Roles of ephrinB ligands and EphB receptors in cardiovascular development: demarcation of arterial/venous domains, vascular morphogenesis, and sprouting angiogenesis
- PMID: 9990854
- PMCID: PMC316426
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.13.3.295
Roles of ephrinB ligands and EphB receptors in cardiovascular development: demarcation of arterial/venous domains, vascular morphogenesis, and sprouting angiogenesis
Abstract
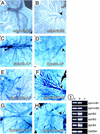
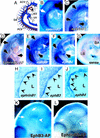
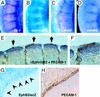
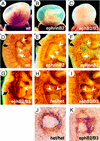
Eph receptor tyrosine kinases and their cell-surface-bound ligands, the ephrins, regulate axon guidance and bundling in the developing brain, control cell migration and adhesion, and help patterning the embryo. Here we report that two ephrinB ligands and three EphB receptors are expressed in and regulate the formation of the vascular network. Mice lacking ephrinB2 and a proportion of double mutants deficient in EphB2 and EphB3 receptor signaling die in utero before embryonic day 11.5 (E11.5) because of defects in the remodeling of the embryonic vascular system. Our phenotypic analysis suggests complex interactions and multiple functions of Eph receptors and ephrins in the embryonic vasculature. Interaction between ephrinB2 on arteries and its EphB receptors on veins suggests a role in defining boundaries between arterial and venous domains. Expression of ephrinB1 by arterial and venous endothelial cells and EphB3 by veins and some arteries indicates that endothelial cell-to-cell interactions between ephrins and Eph receptors are not restricted to the border between arteries and veins. Furthermore, expression of ephrinB2 and EphB2 in mesenchyme adjacent to vessels and vascular defects in ephB2/ephB3 double mutants indicate a requirement for ephrin-Eph signaling between endothelial cells and surrounding mesenchymal cells. Finally, ephrinB ligands induce capillary sprouting in vitro with a similar efficiency as angiopoietin-1 (Ang1) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), demonstrating a stimulatory role of ephrins in the remodeling of the developing vascular system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EphB ligand, ephrinB2, suppresses the VEGF- and angiopoietin 1-induced Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in venous endothelial cells.FASEB J. 2002 Jul;16(9):1126-8. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0805fje. Epub 2002 May 21. FASEB J. 2002. PMID: 12039842
-
Symmetrical mutant phenotypes of the receptor EphB4 and its specific transmembrane ligand ephrin-B2 in cardiovascular development.Mol Cell. 1999 Sep;4(3):403-14. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80342-1. Mol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10518221
-
The receptor tyrosine kinase EphB4 and ephrin-B ligands restrict angiogenic growth of embryonic veins in Xenopus laevis.Development. 2000 Jan;127(2):269-78. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.2.269. Development. 2000. PMID: 10603345
-
Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis as mechanisms of vascular network formation, growth and remodeling.J Neurooncol. 2000 Oct-Nov;50(1-2):1-15. doi: 10.1023/a:1006493130855. J Neurooncol. 2000. PMID: 11245270 Review.
-
Roles of Eph receptors and ephrins in segmental patterning.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000 Jul 29;355(1399):993-1002. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2000.0635. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000. PMID: 11128993 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inducible deletion of endothelial cell Efnb2 delays capillary regeneration and attenuates myofibre reinnervation following myotoxin injury in mice.J Physiol. 2024 Oct;602(19):4907-4927. doi: 10.1113/JP285402. Epub 2024 Aug 28. J Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39196901
-
Recent advances of the Ephrin and Eph family in cardiovascular development and pathologies.iScience. 2024 Jul 19;27(8):110556. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110556. eCollection 2024 Aug 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39188984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methylome analysis of endothelial cells suggests new insights on sporadic brain arteriovenous malformation.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 30;10(15):e35126. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35126. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170526 Free PMC article.
-
PDX1+ cell budding morphogenesis in a stem cell-derived islet spheroid system.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 13;15(1):5894. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50109-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39003281 Free PMC article.
-
Ephs in cancer progression: complexity and context-dependent nature in signaling, angiogenesis and immunity.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 May 29;22(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01580-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38811954 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bouillet P, Oulad-Abdelghani M, Vicaire S, Garnier J-M, Schuhbaur B, Dolle P, Chambon P. Efficient cloning of cDNAs of retinoic acid-responsive genes in P19 embryonal carcinoma cells and characterization of a novel mouse gene, Stra1 (mouse Lerk2/Eplg2) Dev Biol. 1995;170:420–433. - PubMed
-
- Brambilla R, Klein R. Telling axons where to grow: A role for Eph receptor tyrosine kinases in guidance. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1995;6:487–495. - PubMed
-
- Brennan C, Monschau B, Lindberg R, Guthrie B, Drescher U, Bonhoeffer F, Holder N. Two Eph receptor tyrosine kinase ligands control axon growth and may be involved in the creation of the retinotectal map in the zebrafish. Development. 1997;124:655–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
