Chemokines regulate hippocampal neuronal signaling and gp120 neurotoxicity
- PMID: 9826729
- PMCID: PMC24402
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.24.14500
Chemokines regulate hippocampal neuronal signaling and gp120 neurotoxicity
Abstract
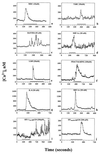
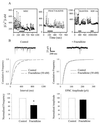
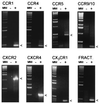
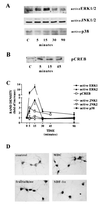
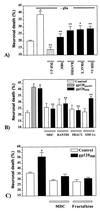
The HIV-1 envelope protein gp120 induces apoptosis in hippocampal neurons. Because chemokine receptors act as cellular receptors for HIV-1, we examined rat hippocampal neurons for the presence of functional chemokine receptors. Fura-2-based Ca imaging showed that numerous chemokines, including SDF-1alpha, RANTES, and fractalkine, affect neuronal Ca signaling, suggesting that hippocampal neurons possess a wide variety of chemokine receptors. Chemokines also blocked the frequency of spontaneous glutamatergic excitatory postsynaptic currents recorded from these neurons and reduced voltage-dependent Ca currents in the same neurons. Reverse transcription-PCR demonstrated the expression of CCR1, CCR4, CCR5, CCR9/10, CXCR2, CXCR4, and CX3CR1, as well as the chemokine fractalkine in these neurons. Both fractalkine and macrophage-derived chemokine (MDC) produced a time-dependent activation of extracellular response kinases (ERK)-1/2, whereas no activation of c-JUN NH2-terminal protein kinase (JNK)/stress-activated protein kinase, or p38 was evident. Furthermore, these two chemokines, as well as SDF-1alpha, activated the Ca- and cAMP-dependent transcription factor CREB. Several chemokines were able also to block gp120-induced apoptosis of hippocampal neurons, both in the presence and absence of the glial feeder layer. These data suggest that chemokine receptors may directly mediate gp120 neurotoxicity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemokines and activated macrophages in HIV gp120-induced neuronal apoptosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Jul 6;96(14):8212-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.14.8212. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10393974 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular CXCR4 signaling, neuronal apoptosis and neuropathogenic mechanisms of HIV-1-associated dementia.J Neuroimmunol. 1999 Aug 3;98(2):185-200. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(99)00049-1. J Neuroimmunol. 1999. PMID: 10430052
-
Chemokines and glycoprotein120 produce pain hypersensitivity by directly exciting primary nociceptive neurons.J Neurosci. 2001 Jul 15;21(14):5027-35. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-14-05027.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11438578 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage activation through CCR5- and CXCR4-mediated gp120-elicited signaling pathways.J Leukoc Biol. 2003 Nov;74(5):676-82. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0503206. Epub 2003 Jul 22. J Leukoc Biol. 2003. PMID: 12960231 Review.
-
AIDS and the brain: is there a chemokine connection?Trends Neurosci. 1999 Oct;22(10):471-9. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(99)01408-3. Trends Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10481195 Review.
Cited by
-
Microglial control of neuronal activity.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Mar 28;7:32. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00032. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23543873 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variation and HIV-associated neurologic disease.Adv Virus Res. 2013;87:183-240. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407698-3.00006-5. Adv Virus Res. 2013. PMID: 23809924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokines and viral diseases of the central nervous system.Adv Virus Res. 2001;56:127-73. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(01)56006-6. Adv Virus Res. 2001. PMID: 11450298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virus infection switches TLR-3-positive human neurons to become strong producers of beta interferon.J Virol. 2005 Oct;79(20):12893-904. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.20.12893-12904.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16188991 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways to neuronal damage and apoptosis in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-associated dementia: Chemokine receptors, excitotoxicity, and beyond.J Neurovirol. 2004;10 Suppl 1:97-101. doi: 10.1080/753312759. J Neurovirol. 2004. PMID: 14982746 Review.
References
-
- Price R W, Brew B, Sidtis J, Rosenbaum M, Scheck A C, Cleary P. Science. 1988;239:586–592. - PubMed
-
- Masliah E, Ge N, Achim C L, Hansen L A, Wiley C A. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1992;51:585–593. - PubMed
-
- Toggas S M, Masliah E, Rockenstein E M, Rall G F, Abraham C R, Mucke L. Nature (London) 1994;367:188–193. - PubMed
-
- Brenneman D E, Westbrook G L, Fitzgerald S P, Ennist D L, Elkins K L, Ruff M R, Pert C B. Nature (London) 1988;335:639–642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

