Stat5b is essential for natural killer cell-mediated proliferation and cytolytic activity
- PMID: 9841920
- PMCID: PMC2212377
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.188.11.2067
Stat5b is essential for natural killer cell-mediated proliferation and cytolytic activity
Abstract
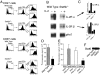
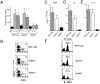
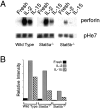
We have analyzed the immune system in Stat5-deficient mice. Although Stat5a-/- splenocytes have a partial defect in anti-CD3-induced proliferation that can be overcome by high dose interleukin (IL)-2, we now demonstrate that defective proliferation in Stat5b-/- splenocytes cannot be corrected by this treatment. Interestingly, this finding may be at least partially explained by diminished expression of the IL-2 receptor beta chain (IL-2Rbeta), which is a component of the receptors for both IL-2 and IL-15, although other defects may also exist. Similar to the defect in proliferation in activated splenocytes, freshly isolated splenocytes from Stat5b-/- mice exhibited greatly diminished proliferation in response to IL-2 and IL-15. This results from both a decrease in the number and responsiveness of natural killer (NK) cells. Corresponding to the diminished proliferation, basal as well as IL-2- and IL-15-mediated boosting of NK cytolytic activity was also greatly diminished. These data indicate an essential nonredundant role for Stat5b for potent NK cell-mediated proliferation and cytolytic activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Both stat5a and stat5b are required for antigen-induced eosinophil and T-cell recruitment into the tissue.Blood. 2000 Feb 15;95(4):1370-7. Blood. 2000. PMID: 10666213
-
Characterization of cytokine differential induction of STAT complexes in primary human T and NK cells.J Leukoc Biol. 1998 Aug;64(2):245-58. doi: 10.1002/jlb.64.2.245. J Leukoc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9715265
-
Proliferation and differentiation of CD8+ T cells in the absence of IL-2/15 receptor beta-chain expression or STAT5 activation.J Immunol. 2004 Sep 1;173(5):3131-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.5.3131. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15322173
-
An indirect effect of Stat5a in IL-2-induced proliferation: a critical role for Stat5a in IL-2-mediated IL-2 receptor alpha chain induction.Immunity. 1997 Nov;7(5):691-701. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80389-1. Immunity. 1997. PMID: 9390692
-
The role of Stat5a and Stat5b in signaling by IL-2 family cytokines.Oncogene. 2000 May 15;19(21):2566-76. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203523. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10851055 Review.
Cited by
-
JAKs and STATs in immunity, immunodeficiency, and cancer.N Engl J Med. 2013 Jan 10;368(2):161-70. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1202117. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 23301733 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Long-term follow-up of STAT5B deficiency in three argentinian patients: clinical and immunological features.J Clin Immunol. 2015 Apr;35(3):264-72. doi: 10.1007/s10875-015-0145-5. Epub 2015 Mar 11. J Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25753012
-
STAT5b: A master regulator of key biological pathways.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 23;13:1025373. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1025373. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36755813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of cytokine receptors by IL-2 broadly regulates differentiation into helper T cell lineages.Nat Immunol. 2011 Jun;12(6):551-9. doi: 10.1038/ni.2030. Epub 2011 Apr 24. Nat Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21516110 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo identification of novel STAT5 target genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jun;36(11):3802-18. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn271. Epub 2008 May 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18492722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ihle JN. STATs: signal transducers and activators of transcription. Cell. 1996;84:331–334. - PubMed
-
- Horvath CM, Darnell JE., Jr The state of STATs: recent developments in the study of signal transduction to the nucleus. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:233–239. - PubMed
-
- Leonard WJ, O'Shea JJ. Jaks and STATs: biological implications. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:293–322. - PubMed
-
- Durbin JE, Hackenmiller R, Simon MC, Levy DE. Targeted disruption of the mouse Stat1 gene results in compromised innate immunity to viral disease. Cell. 1996;84:443–450. - PubMed
-
- Meraz MA, White JM, Sheehan KC, Bach EA, Rodig SJ, Dighe AS, Kaplan DH, Riley JK, Greenlund AC, Campbell D, et al. Targeted disruption of the Stat1 gene in mice reveals unexpected physiologic specificity in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Cell. 1996;84:431–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

