Mutation of Pten/Mmac1 in mice causes neoplasia in multiple organ systems
- PMID: 9990064
- PMCID: PMC15517
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.4.1563
Mutation of Pten/Mmac1 in mice causes neoplasia in multiple organ systems
Abstract
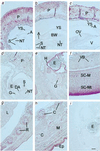
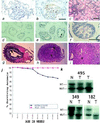
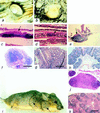
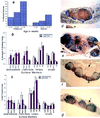
Pten/Mmac1+/- heterozygous mice exhibited neoplasms in multiple organs including the endometrium, liver, prostate, gastrointestinal tract, thyroid, and thymus. Loss of the wild-type allele was detected in neoplasms of the thymus and liver. Surprisingly, tumors of the gastrointestinal epithelium developed in association with gut lymphoid tissue. Tumors of the endometrium, thyroid, prostate, and liver were not associated with lymphoid tissue and appeared to be highly mitotic. In addition, these mice have nonneoplastic hyperplasia of lymph nodes that was caused by an inherited defect in apoptosis detected in B cells and macrophages. Examination of peripheral lymphoid tissue including lymphoid aggregates associated with polyps revealed that the normal organization of B and T cells was disrupted in heterozygous animals. Taken together, these data suggest that PTEN is a regulator of apoptosis and proliferation that behaves as a "landscaper" tumor suppressor in the gut and a "gatekeeper" tumor suppressor in other organs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High incidence of breast and endometrial neoplasia resembling human Cowden syndrome in pten+/- mice.Cancer Res. 2000 Jul 1;60(13):3605-11. Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10910075
-
Pten is essential for embryonic development and tumour suppression.Nat Genet. 1998 Aug;19(4):348-55. doi: 10.1038/1235. Nat Genet. 1998. PMID: 9697695
-
High cancer susceptibility and embryonic lethality associated with mutation of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in mice.Curr Biol. 1998 Oct 22;8(21):1169-78. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(07)00488-5. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9799734
-
[Cowden disease].Nihon Rinsho. 2000 Jul;58(7):1479-83. Nihon Rinsho. 2000. PMID: 10921327 Review. Japanese.
-
The role of PTEN, a phosphatase gene, in inherited and sporadic nonmedullary thyroid tumors.Recent Prog Horm Res. 1999;54:441-52; discussion 453. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1999. PMID: 10548886 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced serotonin reuptake transporter (SERT) function causes insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis independent of food intake.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32511. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032511. Epub 2012 Mar 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22412882 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically engineered mouse models of PI3K signaling in breast cancer.Mol Oncol. 2013 Apr;7(2):146-64. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Mol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23478237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical Remodeling of Human Prostate Cancer through the PTEN/AKT Pathway.Adv Urol. 2012;2012:419348. doi: 10.1155/2012/419348. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Adv Urol. 2012. PMID: 22454635 Free PMC article.
-
From genomics to functions: preclinical mouse models for understanding oncogenic pathways in prostate cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2019 Oct 1;9(10):2079-2102. eCollection 2019. Am J Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31720076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromosome missegregation causes colon cancer by APC loss of heterozygosity.Cell Cycle. 2010 May;9(9):1711-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.9.11314. Epub 2010 May 27. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20404532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podsypanina K, Bose S, Wang S I, Puc J, Miliaresis C, Rodgers L, McCombie R, et al. Science. 1997;275:1943–1947. - PubMed
-
- Steck P A, Pershouse M A, Jasser S A, Yung W K, Lin H, Ligon A H, Langford L A, Baumgard M L, Hattier T, Davis T, et al. Nat Genet. 1997;15:356–362. - PubMed
-
- Li D M, Sun H. Cancer Res. 1997;57:2124–2129. - PubMed
-
- Wang S I, Puc J, Li J, Bruce J N, Cairns P, Sidransky D, Parsons R. Cancer Res. 1997;57:4183–4186. - PubMed
-
- Wang S I, Parsons R, Ittmann M. Clin Cancer Res. 1998;4:811–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

