A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- PMID: 9861027
- PMCID: PMC28101
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15665
A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999 Mar 2;96(5):2569
Abstract
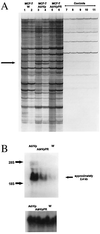
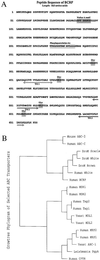
MCF-7/AdrVp is a multidrug-resistant human breast cancer subline that displays an ATP-dependent reduction in the intracellular accumulation of anthracycline anticancer drugs in the absence of overexpression of known multidrug resistance transporters such as P glycoprotein or the multidrug resistance protein. RNA fingerprinting led to the identification of a 2.4-kb mRNA that is overexpressed in MCF-7/AdrVp cells relative to parental MCF-7 cells. The mRNA encodes a 655-aa [corrected] member of the ATP-binding cassette superfamily of transporters that we term breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). Enforced expression of the full-length BCRP cDNA in MCF-7 breast cancer cells confers resistance to mitoxantrone, doxorubicin, and daunorubicin, reduces daunorubicin accumulation and retention, and causes an ATP-dependent enhancement of the efflux of rhodamine 123 in the cloned transfected cells. BCRP is a xenobiotic transporter that appears to play a major role in the multidrug resistance phenotype of MCF-7/AdrVp human breast cancer cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multidrug resistance mediated by the breast cancer resistance protein BCRP (ABCG2).Oncogene. 2003 Oct 20;22(47):7340-58. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206938. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 14576842 Review.
-
Impact of BCRP/MXR, MRP1 and MDR1/P-Glycoprotein on thermoresistant variants of atypical and classical multidrug resistant cancer cells.Int J Cancer. 2002 Feb 20;97(6):751-60. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10131. Int J Cancer. 2002. PMID: 11857350
-
[Regulation mechanism of breast cancer resistance protein by toremifene to reverse BCRP-mediated multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2011 Sep;33(9):654-60. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22340044 Chinese.
-
Transcriptional modulation of BCRP gene to reverse multidrug resistance by toremifene in breast adenocarcinoma cells.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Oct;123(3):679-89. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0660-2. Epub 2009 Dec 6. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010. PMID: 19967559
-
Effect of the breast-cancer resistance protein on atypical multidrug resistance.Lancet Oncol. 2000 Nov;1:169-75. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(00)00032-2. Lancet Oncol. 2000. PMID: 11905655 Review.
Cited by
-
Common variants in ABCB1, ABCC2 and ABCG2 genes and clinical outcomes among women with advanced stage ovarian cancer treated with platinum and taxane-based chemotherapy: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study.Gynecol Oncol. 2012 Mar;124(3):575-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.11.022. Epub 2011 Nov 21. Gynecol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22112610 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) localises to the nucleus in glioblastoma multiforme cells.Xenobiotica. 2012 Aug;42(8):748-55. doi: 10.3109/00498254.2012.662726. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Xenobiotica. 2012. PMID: 22401348 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of multidrug resistance proteins by genistein in a hepatocarcinoma cell line: impact on sorafenib cytotoxicity.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 17;10(3):e0119502. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119502. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25781341 Free PMC article.
-
A novel nanoparticle formulation overcomes multiple types of membrane efflux pumps in human breast cancer cells.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2012 Apr;2(2):95-105. doi: 10.1007/s13346-011-0051-1. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 25786718
-
Methods to Discover Alternative Promoter Usage and Transcriptional Regulation of Murine Bcrp1.J Vis Exp. 2016 May 27;(111):53827. doi: 10.3791/53827. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 27286290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kessel D, Botterill V, Wodinsky I. Cancer Res. 1968;28:938–941. - PubMed
-
- Biedler J L, Riehm H. Cancer Res. 1970;30:1174–1184. - PubMed
-
- Ling V, Thompson L H. J Cell Physiol. 1974;83:103–116. - PubMed
-
- Gros P, Ben Neryah Y B, Croop J M, Housman D E. Nature (London) 1986;323:728–731. - PubMed
-
- Cole S P C, Bhardwaj G, Gerlach J H, Mackie J E, Grant C E, Almquist K C, Stewart A J, Kurz E U, Duncan A M V, et al. Science. 1992;258:1650–1654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

