Endotoxin-tolerant mice have mutations in Toll-like receptor 4 (Tlr4)
- PMID: 9989976
- PMCID: PMC2192941
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.4.615
Endotoxin-tolerant mice have mutations in Toll-like receptor 4 (Tlr4)
Erratum in
- J Exp Med 1999 May 3;189(9):following 1518
Abstract
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) provokes a vigorous, generalized proinflammatory state in the infected host. Genetic regulation of this response has been localized to the Lps locus on mouse chromosome 4, through study of the C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr inbred strains. Both C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice are homozygous for a mutant Lps allele (Lpsd/d) that confers hyporesponsiveness to LPS challenge, and therefore exhibit natural tolerance to its lethal effects. Genetic and physical mapping of 1,345 backcross progeny segregating this mutant phenotype confined Lps to a 0.9-cM interval spanning 1.7 Mb. Three transcription units were identified within the candidate interval, including Toll-like receptor 4 (Tlr4), part of a protein family with members that have been implicated in LPS-induced cell signaling. C3H/HeJ mice have a point mutation within the coding region of the Tlr4 gene, resulting in a nonconservative substitution of a highly conserved proline by histidine at codon 712, whereas C57BL/ 10ScCr mice exhibit a deletion of Tlr4. Identification of distinct mutations involving the same gene at the Lps locus in two different hyporesponsive inbred mouse strains strongly supports the hypothesis that altered Tlr4 function is responsible for endotoxin tolerance.
Figures
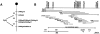

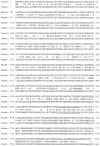
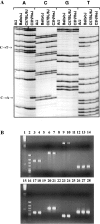

Comment in
-
Toll, a new piece in the puzzle of innate immunity.J Exp Med. 1999 Feb 15;189(4):605-9. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.4.605. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 9989974 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene.Science. 1998 Dec 11;282(5396):2085-8. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5396.2085. Science. 1998. PMID: 9851930
-
Cutting edge: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to lipopolysaccharide: evidence for TLR4 as the Lps gene product.J Immunol. 1999 Apr 1;162(7):3749-52. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10201887
-
Limits of a deletion spanning Tlr4 in C57BL/10ScCr mice.J Endotoxin Res. 2000;6(1):51-6. doi: 10.1177/09680519000060010701. J Endotoxin Res. 2000. PMID: 11061032
-
Positional cloning of Lps, and the general role of toll-like receptors in the innate immune response.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2000 Jun;11(2):143-52. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2000. PMID: 10903793 Review.
-
The Lps locus: genetic regulation of host responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharide.Inflamm Res. 1999 Dec;48(12):613-20. doi: 10.1007/s000110050511. Inflamm Res. 1999. PMID: 10669111 Review.
Cited by
-
HLA-A2.1-restricted ECM1-derived epitope LA through DC cross-activation priming CD8+ T and NK cells: a novel therapeutic tumour vaccine.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Apr 28;14(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01081-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33910591 Free PMC article.
-
Podocyte apoptosis is prevented by blocking the Toll-like receptor pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2015 May 7;6(5):e1752. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.125. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 25950482 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide detection by the innate immune system may be an uncommon defence strategy used in nature.Open Biol. 2022 Oct;12(10):220146. doi: 10.1098/rsob.220146. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Open Biol. 2022. PMID: 36196535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum soluble toll-like receptor 4 and risk for clinical severity in COVID-19 patients.Pneumonia (Nathan). 2024 Jan 5;16(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s41479-023-00121-9. Pneumonia (Nathan). 2024. PMID: 38178206 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TLR4 rs4986790A>G and rs4986791C>T Polymorphisms in the Risk of Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015;2015:141070. doi: 10.1155/2015/141070. Epub 2015 May 18. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015. PMID: 26089865 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Increases in national hospital discharge survey rates for septicemia—United States, . –1987. 1990. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1979;39:31–34. - PubMed
-
- Glauser MP, Heumann D, Baumgartner JD, Cohen J. Pathogenesis and potential strategies for prevention and treatment of septic shock: an update. Clin Infect Dis. 1994;18:S205–S216. - PubMed
-
- Burrell R. Human responses to bacterial endotoxin. Circ Shock. 1994;43:137–153. - PubMed
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RMH, Sibbald WJ. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Chest. 1992;101:1644–1655. - PubMed
-
- Sultzer BM. Genetic control of leukocyte responses to endotoxin. Nature. 1968;219:1253–1254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

