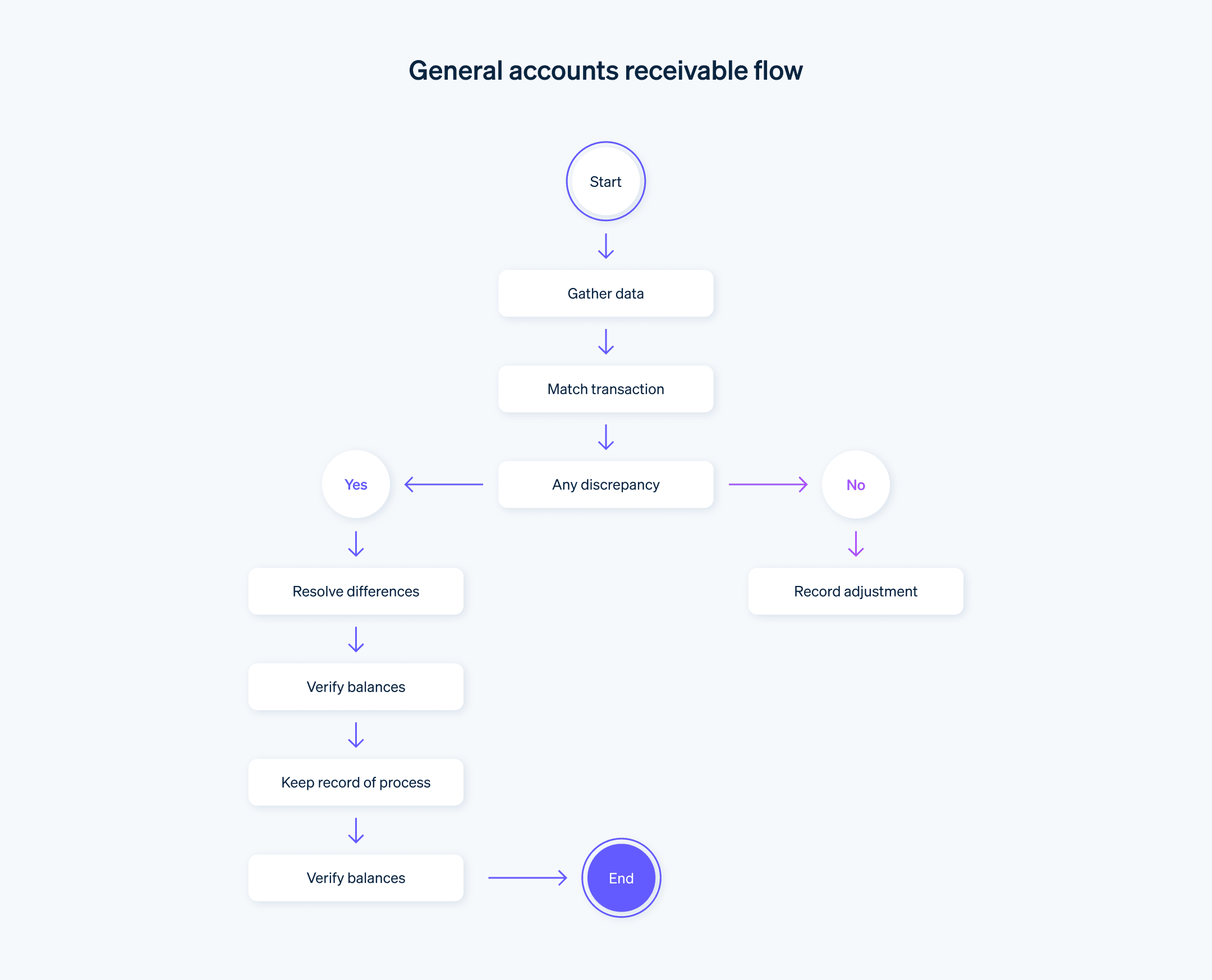
Types of accounting reconciliation
Accounting reconciliation involves comparing and verifying financial transactions and balances to identify and resolve discrepancies. Here are the different types of accounting reconciliation:
Bank reconciliation
Comparing the transactions and balances in a business's bank statement with the entries in the cash book or general ledgerAccounts receivable reconciliation
Verifying the accuracy and completeness of accounts receivable balances by comparing them with supporting documentation, such as customer invoices and payment receiptsAccounts payable reconciliation
Verifying the accuracy and completeness of accounts payable balances by comparing them with supplier invoices and payment recordsIntercompany reconciliation
Reconciling intercompany transactions and balances between subsidiaries or divisions to protect accuracy and eliminate errorsInventory reconciliation
Comparing physical inventory counts with recorded inventory balances to identify discrepancies and address issues such as theft or recording errorsGeneral ledger reconciliation
Reconciling various general ledger accounts to make sure that the recorded transactions and balances are complete and accurateFixed assets reconciliation
Verifying fixed asset records by comparing them with purchase invoices, depreciation schedules and disposal recordsTax reconciliation
Comparing tax records, such as sales tax or income tax, with corresponding financial records to make sure that the reporting of tax liabilities is accurateCredit card and debit card reconciliation
Matching transactions recorded in credit card or debit card statements with financial records to ensure accuracy and completenessDigital wallet reconciliation
Verifying digital wallet transactions with the business's financial recordsGlobal currencies reconciliation
Ensuring the accuracy of foreign currency transactions by comparing them with exchange rates and financial recordsReal-time automatic payment reconciliation
Automating payment reconciliation processes in real time to match and reconcile payments accurately and efficiently
These different types of reconciliation are important for maintaining accurate financial records, detecting errors and fraud, and ensuring the reliability of the accounting system. They give organisations a clear and accurate picture of their financial position, which enables them to make informed business decisions.
Why accounting reconciliation matters for businesses
Accounting reconciliation is essential for businesses. Here's why:
Accurate financial records
By comparing different sets of data, reconciliation ensures that financial records are accurate and reliable. When a business processes or records financial transactions, discrepancies, errors and omissions can occur, and reconciliation helps to identify these discrepancies and correct them. This ensures that financial statements and reports present an accurate and fair view of the business's financial position.Fraud detection
Reconciliation is a critical internal control mechanism to detect fraudulent activities. By comparing records, such as bank statements, invoices and payment receipts, businesses can identify discrepancies or irregularities that may indicate fraudulent transactions, thereby protecting the business's assets and financial interests.Decision-making
Reconciliation ensures that the data used for decision-making is reliable and complete. By reconciling different accounts and financial records, businesses gain confidence in the precision of their information, which allows them to make strategic decisions based on sound financial insights.Compliance and regulatory requirements
Reconciliation helps businesses meet compliance and regulatory obligations. For instance, through accurate bank reconciliation, a business can ensure that it complies with auditing standards and creates financial statements that adhere to regulatory guidelines. Failure to reconcile accounts properly can lead to non-compliance, penalties or legal consequences.Risk management
Reconciliation helps manage financial risks by identifying errors, discrepancies or irregularities promptly. By reconciling accounts, businesses can detect potential risks such as cash flow issues, inventory discrepancies and incorrect tax calculations. Identifying risks early allows businesses to take appropriate action and safeguard their financial stability.Building stakeholder trust
Reconciliation means that financial statements are prepared with integrity and transparency, which builds trust and credibility among stakeholders such as investors, lenders and shareholders. This trust strengthens the business's reputation and increases confidence in its financial health.
Accounting reconciliation best practices
By following these accounting reconciliation best practices, businesses can enhance the accuracy of financial records, strengthen internal controls, detect and prevent fraud, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements. These practices contribute to reliable financial reporting, which is integral to almost every aspect of operating and growing a business.
Accounting reconciliation best practices for businesses include:
Regular reconciliation
Conduct reconciliations on a regular basis, ideally monthly or as frequently as necessary based on the volume of transactions. Prompt and consistent reconciliation means that a business can identify and resolve discrepancies quickly, before they cause problems down the line.Documentation and record-keeping
Maintain detailed documentation of the reconciliation process, including bank statements, invoices, receipts and other relevant records. Proper documentation of the reconciliation process facilitates future audits or reviews, and helps to identify and resolve discrepancies.Segregation of duties
Implement segregation of duties to make sure that different individuals are responsible for different aspects of the process, such as recording, reconciling and approving financial transactions. This separation guarantees that multiple sets of eyes review the financial information at different points in the reconciliation process, helping prevent errors and fraud.Clear reconciliation procedures
Establish standardised reconciliation procedures, clearly defining appropriate steps, roles and responsibilities of individuals, and specific deadlines. Clear procedures promote consistency, minimise errors, and make sure that the reconciliation process is conducted in an organised manner.Reconciliation automation
When possible, use accounting software or reconciliation tools to automate the reconciliation process. Automation reduces manual errors, improves efficiency and provides a systematic framework for reconciling accounts and records.Comparison and investigation
Conduct a thorough comparison of financial records, identifying any discrepancies. Investigate and resolve these discrepancies promptly by tracing the root causes, correcting errors and adjusting the financial records accordingly. Proper investigation helps to prevent recurring errors and ensure that financial information is accurate.Ongoing communication
Foster open communication among relevant departments and individuals in the reconciliation process. Regular communication helps to resolve issues, clarify doubts and share information effectively. A comprehensive and accurate reconciliation process depends on collaboration and coordination among different stakeholders.Reconciliation review and approval
Implement a review and approval process to ensure an independent review of reconciled records. This process should include reviewing the accuracy and appropriateness of the reconciled balances and investigating any significant discrepancies. Approval by a designated authority adds an extra layer of assurance to the reconciliation process.Continuous improvement
Evaluate and enhance the reconciliation process regularly by identifying areas for improvement. Analyse patterns of discrepancies, identify potential weaknesses and implement appropriate measures to prevent future errors. By refining the reconciliation process on an ongoing basis, businesses can maximise accuracy, efficiency and overall financial control.
Accounting reconciliation with Stripe
Stripe offers a powerful reconciliation solution that streamlines the process for businesses. Stripe's reconciliation solution automates the reconciliation process for businesses and offers a comprehensive picture of your money movement.
Stripe's reconciliation process involves comparing your business's internal records, such as invoices, with external records such as settlement files, payout files and bank statements. Stripe's automated system handles this comparison, enabling you to capture revenue accurately and reconcile your internal accounting systems with Stripe-processed charges and refunds at a transaction level.
The Stripe reconciliation solution provides several benefits for businesses:
It allows you to track your cash on a daily basis, so your financial records stay aligned with funds received. By identifying any gaps in fund flows or data discrepancies, you can address leaks quickly and minimise financial losses.
Stripe reconciliation offers visibility into the complete life cycle of each transaction. You can easily trace and monitor the flow of funds, ensuring that every transaction is accurately recorded and accounted for. This level of transparency helps protect your business by identifying any potential errors or irregularities.
Stripe reconciliation is especially beneficial for businesses with high transaction volumes. If your business processes thousands of transactions each month, the automation and scalability of Stripe's reconciliation solution can streamline your financial operations.
If your business deals with complex transaction scenarios, such as long transaction life cycles spread across multiple periods, or customers using multiple payment methods in a single transaction, Stripe's reconciliation solution can handle these complexities effectively. It provides the necessary flexibility and accuracy to reconcile diverse transaction types and ensure accurate financial reporting.
Stripe's reconciliation solution automates and simplifies the process of comparing internal records with external records, enabling businesses to accurately capture revenue, track cash flow, identify discrepancies and implement robust financial controls. Whether you have high transaction volumes or complex transaction scenarios, Stripe's reconciliation solution offers scalable and reliable support for your financial operations. To learn more or get started, go here.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent lawyer or accountant licensed to practise in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.