Mice lacking expression of secondary lymphoid organ chemokine have defects in lymphocyte homing and dendritic cell localization
- PMID: 9927507
- PMCID: PMC2192914
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.3.451
Mice lacking expression of secondary lymphoid organ chemokine have defects in lymphocyte homing and dendritic cell localization
Abstract
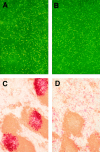
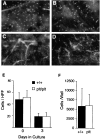
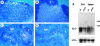
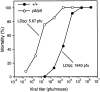
Secondary lymphoid organ chemokine (SLC) is expressed in high endothelial venules and in T cell zones of spleen and lymph nodes (LNs) and strongly attracts naive T cells. In mice homozygous for the paucity of lymph node T cell (plt) mutation, naive T cells fail to home to LNs or the lymphoid regions of spleen. Here we demonstrate that expression of SLC is undetectable in plt mice. In addition to the defect in T cell homing, we demonstrate that dendritic cells (DCs) fail to accumulate in spleen and LN T cell zones of plt mice. DC migration to LNs after contact sensitization is also substantially reduced. The physiologic significance of these abnormalities in plt mice is indicated by a markedly increased sensitivity to infection with murine hepatitis virus. The plt mutation maps to the SLC locus; however, the sequence of SLC introns and exons in plt mice is normal. These findings suggest that the abnormalities in plt mice are due to a genetic defect in the expression of SLC and that SLC mediates the entry of naive T cells and antigen-stimulated DCs into the T cell zones of secondary lymphoid organs.
Figures
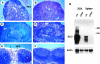
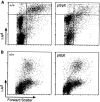
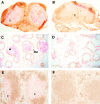
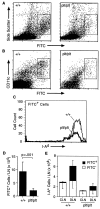
Comment in
-
Chemokines and the homing of dendritic cells to the T cell areas of lymphoid organs.J Exp Med. 1999 Feb 1;189(3):447-50. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.3.447. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 9927506 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Gene duplications at the chemokine locus on mouse chromosome 4: multiple strain-specific haplotypes and the deletion of secondary lymphoid-organ chemokine and EBI-1 ligand chemokine genes in the plt mutation.J Immunol. 2001 Jan 1;166(1):361-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.1.361. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11123313
-
The chemokine SLC is expressed in T cell areas of lymph nodes and mucosal lymphoid tissues and attracts activated T cells via CCR7.Eur J Immunol. 1998 Jun;28(6):2025-34. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199806)28:06<2025::AID-IMMU2025>3.0.CO;2-C. Eur J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9645384
-
Mice lacking expression of the chemokines CCL21-ser and CCL19 (plt mice) demonstrate delayed but enhanced T cell immune responses.J Exp Med. 2001 Jan 15;193(2):207-18. doi: 10.1084/jem.193.2.207. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11148224 Free PMC article.
-
Leukocyte migration: scent of the T zone.Curr Biol. 2000 Jan 13;10(1):R30-3. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)00253-5. Curr Biol. 2000. PMID: 10660291 Review.
-
A myriad of functions and complex regulation of the CCR7/CCL19/CCL21 chemokine axis in the adaptive immune system.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Jun;24(3):269-83. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.03.001. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 23587803 Review.
Cited by
-
PSGL-1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibition for CD4+ T Cell Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 23;12:636238. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636238. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33708224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific remodeling of splenic architecture by cytomegalovirus.PLoS Pathog. 2006 Mar;2(3):e16. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020016. Epub 2006 Mar 3. PLoS Pathog. 2006. PMID: 16518465 Free PMC article.
-
The secretory IFN-gamma response of single CD4 memory cells after activation on different antigen presenting cell types.Clin Immunol. 2007 Sep;124(3):267-76. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2007.05.012. Epub 2007 Jul 13. Clin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17632036 Free PMC article.
-
Aberration of CCR7 CD8 memory T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: an inducer of T helper type 2 bias of CD4 T cells.Immunology. 2004 Jun;112(2):274-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01862.x. Immunology. 2004. PMID: 15147571 Free PMC article.
-
Role of lymphatic vessels in tumor immunity: passive conduits or active participants?J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010 Sep;15(3):341-52. doi: 10.1007/s10911-010-9193-x. Epub 2010 Sep 11. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010. PMID: 20835756 Review.
References
-
- Gretz JE, Kaldjian EP, Anderson AO, Shaw S. Sophisticated strategies for information encounter in the lymph node: the reticular network as a conduit of soluble information and a highway for cell traffic. J Immunol. 1996;157:495–499. - PubMed
-
- Baggiolini M, Dewald B, Moser B. Human chemokines: an update. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:675–705. - PubMed
-
- Baggiolini M. Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature. 1998;392:565–568. - PubMed
-
- Yoshie O, Imai T, Nomiyama H. Novel lymphocyte-specific CC chemokines and their receptors. J Leukocyte Biol. 1997;62:634–644. - PubMed
-
- Goodnow CC, Cyster JG. Lymphocyte homing: the scent of a follicle. Curr Biol. 1997;7:R219–R222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

