The down-regulation of Mt4-like genes by phosphate fertilization occurs systemically and involves phosphate translocation to the shoots
- PMID: 9880366
- PMCID: PMC32226
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.119.1.241
The down-regulation of Mt4-like genes by phosphate fertilization occurs systemically and involves phosphate translocation to the shoots
Abstract
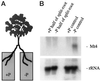
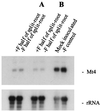
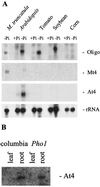
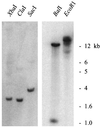
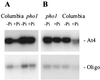
Mt4 is a cDNA representing a phosphate-starvation-inducible gene from Medicago truncatula that is down-regulated in roots in response to inorganic phosphate (Pi) fertilization and colonization by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Split-root experiments revealed that the expression of the Mt4 gene in M. truncatula roots is down-regulated systemically by both Pi fertilization and colonization by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. A comparison of Pi levels in these tissues suggested that this systemic down-regulation is not caused by Pi accumulation. Using a 30-bp region of the Mt4 gene as a probe, Pi-starvation-inducible Mt4-like genes were detected in Arabidopsis and soybean (Glycine max L.), but not in corn (Zea mays L.). Analysis of the expression of the Mt4-like Arabidopsis gene, At4, in wild-type Arabidopsis and pho1, a mutant unable to load Pi into the xylem, suggests that Pi must first be translocated to the shoot for down-regulation to occur. The data from the pho1 and split-root studies are consistent with the presence of a translocatable shoot factor responsible for mediating the systemic down-regulation of Mt4-like genes in roots.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel gene whose expression in Medicago truncatula roots is suppressed in response to colonization by vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal (VAM) fungi and to phosphate nutrition.Plant Mol Biol. 1997 May;34(2):199-208. doi: 10.1023/a:1005841119665. Plant Mol Biol. 1997. PMID: 9207836
-
Characterization of the Mt4 gene from Medicago truncatula.Gene. 1998 Aug 17;216(1):47-53. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(98)00326-6. Gene. 1998. PMID: 9714729
-
Influence of cytokinins on the expression of phosphate starvation responsive genes in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2000 Dec;24(5):559-67. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00893.x. Plant J. 2000. PMID: 11123795
-
Cloning and characterization of two phosphate transporters from Medicago truncatula roots: regulation in response to phosphate and to colonization by arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1998 Jan;11(1):14-22. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.1998.11.1.14. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1998. PMID: 9425684
-
Members of the PHO1 gene family show limited functional redundancy in phosphate transfer to the shoot, and are regulated by phosphate deficiency via distinct pathways.Plant J. 2007 Jun;50(6):982-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03108.x. Epub 2007 Apr 25. Plant J. 2007. PMID: 17461783
Cited by
-
HPS4/SABRE regulates plant responses to phosphate starvation through antagonistic interaction with ethylene signalling.J Exp Bot. 2012 Jul;63(12):4527-38. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers131. Epub 2012 May 21. J Exp Bot. 2012. PMID: 22615140 Free PMC article.
-
Local and distal effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization on direct pathway Pi uptake and root growth in Medicago truncatula.J Exp Bot. 2015 Jul;66(13):4061-73. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv202. Epub 2015 May 4. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 25944927 Free PMC article.
-
Histone acetyltransferase GCN5-mediated regulation of long non-coding RNA At4 contributes to phosphate starvation response in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2019 Nov 18;70(21):6337-6348. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz359. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 31401648 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of the Arabidopsis leaf transcriptome reveals interaction of phosphate and sugar metabolism.Plant Physiol. 2007 Jan;143(1):156-71. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.090167. Epub 2006 Nov 3. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17085508 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and analysis of Arabidopsis expressed sequence tags characteristic of non-coding RNAs.Plant Physiol. 2001 Nov;127(3):765-76. Plant Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11706161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ames BN. Assay of inorganic phosphate, total phosphate and phosphatases. Methods Enzymol. 1966;8:115–118.
-
- Arnon DI, Hoagland DR. Crop production in artificial culture solutions and in soils with special reference to factors influencing yields and absorption of inorganic nutrients. Soil Sci. 1940;50:463–483.
-
- Bariola PA, Howard CJ, Taylor CB, Verburg MT, Jaglan VD, Green PJ. The Arabidopsis ribonuclease gene RNS1 is tightly controlled in response to phosphate limitation. Plant J. 1994;6:673–685. - PubMed
-
- Bieleske RL. Phosphate pools, phosphate transport and phosphate availability. Annu Rev Plant Physiol. 1973;24:225–252.
-
- Burleigh SH, Harrison MJ. A novel gene whose expression in Medicago truncatula roots is suppressed in response to colonization by vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal (VAM) fungi and to phosphate nutrition. Plant Mol Biol. 1997;34:199–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

