Cooperative inhibition of T-cell antigen receptor signaling by a complex between a kinase and a phosphatase
- PMID: 9874568
- PMCID: PMC1887684
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.1.111
Cooperative inhibition of T-cell antigen receptor signaling by a complex between a kinase and a phosphatase
Abstract
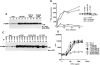
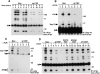
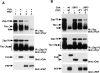
Antigen receptor-triggered T-cell activation is mediated by the sequential action of the Src and Syk/Zap-70 families of protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs). Previously, we reported that another PTK termed p50(csk) was a potent negative regulator of T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling because of its ability to inactivate Src-related kinases. This inhibitory effect required the catalytic activity of Csk, as well as its Src homology (SH)3 and SH2 domains. Subsequent studies uncovered that, via its SH3 domain, p50(csk) was associated with PEP, a proline-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) of unknown function expressed in hemopoietic cells. Herein, we have attempted to identify the role of the Csk-PEP complex in T lymphocytes. The results of our experiments showed that, like Csk, PEP was a strong repressor of TCR signaling. This property was dependent on the phosphatase activity of PEP, as well as on the sequence mediating its binding to p50(csk). Through reconstitution experiments in Cos-1 cells, evidence was obtained that Csk and PEP act synergistically to inhibit protein tyrosine phosphorylation by Src-related kinases, and that this effect requires their association. Finally, experiments with a substrate-trapping mutant of PEP suggested that PEP functions by dephosphorylating and inactivating the PTKs responsible for T-cell activation. In addition to giving novel insights into the mechanisms involved in the negative regulation of T-cell activation, these findings indicate that the association of an inhibitory PTK with a PTP constitutes a more efficient means of inhibiting signal transduction by Src family kinases in vivo.
Figures
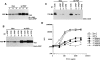
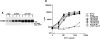
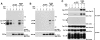

Similar articles
-
SH2 domain-mediated interaction of inhibitory protein tyrosine kinase Csk with protein tyrosine phosphatase-HSCF.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Feb;21(4):1077-88. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.4.1077-1088.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11158295 Free PMC article.
-
Association of inhibitory tyrosine protein kinase p50csk with protein tyrosine phosphatase PEP in T cells and other hemopoietic cells.EMBO J. 1996 Sep 16;15(18):4909-18. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8890164 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory tyrosine protein kinase p50csk is associated with protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTP-PEST in hemopoietic and non-hemopoietic cells.J Biol Chem. 1997 Sep 12;272(37):23455-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.37.23455. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9287362
-
Positive and negative regulation of T-cell activation through kinases and phosphatases.Biochem J. 2003 Apr 1;371(Pt 1):15-27. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021637. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12485116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative regulation of antigen receptor signaling in lymphocytes.J Mol Med (Berl). 1998 Jul;76(8):589-95. doi: 10.1007/s001090050254. J Mol Med (Berl). 1998. PMID: 9694436 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of protein tyrosine phosphatases in regulating the immune system: implications for chronic intestinal inflammation.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015 Mar;21(3):645-55. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000297. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015. PMID: 25581833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The genetic basis of graves' disease.Curr Genomics. 2011 Dec;12(8):542-63. doi: 10.2174/138920211798120772. Curr Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22654555 Free PMC article.
-
The tyrosine kinase Csk dimerizes through Its SH3 domain.PLoS One. 2009 Nov 4;4(11):e7683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007683. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19888460 Free PMC article.
-
PTPN22: structure, function, and developments in inhibitor discovery with applications for immunotherapy.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2022 Aug;17(8):825-837. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2022.2084607. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 35637605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Old and New Susceptibility Genes versus Clinical Manifestations.Curr Genomics. 2014 Feb;15(1):52-65. doi: 10.2174/138920291501140306113715. Curr Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24653663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu W, Harrison SC, Eck MJ. Three-dimensional structure of the tyrosine kinase c-Src. Nature. 1997;385:595–602. - PubMed
-
- Sicheri F, Moarefi I, Kuriyan J. Crystal structure of the Src family tyrosine kinase Hck. Nature. 1997;385:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Moarefi I, LaFevre-Bernt M, Sicheri F, Huse M, Lee C-H, Kuriyan J, Miller WT. Activation of the Src-family tyrosine kinase Hck by SH3 domain displacement. Nature. 1997;385:650–653. - PubMed
-
- Nada S, Okada M, MacAuley A, Cooper JA, Nakagawa H. Cloning of a complementary DNA for a protein-tyrosine kinase that specifically phosphorylates a negative regulatory site of p60c-src . Nature. 1991;351:69–72. - PubMed
-
- Chow LML, Veillette A. The Src and Csk families of protein tyrosine kinases in hemopoietic cells. Semin Immunol. 1995;7:207–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

