Chromosome-specific molecular organization of maize (Zea mays L.) centromeric regions
- PMID: 9789043
- PMCID: PMC23713
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.22.13073
Chromosome-specific molecular organization of maize (Zea mays L.) centromeric regions
Abstract
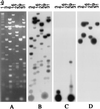
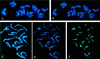
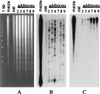
A set of oat-maize chromosome addition lines with individual maize (Zea mays L.) chromosomes present in plants with a complete oat (Avena sativa L.) chromosome complement provides a unique opportunity to analyze the organization of centromeric regions of each maize chromosome. A DNA sequence, MCS1a, described previously as a maize centromere-associated sequence, was used as a probe to isolate cosmid clones from a genomic library made of DNA purified from a maize chromosome 9 addition line. Analysis of six cosmid clones containing centromeric DNA segments revealed a complex organization. The MCS1a sequence was found to comprise a portion of the long terminal repeats of a retrotransposon-like repeated element, termed CentA. Two of the six cosmid clones contained regions composed of a newly identified family of tandem repeats, termed CentC. Copies of CentA and tandem arrays of CentC are interspersed with other repetitive elements, including the previously identified maize retroelements Huck and Prem2. Fluorescence in situ hybridization revealed that CentC and CentA elements are limited to the centromeric region of each maize chromosome. The retroelements Huck and Prem2 are dispersed along all maize chromosomes, although Huck elements are present in an increased concentration around centromeric regions. Significant variation in the size of the blocks of CentC and in the copy number of CentA elements, as well as restriction fragment length variations were detected within the centromeric region of each maize chromosome studied. The different proportions and arrangements of these elements and likely others provide each centromeric region with a unique overall structure.
Figures
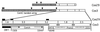
Similar articles
-
Complex structure of knobs and centromeric regions in maize chromosomes.Tsitol Genet. 2000 Mar-Apr;34(2):11-5. Tsitol Genet. 2000. PMID: 10857197 Review.
-
Maize centromeres: organization and functional adaptation in the genetic background of oat.Plant Cell. 2004 Mar;16(3):571-81. doi: 10.1105/tpc.018937. Epub 2004 Feb 18. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 14973167 Free PMC article.
-
Complex structure of knob DNA on maize chromosome 9. Retrotransposon invasion into heterochromatin.Genetics. 1998 Aug;149(4):2025-37. doi: 10.1093/genetics/149.4.2025. Genetics. 1998. PMID: 9691055 Free PMC article.
-
Sequences associated with A chromosome centromeres are present throughout the maize B chromosome.Chromosoma. 2005 Feb;113(7):337-49. doi: 10.1007/s00412-004-0319-z. Epub 2004 Dec 7. Chromosoma. 2005. PMID: 15586285
-
A tale of two centromeres--diversity of structure but conservation of function in plants and animals.Funct Integr Genomics. 2009 Feb;9(1):7-13. doi: 10.1007/s10142-008-0104-9. Epub 2008 Dec 13. Funct Integr Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19083033 Review.
Cited by
-
Sequence of the supernumerary B chromosome of maize provides insight into its drive mechanism and evolution.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jun 8;118(23):e2104254118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2104254118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34088847 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and cytological analyses of large tracks of centromeric DNA reveal the structure and evolutionary dynamics of maize centromeres.Genetics. 2003 Feb;163(2):759-70. doi: 10.1093/genetics/163.2.759. Genetics. 2003. PMID: 12618412 Free PMC article.
-
A test for ectopic exchange catalyzed by Cre recombinase in maize.Theor Appl Genet. 2005 Jul;111(2):378-85. doi: 10.1007/s00122-005-2031-7. Epub 2005 May 24. Theor Appl Genet. 2005. PMID: 15912343
-
Telomeres act autonomously in maize to organize the meiotic bouquet from a semipolarized chromosome orientation.J Cell Biol. 2002 Apr 15;157(2):231-42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200110126. Epub 2002 Apr 15. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11956226 Free PMC article.
-
Centromere Satellite Repeats Have Undergone Rapid Changes in Polyploid Wheat Subgenomes.Plant Cell. 2019 Sep;31(9):2035-2051. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00133. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Plant Cell. 2019. PMID: 31311836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rines H W, Riera-Lizarazu O, Phillips R L. In: Modification of Gene Expression and Non-Mendelian Inheritance. Oono K, Takiwa F, editors. Tsukuba, Japan: NIAR; 1995. pp. 235–251.
-
- Riera-Lizarazu O, Rines H W, Phillips R L. Theor Appl Genet. 1996;93:123–135. - PubMed
-
- Cox D R, Burmeister M, Price E R, Kim S, Myers R M. Science. 1990;250:245–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

