CD44 occupancy prevents macrophage multinucleation
- PMID: 9813101
- PMCID: PMC2148144
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.143.3.837
CD44 occupancy prevents macrophage multinucleation
Abstract
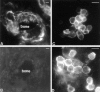
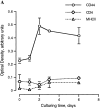
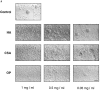
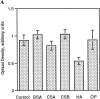
Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte lineage have the capability to adhere to and fuse with each other and to differentiate into osteoclasts and giant cells. To investigate the macrophage adhesion/fusion mechanism, we focused our attention on CD44, a surface glycoprotein known to play a role in hematopoietic cell-cell adhesion. We report that CD44 expression by macrophages is highly and transiently induced by fusogenic conditions both in vitro and in vivo. We show that CD44 ligands, hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfates, and osteopontin prevent macrophage multinucleation. In addition, we report that the recombinant extracellular domain of CD44 binds fusing macrophages and prevents multinucleation in vitro. These data suggest that CD44 may control the mononucleated status of macrophages in tissues by virtue of mediating cell-cell interaction.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The intracellular domain of CD44 promotes the fusion of macrophages.Blood. 2006 Jan 15;107(2):796-805. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-05-1902. Epub 2005 Sep 29. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16195325 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoclasts and giant cells: macrophage-macrophage fusion mechanism.Int J Exp Pathol. 2000 Oct;81(5):291-304. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2000.00164.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2000. PMID: 11168677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of an inducible surface molecule specific to fusing macrophages.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Dec 19;92(26):12210-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.26.12210. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 8618871 Free PMC article.
-
CD44: structure, function, and association with the malignant process.Adv Cancer Res. 1997;71:241-319. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60101-3. Adv Cancer Res. 1997. PMID: 9111868 Review.
-
De novo CD44 expression by proliferating mesangial cells in rat anti-Thy-1 nephritis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996 Jul;7(7):1006-14. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V771006. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996. PMID: 8829115
Cited by
-
The intracellular domain of CD44 promotes the fusion of macrophages.Blood. 2006 Jan 15;107(2):796-805. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-05-1902. Epub 2005 Sep 29. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16195325 Free PMC article.
-
CD44 Can Compensate for IgSF11 Deficiency by Associating with the Scaffold Protein PSD-95 during Osteoclast Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 10;21(7):2646. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072646. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32290171 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and humoral mechanisms of osteoclast formation in Ewing's sarcoma.Br J Cancer. 2007 Jun 4;96(11):1716-22. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603774. Epub 2007 May 29. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17533390 Free PMC article.
-
Regenerative potential of glycosaminoglycans for skin and bone.J Mol Med (Berl). 2012 Jun;90(6):625-35. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0843-2. Epub 2011 Dec 21. J Mol Med (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22187113 Review.
-
Stimulation of osteoclast formation by inflammatory synovial fluid.Virchows Arch. 2006 Jul;449(1):69-77. doi: 10.1007/s00428-006-0200-y. Epub 2006 Apr 21. Virchows Arch. 2006. PMID: 16642388
References
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder C, Feng Y, Kennedy P, Murphy P, Berger E. CC CKR5: A RANTES, MIP-1α, MIP-1β receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Belitsos PC, Hildreth JE, August JT. Homotypic cell aggregation induced by anti-CD44 (Pgp-1) monoclonal antibodies and related to CD44 (Pgp-1) expression. J Immunology. 1990;144:1661–1670. - PubMed
-
- Blobel CP, Wolfsberg TG, Turk CW, Miles DG, Primakoff P, White JM. A potential fusion peptide and an integrin ligand domain in a protein active in sperm-egg fusion. Nature. 1992;356:248–252. - PubMed
-
- Cherr GN, Yudin AI, Katz DF. Organization of the hamster cumulus extracellular matrix A hyaluronate glycoprotein gel which modulates sperm access to the oocyte. Dev Growth Differ. 1990;32:353–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

